April 17, 2025
Updated: April 17, 2025
Everything you need to craft, evaluate, and execute a successful penetration testing RFP
Mohammed Khalil

In today's fast moving cybersecurity world, putting together a solid Request for Proposal (RFP) for penetration testing is a key step in beefing up your defenses against ever growing threats. As we head into 2025, writing a clear and detailed pentest RFP has never been more important. The RFP is the foundation for hiring top notch penetration testers that fit your needs. This guide will break down how to craft an effective pentest RFP in plain language, so you can confidently navigate the process and strengthen your organization's security.
A well structured RFP not only helps you find the right folks for the job but also sets the stage for a successful partnership. It spells out the scope, expectations, and requirements upfront, making sure the vendor you pick is on the same page and can meet your needs. With cyber threats getting more sophisticated, having a solid pentest RFP in place is more important than ever to shore up your cybersecurity posture.
In 2025, pentest RFPs are more important than ever. Cyber threats aren't slowing down, and a solid RFP helps ensure you get the testing expertise you need.
Before diving into the details of writing one, let's make sure we're on the same page about what a penetration testing RFP actually is, why it's important, and how it differs from some other similar documents.
A Penetration Testing RFP is basically a document your organization puts out to potential security vendors asking them to propose how they would conduct a penetration test for you (and what it will cost). It outlines what you're looking for your objectives, the scope of the test, specific requirements, and so on. In response, vendors will submit proposals explaining how they'd perform the test and meet your needs.
If your RFP is well thought out and clearly written, you're more likely to get high quality proposals and ultimately a high quality penetration test. A well crafted RFP helps vendors understand exactly what you want, so they can tailor their proposals accordingly. It also makes it easier for you to compare different vendors. Essentially, the RFP sets expectations on both sides: you get to communicate your needs, and vendors can show how they'll meet them. Skimp on the RFP, and you might end up with mismatched expectations or choosing a vendor that isn't a great fit.
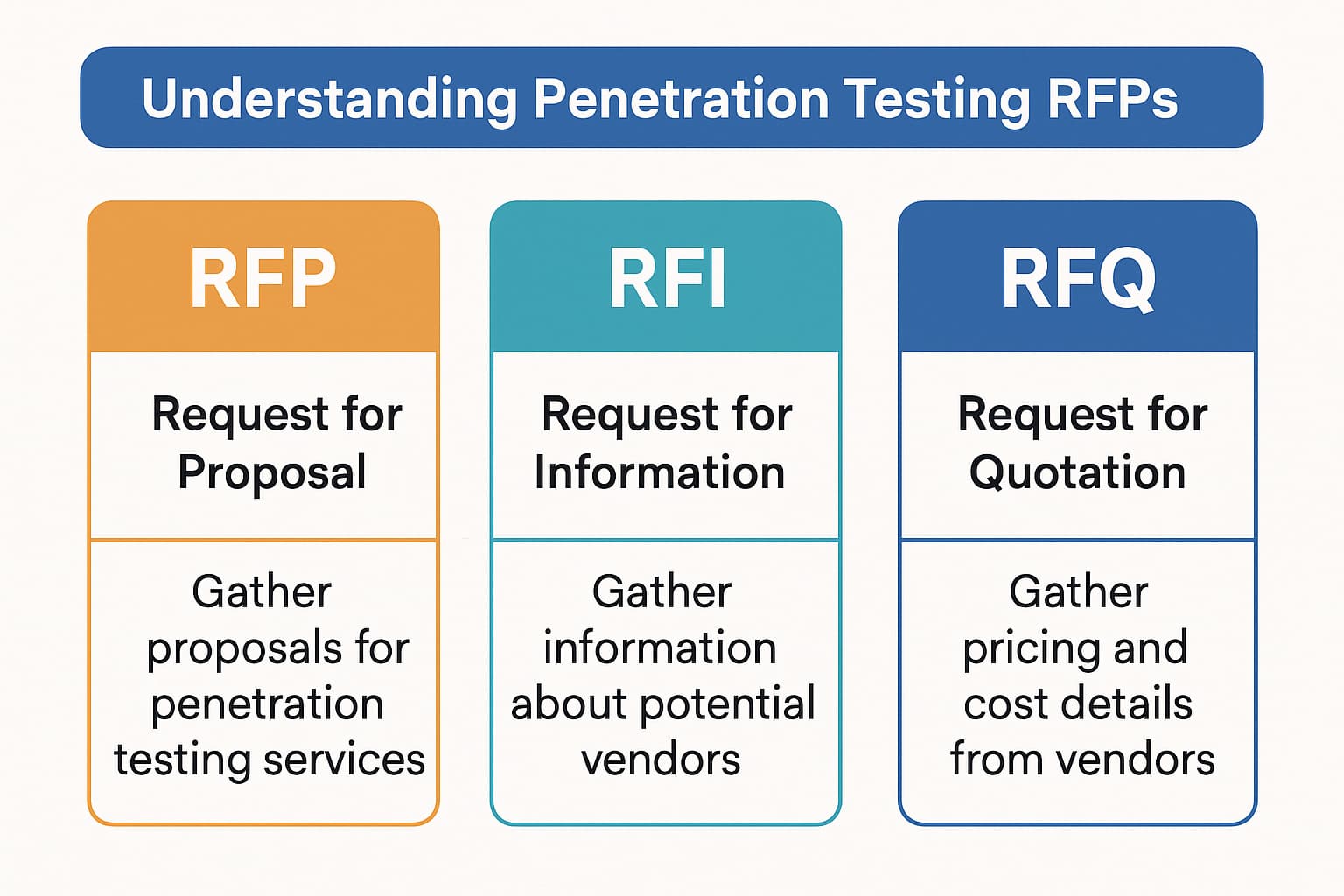
People sometimes confuse an RFP with an RFI or RFQ, but they serve different purposes:
Before you start drafting the RFP, there are a few things you should sort out internally. This prep work will ensure your RFP is targeted and realistic.
Be clear on why you're doing this penetration test. What are the main goals? Are you trying to uncover weaknesses in a new web application? Test the strength of your network defenses? Fulfill a compliance requirement? Knowing your security testing objectives will shape the entire RFP. For instance, if your main objective is to assess the resilience of your network, you'll emphasize that in the RFP so vendors know to focus their proposals on network testing.
Understand your starting point. Take a frank look at your current security measures and known vulnerabilities basically, how strong (or weak) is your defense right now? Are there recent security assessments or incidents you can reference? This self assessment helps you pinpoint what areas the penetration test should target. If you already know, say, your web app has some issues, or your staff isn't great at spotting phishing emails, you can highlight those areas in the RFP. Also, knowing your security posture helps in setting a realistic scope and expectations with the vendor.
Don't write the RFP alone. Security impacts many parts of the organization, so get a team together. Include people from IT/security, and consider looping in folks from development, operations, compliance, and even legal anyone who has a stake in the security of your systems. This team can help define the scope (IT might say "remember to include the cloud infrastructure," legal might add "we need an NDA," etc.), set a reasonable budget, and outline any special requirements. Plus, when it's time to evaluate proposals, this team can help review them from different angles.
It's critical to have a ballpark budget in mind early on. Penetration testing services can vary widely in cost depending on scope and complexity. Figure out how much you're able and willing to spend on this project. The budget should align with your scope if you need an extensive test covering many systems, be prepared that it will cost more than a quick check on one or two apps. Putting a budget (or at least budget range) in the RFP can also help vendors tailor their proposals (and avoid both of you wasting time if there's a huge mismatch). It's all about being realistic: you don't want to ask for the moon on a shoestring budget.
At this stage, the key things you should have nailed down are:
Now let's get into the meat of the RFP document itself. A strong pentest RFP should cover several essential components so that vendors have all the information they need to craft a suitable proposal.
Start your RFP with a brief overview of your company. You don't need to write a novel here just provide enough context. Mention what your organization does (e.g., "We are a fintech company providing online banking services" or "We run a healthcare network with 10 clinics"), and possibly the size of your IT environment (like number of employees or customers, and whether your infrastructure is on prem, cloud, etc.). The goal is to give vendors a sense of who they would be working with and any industry specific considerations. If you have any particular security challenges related to your industry, you can hint at them here (for example, "Being in healthcare, compliance with HIPAA is critical").
After the background, summarize what the penetration testing project is about. This is a high level description of why you want a pentest and what you want tested. For example, "We plan to conduct a penetration test on our customer facing web application and supporting backend APIs, to identify any vulnerabilities that could put customer data at risk." Explain the objectives of the project in plain terms: are you looking to harden your systems, meet compliance requirements, test a new system before go live, etc.? This overview sets the stage so the vendor understands the purpose and importance of the project.
Be very clear about the scope of the pentest what is included and what is not. This is one of the most critical parts of the RFP. List out the specific assets to be tested, such as:
Also mention anything explicitly out of scope. For instance, "Do not perform any tests on our legacy ERP system" or "Social engineering of employees is not allowed" if that's the case. Defining the scope in detail helps prevent misunderstandings. The vendor shouldn't have to guess what to test or worry about accidentally stepping out of bounds you've told them exactly where to play.
Include a timeline for the project. When do you want the testing to start, and during what time window should it occur? Are there any blackout dates (times when testing shouldn't happen, like during a big sale event or end of year financial close)? When do you expect the final report or results? For example, you might write: "Testing should be conducted in March 2025 and completed by March 31, with the final report delivered by April 7." If you have milestones, list them maybe an initial kickoff meeting, a mid test update, and a post test presentation of results. Providing a timeline sets expectations for vendors and allows them to check their availability and resources for your project.
Clearly state what qualifications you expect the vendor (and their testing team) to have. This can include:
This section is basically your "minimum requirements" for a vendor to even be considered. It helps weed out vendors who aren't qualified. Don't be shy here if you only want experienced vendors, say so.
"A well crafted RFP will attract the right talent and ensure the pentest is done professionally." — Cybersecurity Expert
Quick recap of key RFP components to include:
Covering all these in your RFP will give vendors a clear picture of the job and help you get more accurate proposals.
Defining the Scope and Methodology
When it comes to penetration testing, there are different approaches and depths of testing. In your RFP, it's a good idea to specify what kind of test and methodology you expect, so vendors can align their proposals with your expectations.
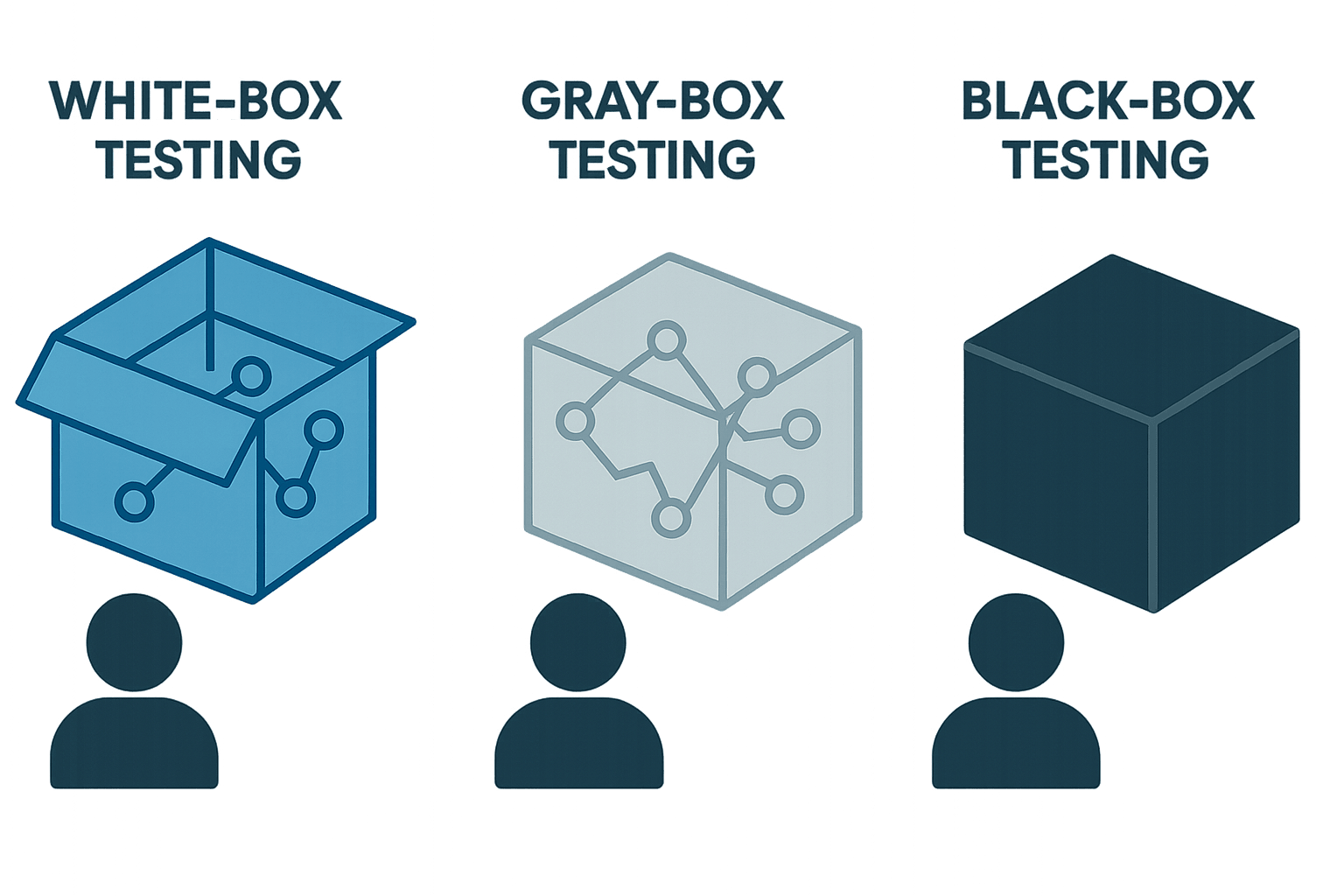
Decide how much information you're going to give the penetration testers about your systems ahead of time:
Each approach has its pros and cons, and one isn't "better" than the others universally it depends on your goals. In your RFP, mention which approach you want. For example, "The engagement will be a gray box test assume the tester has user level credentials to our application," or "This will be a black box test of our external network, with no prior information provided." This way vendors can propose the right resources and effort (white box tests might be quicker since they have all info, black box might take more exploratory work).
Consider whether you need a standard penetration test or a more involved Red Team exercise:
If you want a Red Team style test, say so in the RFP. Something like, "We are looking for a Red Team assessment that includes social engineering attempts," because not all vendors perform Red Team ops by default, and those that do will need to plan for it differently than a standard pentest.
Mention any security standards or frameworks you want the testing to align with. A common one is the OWASP Top 10 (for web apps) basically the top 10 most critical web application security risks. Including something like, "Tests should at minimum cover the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities," tells the vendor that you expect coverage of common issues like SQL injection, XSS, etc.
If you have compliance considerations, you might reference those too. For example, if you're subject to PCI DSS (for payment card data) or HIPAA (healthcare), you could say, "The test should consider vulnerabilities relevant to PCI DSS compliance." While the actual compliance isn't the vendor's job, it signals what matters to you.
The key is to let vendors know if there are any established guidelines you want followed. It also shows that you're informed and want a thorough job (most good vendors will do these anyway, but it never hurts to be explicit).
Establish clear rules for how the test should be conducted. This ensures the pentest doesn't unintentionally cause problems or cross any red lines. Consider including:
These rules of engagement make sure the vendor knows how to conduct the test without stepping on toes or causing unintended damage. Put these details in writing in the RFP, so every vendor knows the boundaries. It protects both you and the vendor.
By defining the methodology and rules clearly, you help ensure the penetration test will run smoothly and yield useful results. Everyone will know what game they're playing from the start, which builds trust and keeps the focus on improving security rather than dealing with mishaps.

Now that you know what to put in the RFP, let's talk about how to write it in a way that appeals to quality vendors. The tone and clarity of your RFP can influence the kind of responses you get.
Speak plainly and avoid unnecessary jargon. Your RFP isn't the place for flowery language or buzzwords you're trying to communicate needs and requirements as clearly as possible. For example, instead of saying "The organization wishes to embark on an extensive penetration testing initiative," just say "We need a thorough penetration test of our systems."
Also, define acronyms the first time you use them (e.g., say "Security Operations Center (SOC)" the first time, then SOC thereafter). Clarity is king: if a sentence can be interpreted in multiple ways, consider rephrasing it. A vendor shouldn't have to guess what you mean. If your RFP is clear and easy to understand, good vendors will appreciate it (and poor ones won't be able to hide behind misunderstandings).
In your RFP, some parts should be very specific (to make sure critical needs are met), while others can be open ended to gauge how vendors think. For example:
The benefit of open ended questions is that the answers will show you how the vendor thinks and communicates. If one vendor gives a very generic answer and another gives a detailed, thoughtful response, that tells you something about who might be more thorough. Just don't overdo it you don't want the RFP to turn into an essay questionnaire. Pick a few key points where you want the vendor's insight, and be specific everywhere else.
If there's particular expertise you value, say so. For example, many organizations request that the testing team include at least one person with the OSCP certification (Offensive Security Certified Professional) because it indicates solid, practical pentesting skills. You could write, "The testing team must include at least one OSCP certified tester (or equivalent)," as a requirement.
Similarly, if you need the vendor to have experience with a certain technology (say, AWS cloud environments, or a specific software platform), mention that too. The key here is to ensure the people doing the work are qualified. Certifications like OSCP, CISSP, CEH, etc., are proxies for skills they aren't everything, but they do show a baseline of knowledge. And if nothing else, including them in the RFP signals that you care about the qualifications of who will be poking at your systems.
It's important to set expectations that are ambitious yet achievable. Vendors will often spot an unrealistic RFP a mile away (and the good ones might not bid on it). For instance, don't expect a small security firm to magically test an entire corporate network with thousands of devices in a two day engagement something will give (either quality or honesty).
In your RFP timeline and requirements, make sure you're giving enough time for a thorough test and enough detail for a thorough report. If you have an ideal timeline, share it, but also ask vendors to propose a timeline if they feel yours is too tight. Being open to slightly adjusting scope or timeline based on vendor feedback can get you better results. The RFP can say, "We aim to complete testing within 4 weeks, but are open to vendor input on the testing schedule to ensure quality results." This shows you're looking for a realistic plan, not just the fastest, cheapest fix.
Clearly define what you expect to receive at the end of the engagement. Typical deliverables for a pentest include multiple reports or documents. Make sure your RFP asks for at least the following:
By spelling out these deliverables, vendors know exactly what they need to deliver. It also helps you compare apples to apples: if one proposal doesn't include an executive summary or a retest where others do, you can ask about it or factor it into your decision. Plus, when the project is done, you'll have the documentation you need to actually improve your security.
(Hint: You can even ask for a sample report (with client details redacted) from the vendor to see how well they communicate findings. Some companies do this as part of the RFP process.)
Once the proposals come in, how do you pick the best one? Here are some tips to evaluate vendors fairly and effectively:
It helps to have a scoring or ranking system to objectively compare proposals. For example, you might rate each proposal on criteria like:
Those percentages are just an example. The idea is to decide what's most important to you and score each proposal against those factors. This way, even if one proposal is a bit more expensive, you might justify it if they score higher in technical quality or experience.
Dig into how each vendor plans to perform the test. Do they mention specific tools or methodologies? Do they talk about manual testing versus automated scans? A strong proposal will often outline a rough game plan: for example, "Week 1 for reconnaissance and automated scanning, Weeks 2 3 for manual exploitation attempts, Week 4 for report writing and quality assurance."
Also, examine their team composition is it one person or a team? Who are they (often proposals include bios)? It's great if they have certifications, but more importantly, do they have real world experience doing what you need? If you're a cloud heavy company, did they mention knowledge of cloud security? If you want a mobile app tested, did they reference mobile pentesting experience? Look beyond buzzwords the substance of their approach matters.
Any reputable vendor should be able to provide references or case studies of past work (unless they're very new, in which case you're taking a bigger gamble). If they give you references, give those references a quick call or email. You'd be surprised how much you can learn by asking, "Were you satisfied with the work? Did they communicate well? Did the test cause any issues? How was their report?"
Case studies (even if anonymized) are also gold they show you how the vendor solved problems for other clients. For example, a case study might reveal that a vendor has done a pentest very similar to yours, which is a good sign. Pay attention to problem solving and thoroughness in these stories. And trust your gut: if a reference gives a lukewarm review, that's a sign to dig deeper or consider other options.
Budget matters, but don't automatically go with the lowest bid. Sometimes a higher quote comes with significantly more value. Read the fine print:
Ultimately, weigh what you're getting for the price. A penetration test is an investment in your security. Saving a little money upfront might cost you more later if the test misses something important. Often, the middle ground bid not cheapest, not most expensive can be a sweet spot, but it all depends on the details.
When engaging a security vendor, there are some legal and compliance boxes you definitely want to check. These might not be the most exciting parts of the RFP, but they're important for protecting your organization.
Always include an NDA (Non Disclosure Agreement) requirement. This means the vendor must agree to keep all the details of your systems and any vulnerabilities they find completely confidential. You don't want your security issues being talked about or shared publicly. Usually, vendors have their own NDA forms, or your legal team can provide one. In the RFP, a simple line like "The vendor will be required to sign a Non Disclosure Agreement before project initiation" is enough to flag this.
"A solid NDA is the first line of defense for protecting your sensitive information during a pentest." — Cybersecurity Expert
Make sure the vendor has appropriate insurance and clarify liability. Penetration testing has inherent risks a test might inadvertently cause a system outage or other issues. You want the vendor to carry insurance that covers any damage that might accidentally happen. Common insurance requirements include:
In the RFP, you might say, "Vendor must carry professional and cyber liability insurance with coverage of at least $X" (your legal team can help with the amounts). Also, include a statement that the vendor assumes responsibility for any damages caused by their testing activities. Most vendors will never have an issue, but it's good to have this in writing.
If your organization is subject to specific regulations or standards, include those compliance requirements. For example:
Also, you can ask for any security certifications or audits the vendor has. Some organizations ask for a copy of the vendor's ISO 27001 certificate or SOC 2 report to ensure the vendor follows good security practices internally. It's a bit meta you're checking the security of your security vendor.
During a pentest, the team might gain access to sensitive data (customer info, personal data, etc.) or produce sensitive information (the report itself is sensitive!). Outline what you expect them to do to protect that data:
These details might also go into the contract later, but raising them in the RFP means the vendor will address them in their proposal. It shows you take security and privacy seriously even during the test.
By covering legal and compliance bases in your RFP, you reduce the risk of hiccups or disputes down the line. Plus, the vendors that respond will know you expect professionalism and thoroughness, which might discourage any less serious players from bidding.

Conclusion
Crafting a penetration testing RFP in everyday language doesn't mean you leave out important details it means communicating them more clearly. By investing the time to write a clear, detailed RFP, you're setting the stage for a successful pentest engagement.
Remember, a pentest RFP is your chance to convey exactly what you need. Be thorough: outline your objectives, scope, timeline, and criteria for success. Be clear: use straightforward language and avoid ambiguities. And be practical: include the necessary legal protections and set realistic expectations.
At the end of the day, the goal is to improve your organization's security. A well written RFP will help attract a capable vendor who understands your needs, and that means you'll get more value out of the penetration test. So, take a bit of extra time to get the RFP right your future self (and your security team) will thank you when the test results come in and they're exactly what you needed.
What is the primary purpose of a Penetration Testing RFP?
Its main purpose is to clearly communicate your penetration testing needs and expectations to potential vendors. In other words, it spells out what you want done (and how/when), so vendors can craft proposals to meet those requirements. A good RFP makes sure both you and the vendor are on the same page from the start.
What is the difference between a Penetration Testing RFP and an RFI?
A Penetration Testing RFP is asking vendors for a proposal on a specific pentesting project including how they'd do it and how much they'd charge. An RFI (Request for Information) is more general you're asking for information about services or capabilities, not for a project plan or price. You might send an RFI to learn about what a pentesting firm offers, then later issue an RFP when you're ready to get actual proposals.
What are the key components of a well crafted Penetration Testing RFP? It should include: a brief company background, an overview of the project and objectives, a clearly defined scope of work, the timeline and schedule for the project, the qualifications you expect from the vendor, and the deliverables/reporting you expect to receive. Basically, it needs to tell the vendor everything about what you need, when you need it, and what you'll judge them on.
What is the difference between white box, gray box, and black box testing?
These terms describe how much knowledge the tester has before starting:
Why is it a good idea to request OSCP certified testers in a Penetration Testing RFP?
OSCP is a well respected certification in the pentesting world that shows a person has hands on hacking skills. If you request an OSCP certified tester, you're basically ensuring that at least one person on the vendor's team has proven they know how to find and exploit vulnerabilities. It's a way to gauge expertise. It's not the only certification that matters, but it's a strong indicator of practical ability.
What are the typical deliverables expected from a penetration testing project?
Usually, you'll get a few key deliverables:
How can organizations ensure they comply with security regulations during a penetration testing project?
The best approach is to build those requirements into the RFP and the engagement. Make sure your RFP asks vendors to follow relevant standards (like OWASP Top 10, NIST guidelines) and to adhere to any compliance frameworks you fall under. For instance, require them to follow HIPAA rules for data if you're in healthcare, or to sign a GDPR data processing agreement if personal data is involved. Also, include requirements for how they handle your data (encryption, secure deletion, etc.). Essentially, be explicit about compliance and data protection in your RFP and contract that way, any vendor you choose has contractually agreed to meet those requirements.
What are key factors to consider when evaluating and selecting a vendor from the proposals?
Pay attention to several things:
It's a balance you want a vendor who is technically competent, reliable, and within your budget. Using a scoring system as mentioned can help weigh these factors so you look at the overall picture rather than focusing on just one thing like cost.
Why is it crucial to establish a clear scope of work and rules of engagement in a Penetration Testing RFP?
Because it prevents misunderstandings and accidents. A clear scope of work tells the vendor exactly what to test (and what not to test), so they don't miss anything important or hit something you didn't intend to include. Clear rules of engagement set the boundaries (like when they can test, how far they can go, who to contact in an emergency). Together, scope and rules ensure the pentest is conducted safely, effectively, and without any unintended consequences (like knocking over a critical server or violating a compliance rule). In short, clarity here means a smoother, problem free engagement.
What is the importance of retesting and verification in a penetration testing project?
Retesting is basically a sanity check after you've fixed the issues. Its importance is high without it, you have to assume that all the fixes worked and covered the vulnerabilities. By having the pentest team come back to verify, you get confirmation that the holes are truly patched. It's like fixing a leaky roof and then spraying water on it to make sure it no longer leaks. Retesting gives you confidence that the vulnerabilities found in the pentest have been effectively resolved, thereby actually improving your security posture, not just identifying problems.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us