December 7, 2025
Updated: December 7, 2025
A comprehensive analysis of 2025 data breach costs, attack vectors, regional trends, and key security lessons.
Mohammed Khalil

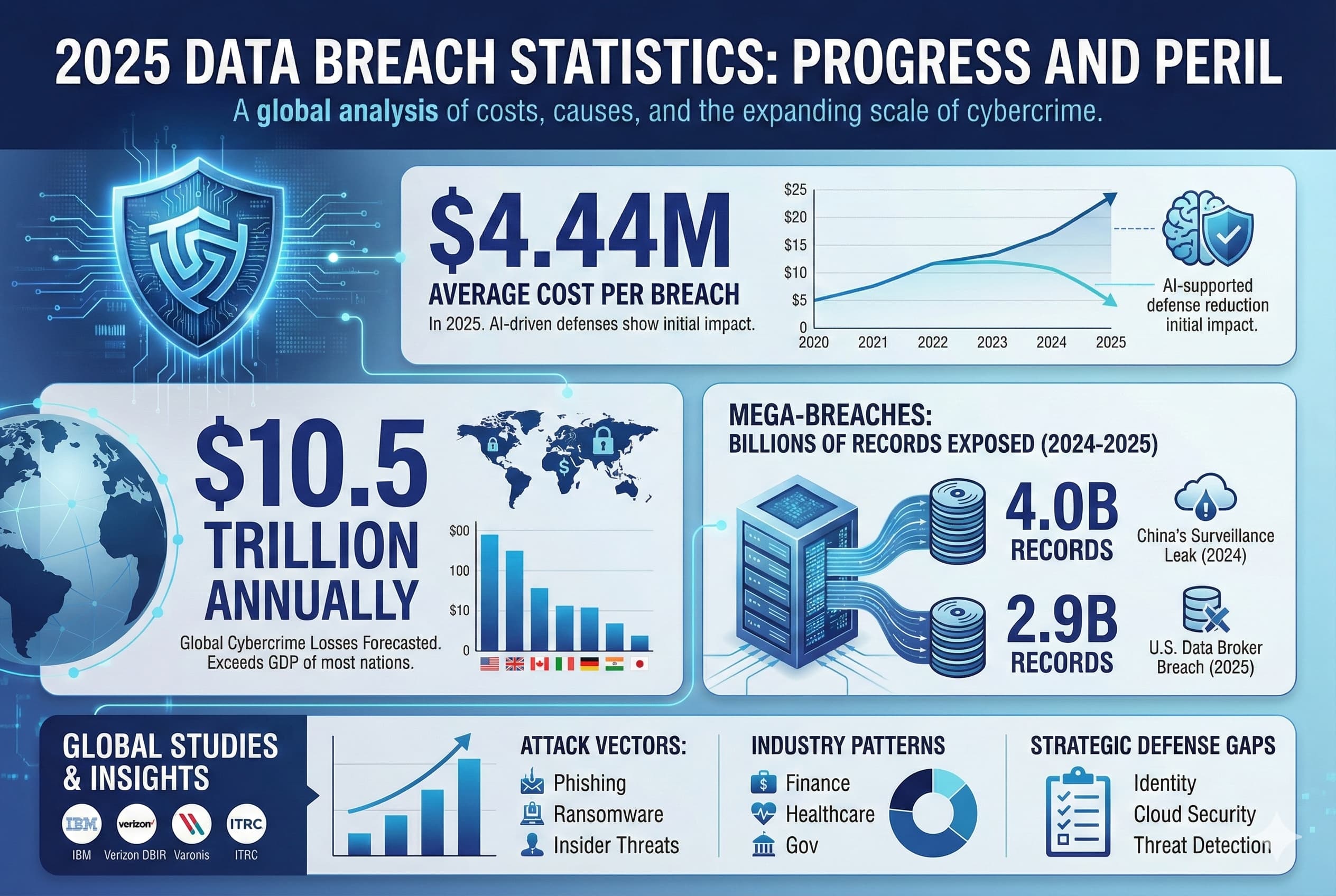
In 2025, data breach statistics paint a picture of both progress and peril. On average, breaches are becoming more expensive to fix. The global average cost reached $4.44 million in 2025 yet effective use of new defenses like AI driven detection has started to pull that number down. At the same time, cybercrime’s sheer scale continues to explode: one industry forecast pegs worldwide cybercrime losses at $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. By any measure, that is more than the GDP of most nations.
Statistics are vital for understanding the changing landscape. For example, 2024 25 saw a spate of mega breaches exposing billions of records China’s public surveillance leak exposed over 4.0 billion records, and a U.S. data broker breach exposed 2.9 billion U.S./UK/CA records. These incidents underscore how a single compromise can create global fallout. This report analyzes thousands of incidents and dozens of studies IBM, Verizon DBIR, Varonis, ITRC, etc. to highlight the costs, causes, and patterns of 2025’s breaches. We provide detailed numbers on breaches and their impacts covering costs by region and industry, attack vectors, emerging threat trends, and case studies of significant breaches. These data driven insights illuminate the gap between defenders and adversaries, and point toward the strategic decisions organizations must make to survive.
Data breach statistics quantify the frequency, scale, and impact of security incidents involving unauthorized access to sensitive data. Think of them as public health stats for cybercrime: measures of how often breaches occur, how fast they’re detected, how many records are stolen, and how much they cost. These stats help organizations benchmark their risk and measure progress over time. For example, knowing that stolen credentials are used in roughly 22% of breaches is like knowing that transmission by droplets accounts for a certain percentage of disease spread, it tells you where to focus defenses. Likewise, understanding that the average breach lifecycle from intrusion to containment has fallen to 241 days in 2025 from 258 in 2024 shows how new tools, especially AI, are accelerating detection.
Just as epidemiologists use infection rates, breach experts use statistics to identify hotspots industries or regions with soaring costs, emerging variants of attack ransomware, supply chain compromise, etc., and leading indicators of spread phishing, shadow IT. For example, the number of breach notifications surged by 312% in the U.S. in 2024, driven by five mega breaches yet the raw count of breach incidents stayed roughly flat ≈3,200. Stats like these highlight hidden trends: breach volume plateaued, but the scale in records lost and costs soared.
Global metrics for 2024 and 2025 show mixed signals: average costs dipped, while attack volume and severity climbed. Table 1 below summarizes key metrics year over year:
| Global Avg. Breach Cost | 2024 | 2025 | Trend / Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Avg. Breach Cost | $4.88M IBM | $4.44M | 9% first decline in 5 years, thanks to faster AI detection |
| Reported Breach Incidents US | ≈$9.38M | $10.22M | +9% U.S. highest globally, driven by fines/litigation |
| Time to Identify Breach MTTI | 3,202 | 3,158 | Flat near 2023 record of 3,202, U.S. reports 3,200 breaches |
| Ransomware Involvement | 194 days 2024 | 181 days | 13 days down 7% YoY, a 9 year low due to automation |
| Supply Chain Breaches | 32% of breaches | 44% of breaches | Up 12pp Verizon DBIR |
| Records Exposed mega breaches | 15% of breaches | 30% of breaches | Doubled 100% YoY increase, per Verizon DBIR |
| Records Exposed mega breaches | 50 60M: $375M average | Mega breach avg cost jumped +$43M YoY |
Global breach costs remain extremely lopsided. The United States now leads by far at $10.22M per breach versus the $4.44M global mean. This U.S. premium is driven by aggressive regulatory fines, class action lawsuits, and the complexity of state notification laws. Other regions saw costs stabilize or fall: Western Europe e.g. UK $4.14M, Germany $4.03M and Asia Pacific Japan $3.65M are around the global average, reflecting mature data protection regimes. The Middle East bucked global trends with a sharp 18% cost drop to SAR 27M = $7.29M, as countries like UAE and Saudi Arabia aggressively deployed AI/ML and encryption in cybersecurity.
By contrast, the developing world and regions with less stringent enforcement generally report lower per breach costs, though data are scarce. Overall, the numbers underscore how geography and regulation shape breach economics: organizations must understand not just their technical risk, but the local legal and market factors that drive final costs.
The financial impact of a breach extends far beyond the breach year. According to IBM, roughly 51% of total breach costs are incurred more than one year after the incident. This long tail comes from prolonged regulatory investigations, multi year identity monitoring for victims, and the cascading revenue loss as customer trust erodes. Breach costs are also highly nonlinear: the average cost per compromised record is now about $160. At that rate, even a breach of 10 million records a common scale costs $1.6 billion on paper. In practice, costs scale up superlinearly: IBM found that breaches exposing 50-60 million records averaged about $375 million in 2024 25 driven by the massive notification and remediation logistics at that scale.
Certain factors push costs higher or lower. For example, breaches that take over 200 days to identify and contain now average around $5.01 million each, $1.39M more than faster resolved incidents. Speed truly saves money. Organizations using AI and automation for threat hunting have benefited greatly: they cut detection times by roughly 80 days on average, saving about $1.9 million per breach. As a result, average breach lifecycles have fallen to 241 days from 258 in 2025, the fastest on record.
The type of data stolen also matters. Sensitive personal data customer PII, medical records can cost more per record $160 than, say, lost credit card numbers. Intellectual property trade secrets is even pricier IBM found IP theft averaged about $178 per record in 2025. In short, mega breaches and breaches in industries with high value data healthcare, finance, critical infrastructure drive the average cost way up. Mitigating factors include strong data encryption, automated incident response, and effective cyber insurance all of which can shave significant dollars off the final tally.
| Cost Component | 2025 Avg USD | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Detection & Containment | $1.47M | Down 10% YoY automation and AI driving efficiency |
| Notification | $1.31M est. | Notified consumers, regulators, credit agencies |
| Legal/Remediation | $1.25M est. | Forensics, legal defense, PR |
| Lost Business downtime | $1.47M est. | Customer attrition & reputation hit |
| Total | $4.44M | Global average cost per breach |
Component breakdowns are approximate. Lost Business was the largest growing cost as customers churn and revenue drops, it fell 6% in 2025 after spiking in 2024.
The dominant ways attackers gain entry have shifted little: social engineering and credential theft remain king. Table 3 summarizes the most common initial attack vectors for 2024 25 based on aggregated reports:
| Attack Vector | % of Breaches | Avg. Cost per Breach USD | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stolen Credentials | 22% | $4.80M | Most frequent vector, often via infostealer malware or leaks |
| Phishing / Social Eng. | 16% | $4.80M | Most expensive initial vector convincing emails |
| Exploited Vuln. | 20% | $4.60M | Up 34% YoY, often unpatched VPNs/edge devices |
| Supply Chain Compromise | 15-30% | $4.91M | Doubled YOY 100% ↑, vendor breaches lead to mega incidents |
| Ransomware/Extortion | 44% | $5.08M | Present in 44% of breaches, extortion demands $1 4M |
| Malicious Insider | 6-11% | $4.92M | Broad range, hardest to detect legitimate access abused |
| Shadow AI | 20% involved | +$0.67M premium | Unsanctioned AI usage by employees, adds $670K to breach cost |
This breakdown highlights that breaches often start the old fashioned way: an attacker obtains valid credentials or tricks a user to give them up. In 2024, 22% of breaches involved stolen credentials and 16% started with phishing emails. Notably, supply chain attacks via a third party vendor or software dependency have surged, now causing roughly 30% of breaches. Once inside, attackers frequently deploy ransomware present in 44% of incidents to extort victims.
Advanced techniques are also emerging: roughly 16% of breaches in 2025 involved AI tools used by attackers. Attackers use generative AI to craft context aware phishing 37% of AI assisted breaches and deepfake audio/video 35% for vishing and impersonation. Additionally, the rise of Shadow AI employees uploading data to public AI without oversight is now a cost multiplier. Shadow breaches carry a $670K premium. In summary, modern attackers increasingly blend credential theft, software exploits, and automated techniques to breach organizations.
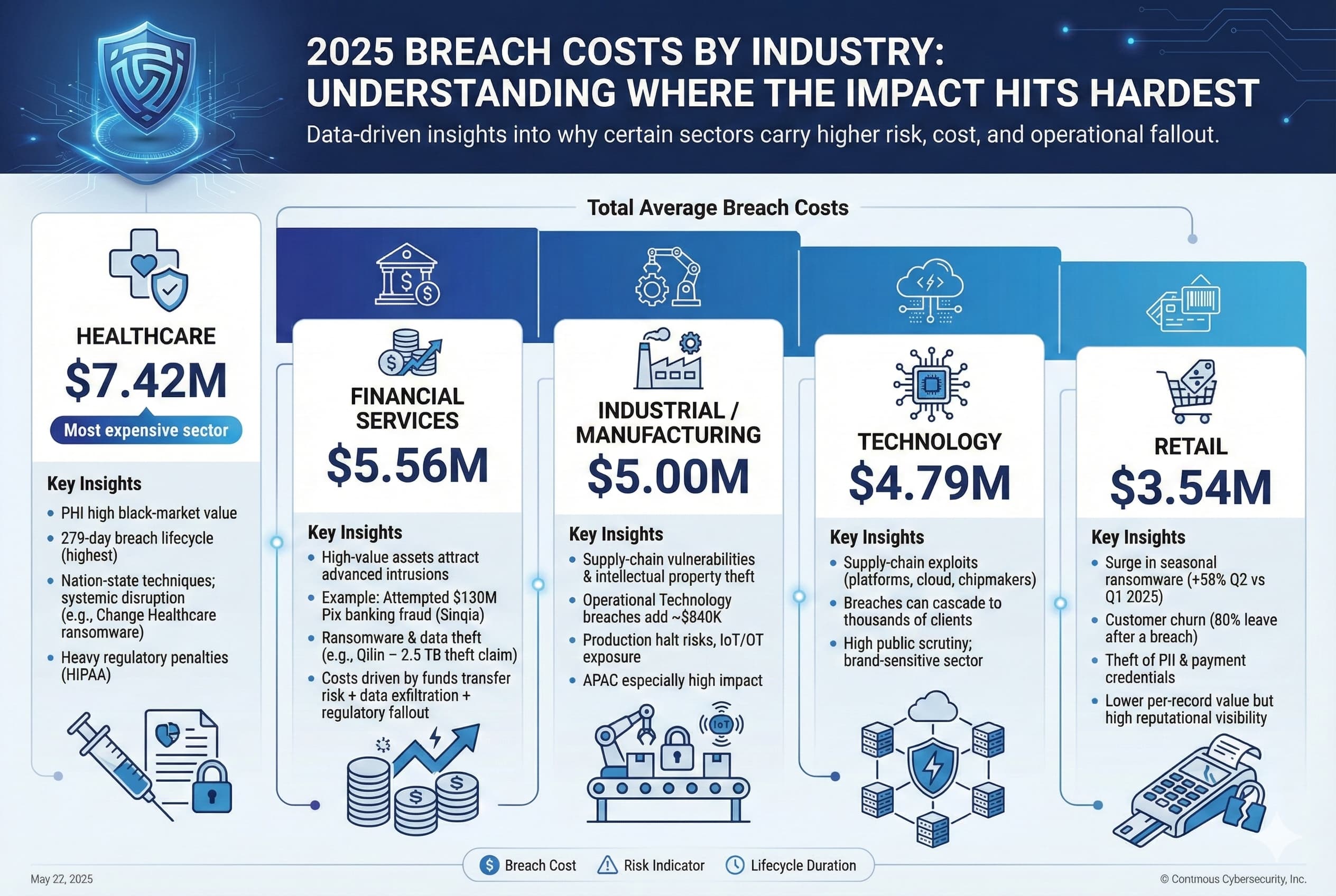
Breach costs and patterns vary widely by industry, reflecting data value and regulatory pressure. Key industry statistics for 2025 include:
By region, law and policy often make the difference. The chart below highlights average breach costs in key regions 2025 data:
| Region | Avg. Breach Cost 2025 | Change YoY | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $10.22 million | +9% | Strict SEC rules, class actions, high notification costs |
| Middle East | $7.29 million | 18% | Rapid AI adoption, strong encryption policies |
| Canada | $4.84 million | ↑ increasing | Aligning with US notification standards |
| United Kingdom | $4.14 million | Stable | Mature GDPR compliance lowers breaches |
| Germany | $4.03 million | ↓ | Industry standards e.g. automotive security, works council oversight |
| France | $3.73 million | 9% | Focus on digital sovereignty, strong telecom sec |
| Japan | $3.65 million | ↓ | Cultural caution with data, less litigation |
| Global Avg. | $4.44 million | 9% | Higher AI defenses globally |
The U.S. clearly pays the highest fare. Regulators SEC, FTC now require rapid breach disclosures, and class action lawsuits are routine. Notably, this U.S. premium of breach costs is not mirrored in Canada, even though Canada’s costs $4.84M are rising. Europe’s mature data protection frameworks GDPR have a mixed effect: fines are high, but organizations in the EU tend to invest more in data governance. Hence, countries like the UK $4.14M and Germany $4.03M actually kept their averages below the global mean.
Asia Pacific shows a split: Japan’s breaches are relatively cheap $3.65M due to privacy culture and fewer class actions, but emerging APAC tech hubs India, Southeast Asia are seeing more high profile attacks. The Middle East $7.29M stands out, its costs fell sharply in 2025 as Gulf states embed AI driven cyber defenses. In summary, while cyber threats are global, breach costs reflect local laws, economies, and incident response capabilities.

Examining specific incidents brings the statistics to life. The following were among the largest breaches in the 2024 25 period:
These cases illustrate the diverse nature of mega breaches in 2025 from state level surveillance databases to educational records to financial giants. For each incident, the ransom or immediate loss is often dwarfed by long term fallout: regulatory penalties, multi year credit monitoring, and shattered trust.
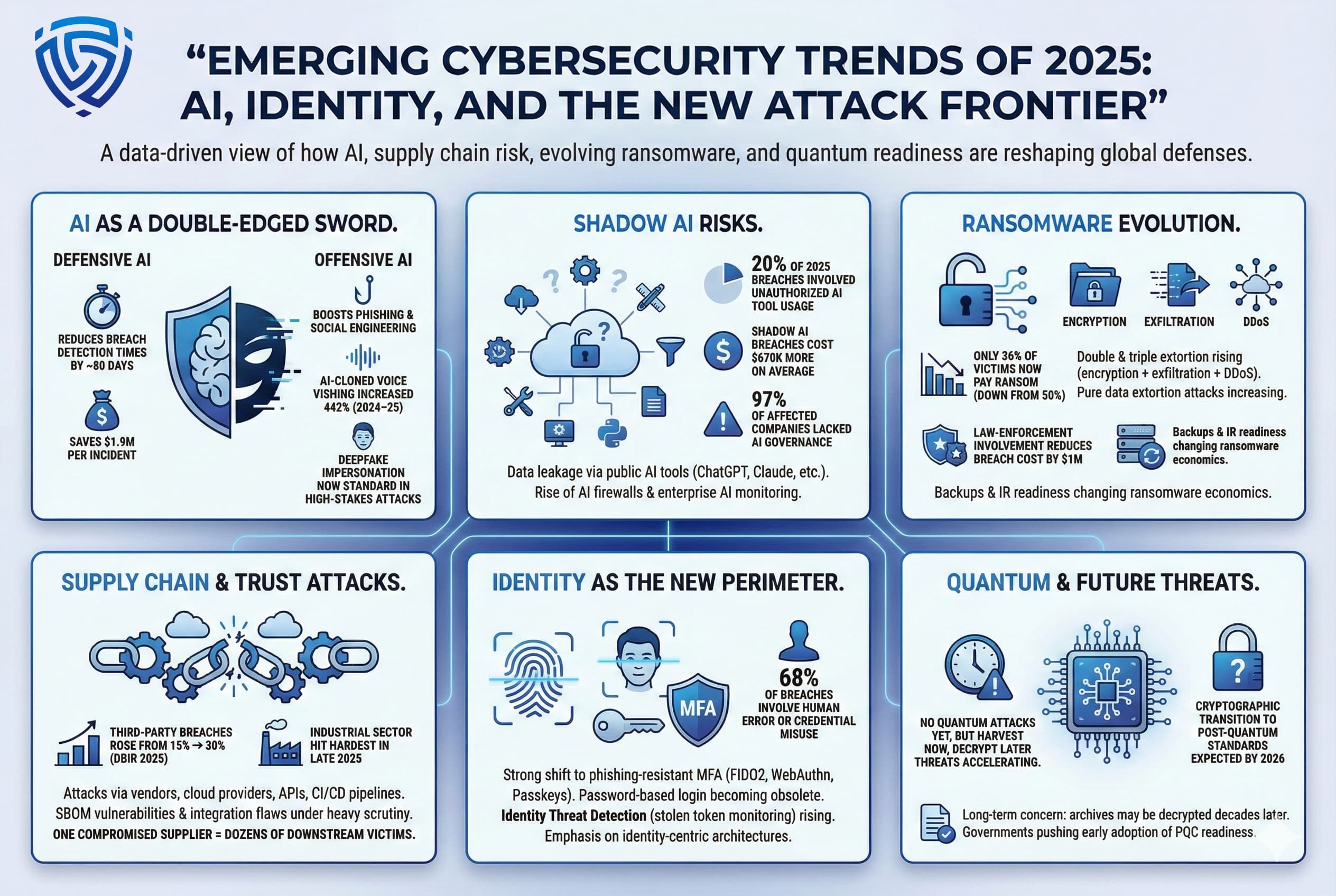
Several trends are reshaping the breach landscape in 2025:
In sum, the data show that cybersecurity and cyberresilience have never been more critical or complex. Attackers continue innovating AI tools, supply chain exploits, deepfakes, but defenders are fighting back with AI driven security, incident preparedness, and identity centric architectures. The statistical divide between AI equipped vs. AI naive organizations is stark: those on the right side of that divide will suffer far smaller breaches both in data lost and dollars paid.
The 2024 25 breach data paint a sobering picture: we are in an accelerating arms race. Some facts stand out. First, the global average cost decline is misleading. It hides the fact that large economies and critical sectors are experiencing record high losses. The U.S. and healthcare, for example, hit all time cost peaks, even as the global figure fell. In practice, this means breaches are becoming more polarized: catastrophically expensive for some large enterprises in litigious jurisdictions, or those hit by mega incidents, while becoming somewhat cheaper for others. Second, AI is now the defining variable. Our analysis shows companies using AI extensively escaped breaches faster and cheaper, creating a security divide. Conversely, those ignoring AI or failing to govern it face escalating risk Shadow AI increased costs, attackers using AI for spear phishing, etc.. Third, trust assumptions are crumbling: identity is effectively the new perimeter. If attackers can log in with valid credentials, they bypass firewalls entirely. Combined with exploding third party interdependencies, this means every organization must assume they will be breached and design for resilience. In other words, the numbers demand a shift from prevention only to business resilience strategies: robust backups, rapid recovery playbooks, cyber insurance, and redundant systems. Finally, the data underscore that cybersecurity is global economics: trillions are at stake, and a breach can tank stock prices overnight. Companies must therefore view security investment not as a cost, but as insuring a multi billion dollar asset.
Based on these trends, organizations should take proactive steps:
By following these practices many of which are interrelated, organizations can materially lower the impact when a breach does occur. The statistics make it clear: time saved is money saved, and prevention of data exposure is far cheaper than remediation.
The global average cost per breach in 2025 was about $4.44 million, down 9% from $4.88M in 2024. This includes all forms of damage, tech fixes, legal fees, lost business, etc..
Healthcare is the costliest $7.42M per breach, due to valuable patient data and complex legacy systems. Financial services is next $5.56M, driven by the direct monetary targets and heavy regulation. By contrast, industries like retail/hospitality have lower averages $3-4M because stolen data e.g. payment info is easier to invalidate.
Ransomware was involved in about 44% of breaches in 2025, up significantly from 32% in 2024. This means attackers deployed encryption or extortion in 44% of incidents. However, a growing majority of victims 64% refuse to pay the ransom, so attackers are shifting tactics.
Shadow AI refers to unsanctioned use of AI like ChatGPT by employees with corporate data. IBM found 20% of breaches involved shadow AI incidents. Because these tools often leak data outside the organization, breaches involving shadow AI cost on average $670K more. In practice, it means employees might accidentally expose secrets when querying public AI, a risk that must be managed with policy and technical controls.
By far, the leading causes are human factors. Stolen or weak credentials are the entry in 22% of breaches, and phishing accounts for 16%. Overall, studies show 68 88% of breaches involve human error or social engineering, one stat at 68%. Technical flaws like unpatched vulnerabilities cause a significant share around 20%, while malicious insiders are relatively rare 6-11% but very costly when they occur.
Several 2024 25 breaches exposed record volumes. For example, the Chinese surveillance data leak contained over 4.0 billion records. Another incident National Public Data exposed 2.9 billion U.S./UK/CA personal records. On a smaller scale, breaches like Ticketmaster’s 2024 hit about 560 million records, and the PowerSchool breach 2024/25 affected 62 million student/teacher records.
Use security AI/automation and incident response best practices. IBM’s data shows AI driven defense can reduce breach costs by about $1.9M on average by speeding up detection. Other cost cutting practices include strong encryption, regular security training to reduce human mistakes, and rapid containment procedures. Engaging law enforcement and cyber insurance can also lower net losses. In short, time saved in detection minutes or hours translates to millions of dollars saved.
The 2024 25 data breach statistics reveal a cyber threat environment in fast motion. On one hand, technological advances AI defense, automated response, and threat intelligence have started to bend some curves favorably: breaches are detected faster, and average costs dipped slightly. On the other hand, adversaries have industrialized their attacks: ransomware, AI powered social engineering, and third party exploits are becoming the norm.
Two narratives emerge. First, a divergence between the haves and have nots: organizations that fully leverage AI, zero trust, and robust resilience plans are pulling ahead, while laggards face breach costs that could be existential. Second, an inevitability of breaches: with threat actors using legitimate logins and supply chain footholds, breaches cannot be stopped 100%. The best strategy is one of resilience and adaptability.
Ultimately, these statistics underscore a simple truth: identity is the new perimeter and AI is mandatory for modern defense. Companies that invest wisely automating detection, enforcing strict identity controls, and securing their AI will blunt many attacks. But the ones that ignore these lessons will find themselves paying ever higher costs as the arms race intensifies. The data from 2025 should serve as a clarion call: to reduce breach costs, organizations must move beyond prevention and build cyber resilience into the very fabric of their operations.
About the Author
Mohammed Khalil is a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike, specializing in advanced penetration testing and offensive security operations. With certifications including CISSP, OSCP, and OSWE, he has led numerous red team engagements for Fortune 500 companies, focusing on cloud security, application vulnerabilities, and adversary emulation. His work involves dissecting complex attack chains and developing resilient defense strategies for clients in the finance, healthcare, and technology sectors.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us