May 15, 2025
Updated: May 15, 2025
A data-driven analysis of ransomware attack frequency, ransom payments, downtime costs, and evolving extortion tactics in 2024–2025.
Mohammed Khalil

Ransomware remains one of the most prominent and destructive cyber threats in 2025, but the dynamics of this crime are changing in profound ways. Ransomware statistics tell the story: on one hand, the volume of attacks has never been higher, on the other hand, organizations have gotten better at withstanding extortion without paying. The result is a kind of paradox: ransomware actors are attacking more targets for shrinking returns.
This report provides a data driven analysis of ransomware trends, patterns, and impacts over the past year 2024–2025, drawing on publicly reported incidents, cybersecurity surveys, and industry research in the style of leading annual threat reports Verizon DBIR, IBM, ENISA, CISA, etc.. The goal is to quantify how often ransomware strikes, how much it costs, how attacker tactics are evolving, and what it all means for businesses and defenders. A few headline findings illustrate why ransomware is at an inflection point:
By diving into the statistics from attack rates and initial access vectors to ransom payments and downtime costs we can gain insight into how ransomware operations are changing and how organizations should adapt. The numbers put hard evidence behind the trends, helping separate hype from real risk. In the sections that follow, we’ll break down the key metrics and findings for 2025 and provide context for each: What are ransomware statistics and why do they matter? What do the global and regional figures show? How are ransom demands and outcomes shifting? Which attack vectors are most common? Who’s being hit the hardest? Finally, we translate these stats into actionable defensive strategies and answer frequently asked questions.
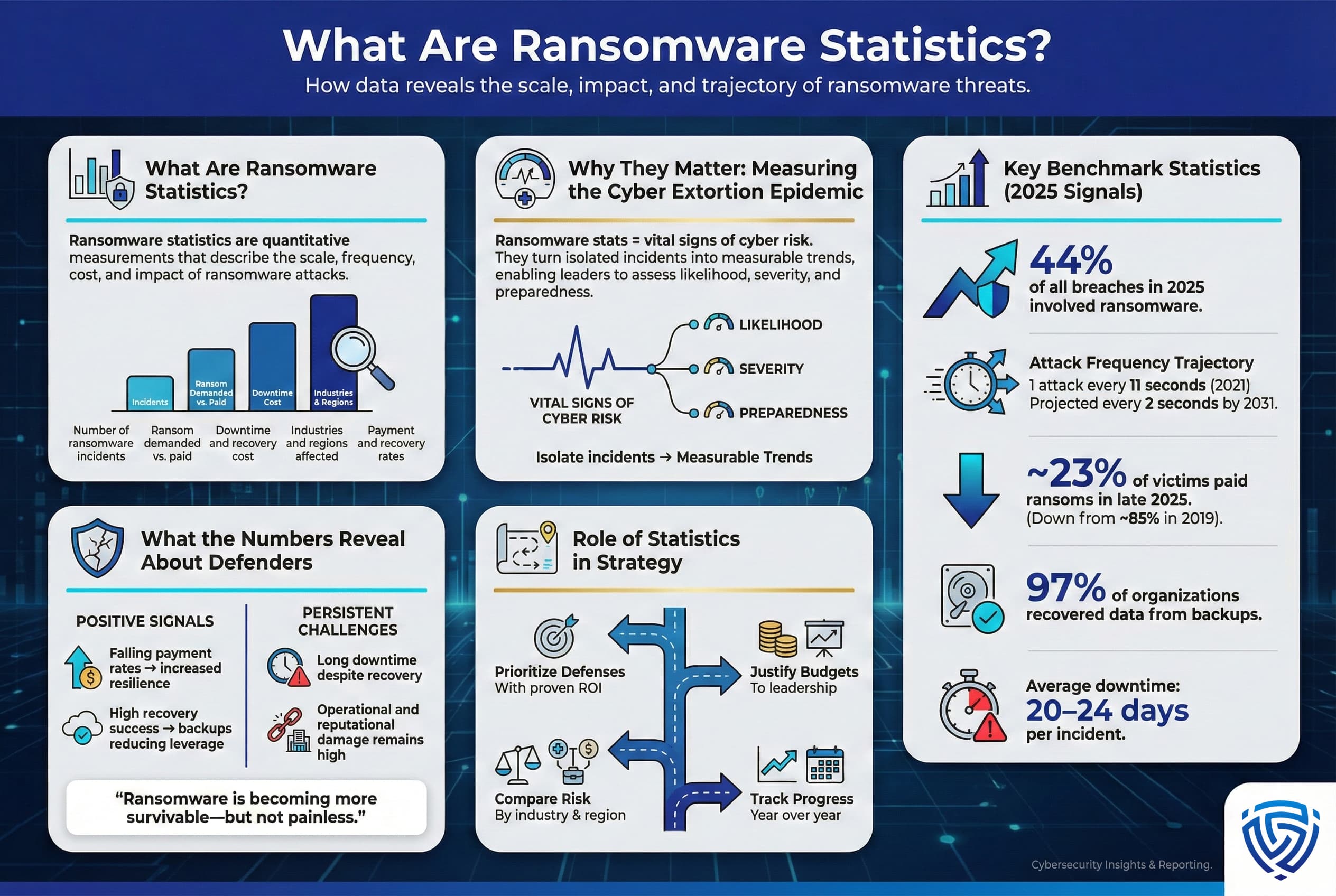
In simple terms, ransomware statistics are the quantitative facts and figures that capture the scale, frequency, and impact of ransomware attacks. They answer questions like: How many ransomware incidents are happening? How much ransom do attackers demand versus what victims actually pay? What does an average ransomware breach cost in downtime and recovery? Which sectors or regions are most affected? These statistics are collected from real world incident reports, surveys of cybersecurity professionals, cryptocurrency tracking, and disclosure data to provide an evidence based picture of the ransomware threat landscape.
Think of ransomware stats as the vital signs of the cyber extortion epidemic much like a doctor checks a patient’s blood pressure and pulse. For example, one widely cited stat from Cybersecurity Ventures predicts a business or consumer will be hit by ransomware every 2 seconds by 2031, up from one every 11 seconds in 2021. This metric alone signals the velocity of attacks is expected to keep increasing dramatically. Another statistic: Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report found that 44% of data breaches in 2025 involved ransomware, up from ~32% the year prior. That indicates ransomware isn’t just a standalone issue, it's present in nearly half of all breaches, often compounding the damage by adding an extortion element to an intrusion.
Crucially, ransomware stats also shed light on defender outcomes. One positive trend is the plummeting payment rate, by late 2025 only ~23% of victims paid ransoms. Compare that to 2019, when an estimated 85% of organizations gave in to attackers’ demands. This number tells a story of improved resilience. Companies are better at restoring systems without paying and more willing to absorb the hit than fund criminals. Likewise, statistics on data recovery show that 97% of organizations can recover encrypted data from backups or other means, removing much of the attackers’ leverage. On the flip side, a stat like the average downtime of 20–24 days per ransomware incident highlights that even without paying a ransom, businesses face significant operational losses.
In summary, ransomware statistics quantify the threat. They turn anecdotal horror stories into measurable trends. This helps business leaders and security teams understand how likely an attack is, how severe the consequences could be, and which defenses are making a difference. By examining these numbers, we can gauge whether we’re getting better or worse at handling ransomware and adjust strategies accordingly. As we proceed, each section of this report will use statistics with sources to illuminate a different aspect of the ransomware problem in 2025.
To appreciate the current ransomware risk, it’s useful to look at the big picture metrics and how they’ve changed from previous years. Below is a snapshot of key global ransomware statistics, comparing roughly 2024 and 2025:
| Metric | 2024 Approx. | 2025 Approx. | Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reported Ransomware Incidents | ~3,200 Jan–Sept | ~4,700 Jan–Sept | ↑ Surge +30–40% YoY |
| Publicly Disclosed Victims on leak sites | ~5,000 for full year | ~6,500+ for full year est. | ↑ More breaches exposed |
| Organizations Paying Ransom | ~49% paid in 2024 | ~23% paid in Q3 2025 | ↓ Plummeting payment rate |
| Median Ransom Payment | ~$200k 2024 overall | ~$140k Q3 2025 | ↓ ~50%+ decrease |
| Average Recovery Cost excl. ransom | ~$1.85M 2023 | ~$1.53M 2025 | ↓ Slight improvement |
| Average Downtime | ~25–29 days | ~24 days | ↓ Faster recovery |
| Attack Frequency | ~1 every 10–11 sec 2020 | ~1 every ~3 sec 2025 est. | ↑ Steep increase projected 1/2 sec by 2031 |
| Global Ransomware Payments | ~$1.1 B 2023 | ~$600–650 M 2025 est. | ↓ Declining revenue |
Two contrasting truths emerge from the global data. First, ransomware activity incidents are at record highs and have effectively become a constant background radiation of the internet. Researchers noted a sustained escalation throughout 2025, with some months hitting all time highs in observed attacks. By one estimate, ransomware attacks worldwide are on track to increase from one every 11 seconds in 2021 to one every 2 seconds by 2031 if unchecked. This means what used to be occasional, isolated events have transformed into a continuous barrage of automated attacks against organizations of all sizes. In early 2025, analysts were tracking over 26,000 cyberattacks per day, many involving ransomware hitting targets globally. The sheer volume suggests that no company can assume it’s too small or obscure to be targeted. Opportunistic ransomware bots are scanning and striking everything from large enterprises to local governments and small businesses.
Yet, the second truth is that ransomware’s profitability has started to crack. Total global ransom payments appear to be down significantly from their peak in 2021–2022. One blockchain analysis found extortion revenue fell from around $1 billion in 2023 to an estimated $600–800 million in 2025. This decline in attacker earnings corresponds to the major drop in payment rate, more victims are simply refusing to pay, thereby starving criminals of income. It’s a remarkable development: even as more organizations are getting hit than ever, a smaller percentage of those attacks are resulting in a payout. In Coveware’s words, cyber extortion’s overall success rate is contracting. Law enforcement and policymakers will point to this as progress indeed, it reflects the impact of improved backups, incident response planning, and perhaps tougher stances legal and ethical against ransom payment.
From a global perspective, this shift has forced ransomware actors to adapt in various ways, which will be explored in later sections. Already we’ve seen a pivot to stealing data so attackers have something to monetize even if the ransom fails and a bifurcation where they either go for many small victims low ransom each, but higher volume or a few extremely large victims hoping for a jackpot payday. The statistics in 2025 bear this out: for instance, the median ransom payment collapsed to ~$100k, indicating mid-sized organizations aren’t paying big money, whereas the average skewed by big cases remained around $0.5–1 million, showing that a handful of giant payments still occur. In short, volume vs. value has diverged lots of attacks, but few big paydays.
Geographically, the worldwide data shows ransomware is a global problem but not evenly distributed. Roughly half of known attacks in 2024 25 were in North America with the U.S. as the top target. Europe accounted for roughly a quarter of cases, the U.K., Germany, Italy among the hardest hit. However, growth is shifting toward regions like Asia Pacific and Latin America. Notably, Latin America saw a 108% YoY increase in cyberattacks Q1 2025 the steepest rise of any region as gangs turn to what they perceive as softer targets in developing economies. We’ll delve more into regional differences later, but the key point is that ransomware is a truly global epidemic, constrained only by where there are internet connected systems and money to be made.
To summarize the global outlook for 2025: ransomware is more prevalent than ever, but defenders are yielding fewer wins to adversaries in terms of ransom paid. This creates a high volume, high stakes standoff. Attackers are hitting more victims hoping someone will pay, and when that fails, they leak data or try new tactics. The statistics indicate a maturation on the defense side, hardening and resilience measures are paying off yet the threat itself remains at an elevated, systemic level. In the next sections, we examine specific facets like ransom economics, attack vectors, industry impacts, and threat actors to understand this evolving chess match between attackers and defenders.
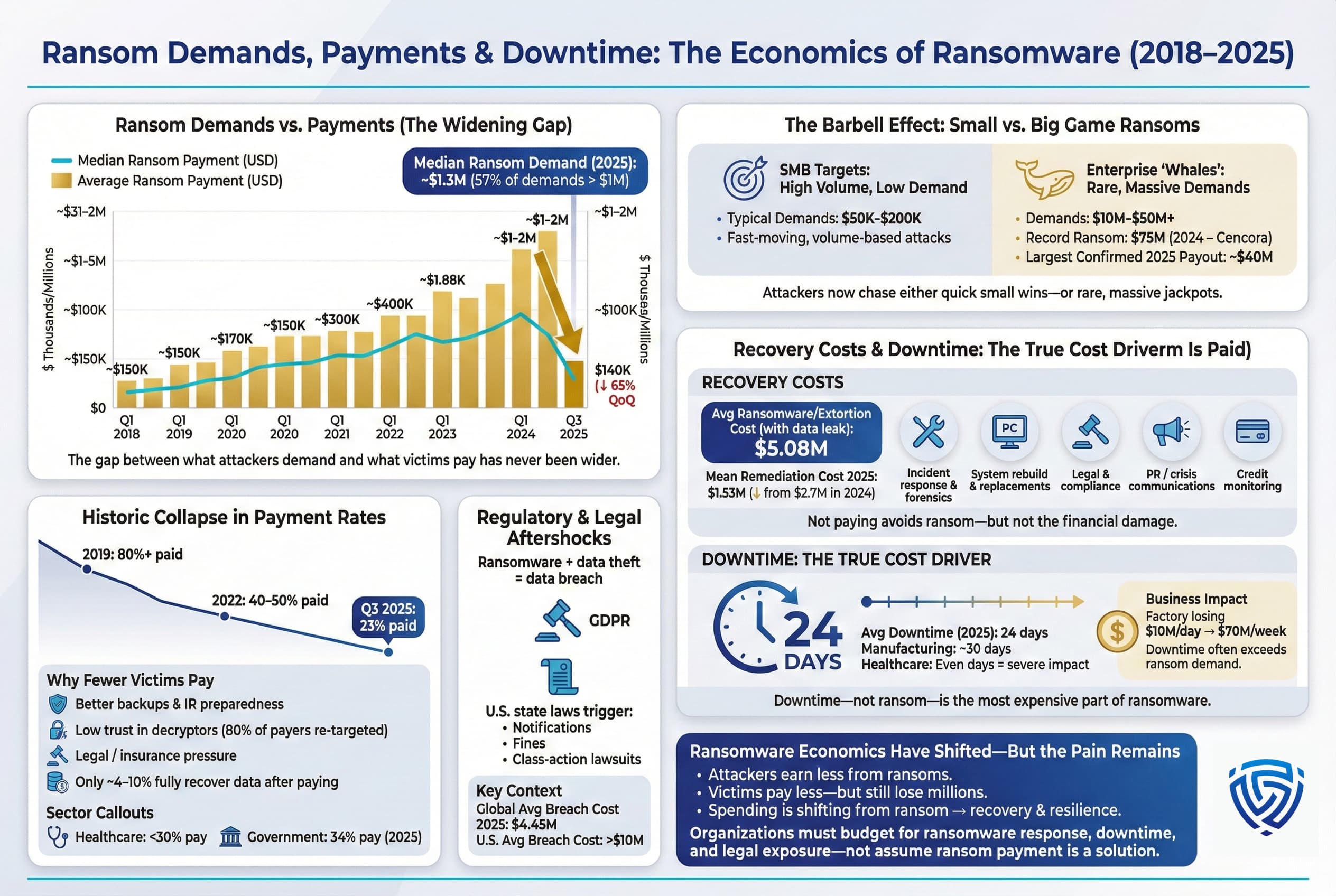
One of the most telling aspects of the ransomware crisis is the economics of ransom demands and payments. Over the past year, there have been striking changes in how much criminals are asking for, how much victims are actually paying, and the costs incurred regardless of payment. These statistics shine a light on attacker strategy and victim behavior.
Figure: Average vs. median ransom payments by quarter 2018–2025. A sharp drop in Q3 2025 reflects fewer large payouts and successful negotiations for lower amounts.
Demand vs. Payment The Growing Gap: In 2025, ransomware groups often initially demanded hefty sums, especially from large enterprises, multi million dollar figures are not uncommon for big targets. However, the amount victims end up paying has dropped dramatically. According to Coveware, the median ransom payment in Q3 2025 was only $140,000, down 65% from the previous quarter. For context, the median was about $400k in 2023 and spiked to ~$1–2M in some 2024 cases, so this is a remarkable collapse. The average payment in Q3 2025 was ~$377,000 but that average is skewed by a few large payments, many victims paying nothing or very little. What this tells us is that victims or their insurers are negotiating hard or refusing outright, especially in the mid market. Ransomware actors have responded by lowering demands for smaller victims knowing they can’t pay millions and concentrating high demands only on the biggest whales.
Indeed, a barbell pattern has emerged: at one end, lower end ransoms have gotten smaller and more frequent e.g. demanding $50k–$200k from a small business and moving on quickly if they say no. At the other end, upper end ransoms have gotten even larger asking tens of millions from a Fortune 500 company in a critical industry. For example, in late 2024 the Dark Angels group successfully extorted $75 million from pharmaceutical giant Cencora AmerisourceBergen, the largest known ransom ever paid. While extremely rare, such windfalls motivate criminals to continue targeting big game organizations where lives or critical services might be on the line, making leadership more likely to pay. In 2025, the largest ransom demand publicly reported was around $50 million in a healthcare breach, and the largest confirmed payout was roughly $40 million per Coveware’s data early 2025 though the $75M record from 2024 still looms. The average demand as of 2025 is hard to pin down, but one industry report put the median demand around $1.3 million and 57% of demands above $1M, whereas the median actual payment was around $1.0 million or less. In short, the gap between what attackers ask for and what victims pay has widened.
Historic Low in Payment Rate: Perhaps the most positive statistic for defenders is the precipitous drop in the proportion of victims who pay anything at all. In 2019, it’s estimated that 80%+ of organizations hit by ransomware ended up paying the ransom. By 2022, that fell to around 40–50%. And by Q3 2025, only 23% of ransomware victims paid. That means nearly 3 out of 4 companies now weather the attack without funding the criminals. This is attributed to multiple factors, Better preparedness companies have offline backups, incident response firms on retainer, and business continuity plans that allow them to restore operations without decryption keys. Eroded trust in attackers. Many victims have learned the hard way that paying doesn’t guarantee smooth recovery, decryption tools can fail, or attackers might still leak data. One statistic revealed that 80% of companies who paid a ransom got hit again later, and only a small fraction perhaps ~4–10% of those who pay get all their data back. With odds like that, more boards conclude that payment isn’t worth it. Legal and insurance pressures law enforcement agencies strongly advise against paying, and in some cases if hackers are sanctioned entities paying could even be illegal. Cyber insurance policies, while they sometimes cover ransom costs, increasingly require clients to show they tried all other recovery options first.
It’s worth noting the payment rate can vary by sector. For example, healthcare organizations pay at lower rates often <30% because many simply cannot afford the ransom or can’t risk the liability if data was stolen anyway. By contrast, some industrial firms or municipalities historically paid more often due to needing immediate restoration of services, though even those sectors are paying less now e.g. Sophos found only 34% of government orgs hit in 2025 paid. The overall trend is clear: Don’t pay is becoming the default stance, a remarkable change in just a few years.
Costs of Recovery and Downtime: Just because victims aren’t paying ransoms doesn’t mean ransomware is free for them. Far from it the costs of incident response, IT remediation, lost business, and legal fallout are enormous. IBM’s research consistently shows ransomware or destructive attacks to be among the most expensive types of breaches. In 2025, the average cost of a ransomware/data extortion incident was estimated at $5.08 million when the attack involved public disclosure. Even incidents that are contained quietly can cost a couple million in recovery expenses. A recent survey by Sophos put the mean remediation cost at $1.53 million in 2025 down from $2.7M in 2024, which suggests incident response is getting more efficient. This figure typically includes: forensic investigators to find and purge malware, data recovery specialists, hardware/software replacement for destroyed systems, outside legal counsel, public relations/crisis management, and credit monitoring for affected customers if data was stolen.
Downtime remains the single biggest cost contributor. When critical systems or production lines are down for days or weeks, the business interruption losses accumulate rapidly. In 2025, companies reported an average of about 24 days of downtime from ransomware attacks. Certain sectors had it worse for instance, manufacturing organizations took an average of 30 days to fully restore operations in one survey down from 36 days prior year. In healthcare, even a few days of downtime can be devastating, hospitals divert patients, cancel surgeries, etc., leading to lost revenue and potential harm. One UK healthcare laboratory attack in 2024 caused months of disruption in diagnostics, a year later the ripple effects were still being felt. The cost of lost productivity and sales during downtime often exceeds the ransom demand e.g., if a factory making $10M a day in product is down for a week, that’s $70M lost, far above a typical ransom demand. This is why many organizations invest so much in resilience e.g. redundant systems, failover to backups, etc. every day shaved off the outage is money saved.
Another cost factor is the post incident regulatory and legal impact. Under laws like GDPR in Europe or various U.S. state laws, a ransomware incident that results in personal data exposure is essentially a data breach and triggers notification requirements and possible fines. That adds direct costs, regulatory penalties, breach notifications, class action lawsuits on top of the IT recovery. For instance, a U.S. company might face lawsuits if customer data is leaked, even if they refused to pay the ransom. These downstream costs are harder to quantify in averages, but they contribute to why the global average breach cost hit $4.45M in 2025 and why the U.S. average breach cost is over $10M ransomware incidents often tick all the worst case boxes system downtime, data breach, and compliance failure in one.
In summary, the ransom part of a ransomware attack is increasingly a zero sum game for attackers, fewer victims are paying, and those who do pay are paying less. But from the victim’s perspective, whether or not a ransom is paid, the incident can still be extremely costly. Organizations are essentially investing the money saved on ransoms into recovery and hardening. It’s arguably a better allocation since it doesn’t encourage criminals, but it’s still a significant financial drain. The statistics underline a crucial planning point: companies must budget for ransomware response and resilience, not just prevention. Assuming we’ll just pay the ransom and be done is neither a safe nor reliably effective strategy in 2025.
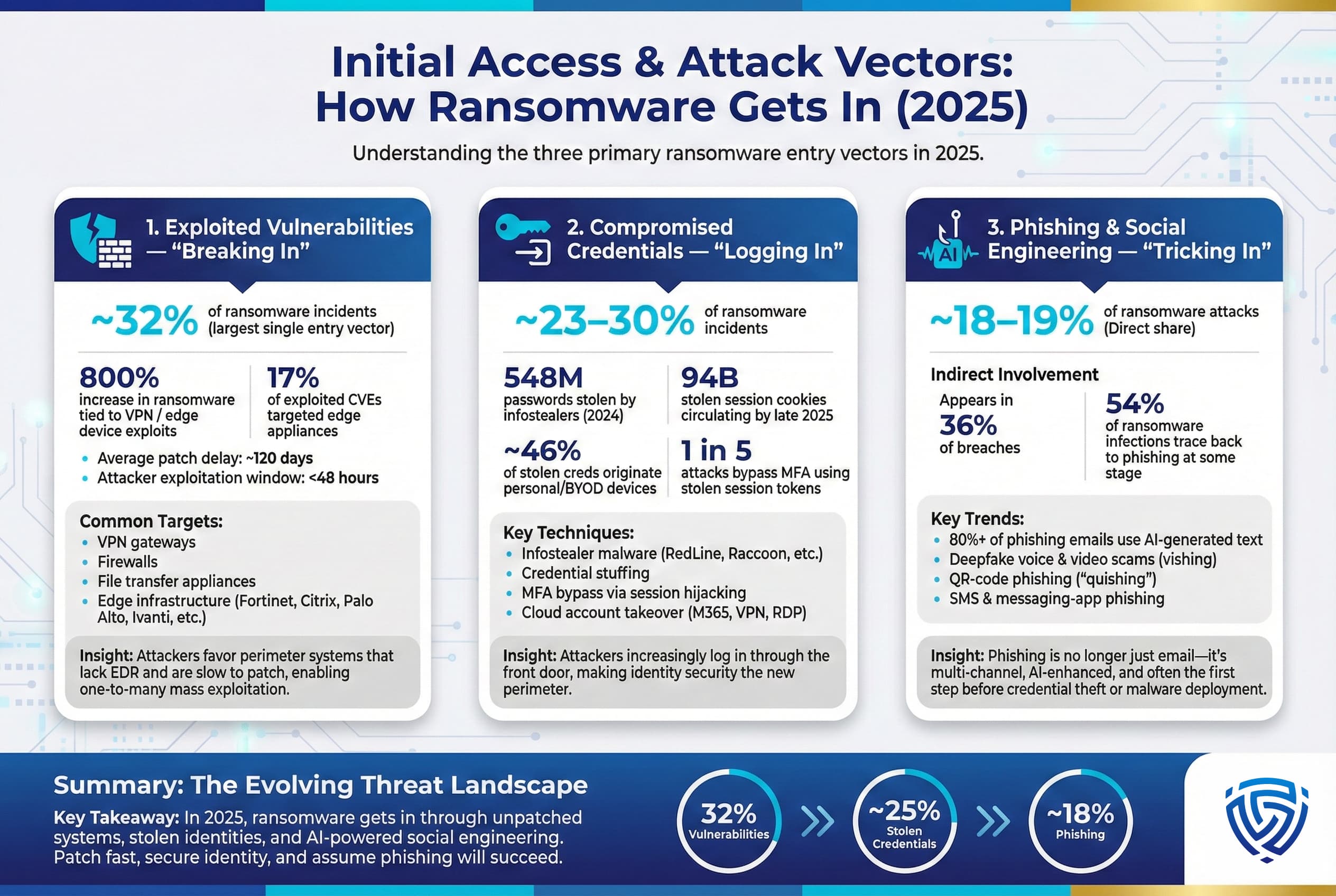
How are ransomware attackers getting into networks in the first place? The entry point often called the initial access vector is a critical piece of the puzzle for defenders to understand. In 2025, ransomware groups exploited two primary pathways into organizations: software vulnerabilities breaking in and stolen credentials logging in. Additionally, social engineering via phishing remains a persistent third vector. Let’s examine the stats behind these attack vectors:
1. Exploited Vulnerabilities Breaking In: Unpatched software flaws in internet facing systems continued to be a top entry method, responsible for an estimated 32% of ransomware attacks in 2025. This made it the single most common root cause in some analyses. Notably, attackers shifted their focus to edge infrastructure VPN gateways, firewalls, file servers, etc. that sit on the network perimeter and often can’t be protected by traditional antivirus. There was an 800% increase in ransomware incidents traced to exploit VPN/edge device vulnerabilities in 2025, according to industry observations. Products from vendors like Fortinet, Citrix, Palo Alto, and Ivanti had critical flaws e.g., CVEs in 2023 2024 that ransomware affiliates raced to weaponize. One report by Recorded Future found that edge/gateway appliances accounted for 17% of all exploited vulnerabilities in the first half of 2025 equal to the share of exploits against Microsoft products. Why the edge? These systems often lacked endpoint detection agents and were overlooked in patch cycles, making them low hanging fruit. Attackers would scan the entire internet for a new vulnerability within 48 hours of a patch release and start compromise attempts. Unfortunately, many organizations take weeks or months to apply such patches, leaving a huge window of opportunity. The average lag to patch critical vulns was ~120 days in some studies, versus <2 days for attackers to exploit a dangerous gap.
Real incidents illustrate this mass exploit trend. For example, in June 2023 and again in 2024, the Clop ransomware group exploited a zero day in a popular file transfer appliance MoveIt, Accellion FTA, etc., breaching hundreds of organizations in one sweep via their third party vendors. In 2025 this continued: ransomware crews pounced on newly disclosed flaws in products like Citrix NetScaler and Progress WS_FTP server, leading to rapid fire intrusions worldwide before companies could patch. The strategy is clear: rather than phishing one target at a time, criminals are increasingly looking for one to many exploits that can open dozens or hundreds of doors at once. This makes vulnerability management and timely patching more critical than ever in ransomware defense.
2. Compromised Credentials Logging In: The other primary avenue is the use of valid credentials to simply log into a network or cloud service. Roughly 23% of ransomware incidents in 2025 stemmed from stolen or weak credentials estimates range 23–30%. Attackers love this vector because it often bypasses security controls if they have a legitimate username/password and sometimes a stolen MFA token or cookie, they can authenticate through VPNs or remote desktops as an authorized user, flying under the radar. The surge in this vector has been driven largely by info stealer malware and the underground markets selling credentials. In 2025, info stealer infections exploded, one analysis found stealer malware like RedLine and Raccoon harvested 548 million passwords and 17 billion session cookies in 2024 alone, and the trend continued upward in 2025. In fact, an estimated 94 billion stolen authentication cookies were circulating on the dark web by late 2025 a ~74% YoY increase allowing attackers to hijack active login sessions without needing the password.
The result is a flood of corporate login details for sale. One report noted about 30% of infostealer malware logs came from devices with enterprise credentials or applications. Even personal devices aren’t exempt, over 46% of stolen logs were from home or BYOD devices used for work, meaning employees’ mixing of work accounts on personal machines is seeding credentials to criminals. Ransomware affiliates will simply buy these credentials often for a few dollars and try them to gain initial access. In many cases, they don’t even need to crack passwords thanks to these logs. Furthermore, the criminals now target session tokens: nearly 1 in 5 attacks involve using a stolen session cookie to bypass multi factor authentication MFA by impersonating a pre authenticated session. For instance, in 2025 the FBI warned of rampant use of stolen Microsoft 365 session tokens that let hackers into cloud email accounts despite MFA. This tactic, essentially MFA bypass via session hijacking, is a direct result of the infostealer epidemic.
It’s also notable that brute force and old school credential attacks like spraying default passwords or exploiting RDP with weak logins still happen, but they’ve been somewhat supplanted by these more automated malware driven thefts. Credential stuffing using leaked password databases to try logins on various accounts accounted for about 22% of breaches in 2024 25, indicating password reuse is still a huge problem. Overall, the stats paint a clear picture: identity compromise is a leading cause of ransomware incidents. Attackers are logging in through the front door because some user’s password was stolen in a breach or malware infection. This underscores why multi factor authentication, password managers, and monitoring of logins are emphasized in best practices. However, as noted, even MFA isn’t foolproof if session cookies are stolen, highlighting the need for more phishing resistant methods like FIDO2 keys and vigilant detection of anomalous logins.
3. Phishing & Social Engineering: While exploitation and credentials dominate, phishing remains a consistent threat vector often it’s the precursor that delivers the malware or steals the credentials. Roughly 18–19% of ransomware attacks in 2025 were attributed directly to malicious email or phishing as the initial entry. And phishing is indirectly involved in many more phishing someone’s VPN password, phishing to get an initial foothold before deploying ransomware, etc.. One striking development in 2025 is the degree to which phishing operations have been supercharged by AI. Over 80% of phishing emails now contain some AI generated text, according to security analyses. Attackers are using tools like ChatGPT to write flawless, convincing emails in any language, eliminating the tell-tale grammar mistakes that users might catch. They’re also generating fake voices and videos deepfakes for use in voice phishing vishing 2025 saw incidents where a deepfake audio of a CEO was used to trick an employee into a fraudulent transfer, for example. These advances mean phishing messages are more persuasive and harder to distinguish from legitimate communications.
Attackers also expanded phishing beyond email: SMS/text phishing smishing, voice calls, messaging apps, and even malicious QR codes squishing all saw increased use. For instance, millions of QR code phishing emails were sent per day in 2025, exploiting curiosity to get users to scan codes with their phones. The key takeaway is that phishing is still a major enabler of ransomware whether by delivering an initial malware dropper, capturing credentials, or helping move laterally within a network, phishing an admin, etc.. It often works hand in hand with other vectors: e.g., an attacker might phishing a user to get a foothold, then exploit a vulnerability to escalate privileges, then deploy ransomware. According to Verizon’s data, phishing was the top action variety in breaches in 2025, appearing in 36% of cases, and 54% of ransomware infections could be traced back to a phishing email at some stage.
In summary, the initial access trends in 2025 emphasize two things: the importance of keeping systems up to date to close those exploit windows and the importance of identity security to prevent stolen credentials from being an easy in. If 32% of intrusions start with a known vulnerability, robust patch management and virtual patching workarounds, shielding can eliminate a huge chunk of risk. Likewise, if ~25% start with stolen credentials, practices like strong unique passwords, multi factor auth, detection of unusual login patterns, and reducing password reuse can similarly cut risk. Phishing, which overlaps with both people can be phished for passwords or to run malware, is more of a human challenge requiring user education, email filtering, and an assumption of breach Zero Trust mentality. The 2025 stats clearly tell defenders: focus on the basics, patch your external systems and lock down your authentication because that’s how ransomware is most likely to get in.
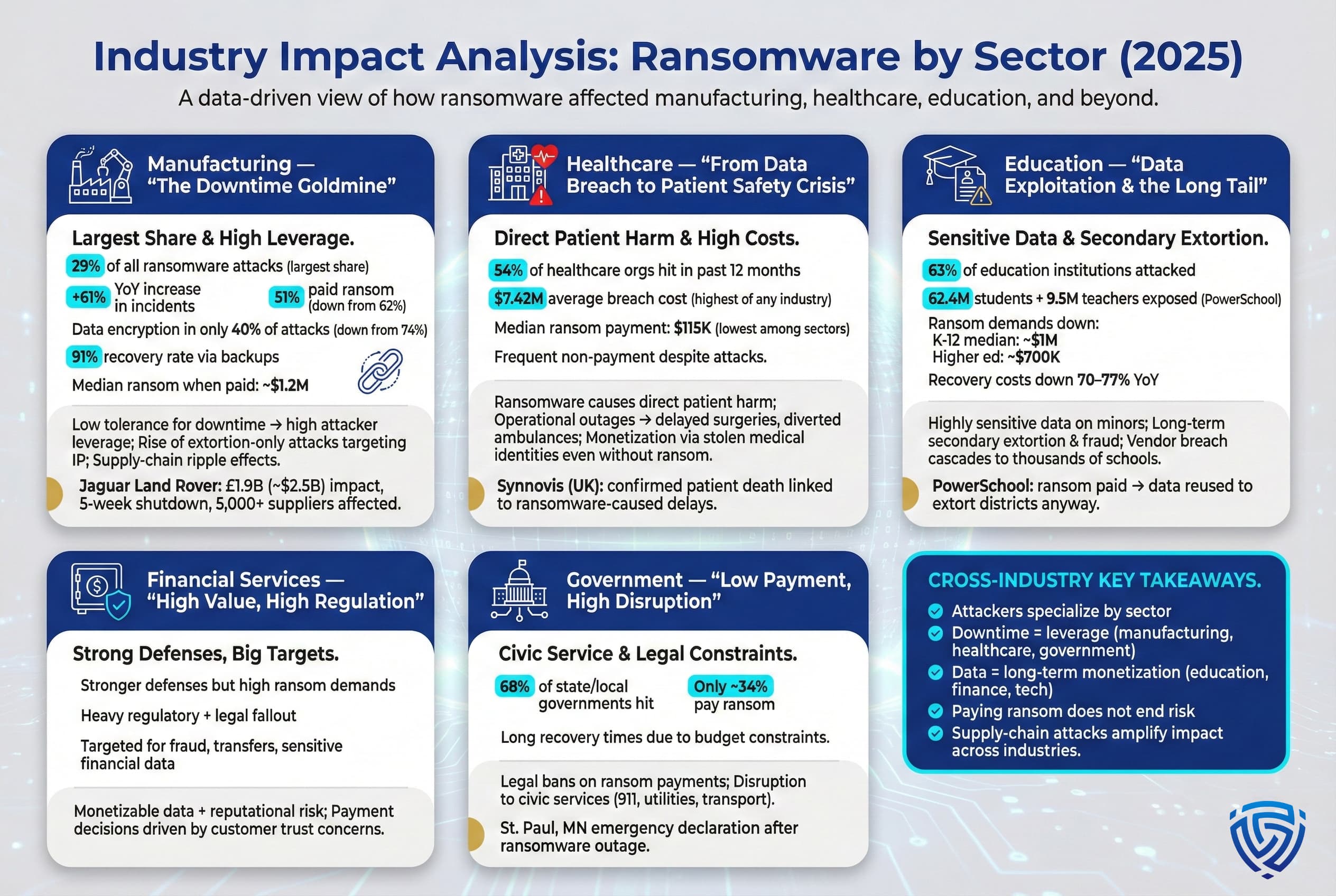
Ransomware is not an equal opportunity threat, some industries are targeted far more heavily than others due to the nature of their operations and data. In 2025, statistics show distinct patterns in how ransomware groups picked their victims and the impact those attacks had. Three sectors in particular stand out: Manufacturing, Healthcare, and Education, with Government and Finance also notable. Let’s examine each:
Manufacturing: The Downtime Goldmine
Manufacturing and production organizations became the #1 target for ransomware by volume in 2025, experiencing an estimated 29% of all recorded attacks, the highest share of any sector. This represented a massive 61% increase in manufacturing ransomware incidents compared to the prior year. The reason is straightforward: manufacturers have extremely low tolerance for downtime. When a factory or supply chain is disrupted, every hour can mean millions in lost revenue and contractual penalties. Ransomware gangs know this and use it as leverage. A manufacturer is more likely to pay a ransom if it means getting critical production lines back up faster especially in industries like automotive, semiconductors, etc., where just in time production is the norm.
However, 2025 also showed that manufacturing firms are improving at dealing with attacks. One survey found data encryption occurred in only 40% of manufacturing ransomware attacks, down from 74% in 2024. In other words, in many cases the attackers got in but were stopped before they could encrypt everything, perhaps through better network segmentation of OT operational technology systems, or faster detection/response by security teams. Additionally, 91% of manufacturing organizations that did have data encrypted were able to recover it mostly via backups. These stats suggest that robust backup and incident response drills in manufacturing are paying off, companies can restore machinery controls and databases without caving in. In fact, about 10% of attacks on manufacturers in 2025 were extortion only , no encryption, just data theft, triple the rate from the year before. This indicates that adversaries sometimes didn’t bother encrypting or were foiled in the attempt, and instead tried to ransom by threatening leaked IP e.g. proprietary designs, formulas. Manufacturing is rich in intellectual property that competitors might love to see, so even if operations resumed via backups, the data leak threat remains serious.
A high profile case in 2025 was the Jaguar Land Rover JLR attack. In August, JLR had to halt production for five weeks after ransomware hit a key supplier and spread into their systems. It was dubbed the most economically damaging cyberattack in UK history, projected to cost JLR £1.9 billion ~$2.5B in losses. Over 5,000 downstream suppliers were also impacted by the cascading shutdown. The group claiming responsibility Scattered Lapsus$ Hunters exploited the supply chain to hit JLR. This case underscores how disruptive ransomware in manufacturing can be: it’s not just one company, but an entire ecosystem of suppliers and distributors that can grind to a halt. While JLR did not publicly confirm paying any ransom and likely did not, the incident showed that even without a payout, the damage was immense. This raises a strategic concern: ransomware attacks on critical manufacturing can become issues of national security and economic stability, not just private IT incidents.
Despite resilience gains, manufacturing organizations still paid ransoms more often than some sectors in the Sophos 2025 survey, about 51% of manufacturing victims ended up paying something, though down from 62% prior year. And the ransoms in manufacturing tended to be high when paid median ~$1.2M in one dataset, reflecting the high stakes. The average recovery cost excluding ransom for manufacturing was around $1.3M, slightly below the global average, which implies they’ve gotten quicker at restoration. In summary, manufacturing in 2025 was ground zero for ransomware battles, attackers doubled down on it, but many firms successfully deflected the worst outcomes, albeit not without significant pain.
Healthcare: From Data Breach to Patient Safety Crisis
Healthcare organizations, hospitals, clinics, pharma, etc. have long been ransomware targets due to the sensitivity of patient data and the criticality of systems. In 2025, the healthcare sector continued to experience a high volume of attacks by one mid 2025 tally, over half 54% of healthcare organizations globally had been hit by ransomware in the prior 12 months source: IT security surveys. This is an astonishing figure that underscores how pervasive the threat is in health, essentially a coin flip odds each year.
What really sets healthcare apart is the impact. For 14 years running, healthcare has had the highest average data breach cost of any industry, and in 2025 that was $7.42 million per incident. A big chunk of that is due to ransomware related breaches. When hospitals are attacked, not only do they face IT recovery costs and regulatory fines, HIPAA penalties, etc., but there’s also the cost of diverting patients, canceling procedures, and potential lawsuits if patient care is harmed. Unfortunately, 2025 provided concrete evidence of harm: an attack on Synnovis, a U.K. pathology services provider, in late 2024 crippled blood testing across dozens of hospitals. In 2025, an investigation formally concluded that the delays caused by that cyberattack were a contributing factor in a patient’s death, one of the first confirmed cases of a cyberattack leading to loss of life. Additionally, at least 170 patients suffered care harm and thousands of appointments including cancer treatments were canceled due to that incident. This sparked global discussions about categorizing healthcare ransomware as a national security threat since it can directly jeopardize lives, akin to a terrorist attack on infrastructure.
In terms of ransom payments, healthcare entities are actually less likely to pay large sums. The median ransom demand in healthcare might be in the mid six figures one stat says ~$750k average demand, but many negotiate down. Sophos reported healthcare providers paid the lowest ransoms of all industries in 2025 on average $115,000 median payment, which is peanuts compared to sectors like oil & gas or tech. This is partly because many hospitals simply cannot afford multi million payouts, they operate on thin budgets, and partly because once sensitive medical data is stolen, the damage to trust and privacy is done paying won’t undo patient data leaks. In the Synnovis case, the lab did not pay the roughly $50M demanded, and the attackers dumped hundreds of thousands of patient records online, including highly sensitive health details. Those patients and the healthcare system bear the consequences for years of monitoring, identity theft risk, etc..
So, while healthcare doesn’t fund the criminals much, the criminals still attack healthcare frequently because even without ransom, they can monetize stolen data selling medical identities, etc. or simply take pride in the disruption caused. In 2025, we saw several major hospital and clinic outages from ransomware: e.g., in the U.S., Prospect Medical Holdings had multiple hospitals offline for days, in Australia, a regional health network was hit, delaying surgeries. Each of these incidents carries a human cost beyond money. The statistics now reflect that: governments are starting to track cyber induced adverse health outcomes. For defenders in healthcare, the imperative is clear: preventing ransomware is about patient safety, not just IT. Encouragingly, many hospitals improved segmentation and incident response, some attacks were contained to administrative networks without affecting bedside devices, for example. But given the stakes, healthcare remains arguably the highest risk sector for ransomware, where the consequences are literally life and death.
Education: Data Exploitation and the Long Tail
The education sector school districts, universities, education technology firms continued to be heavily targeted in 2025, albeit with some nuances. Schools often have tight budgets and perhaps weaker security, making them attractive targets. Survey data showed around 63% of education institutions higher ed & K 12 combined experienced a ransomware attack in the past year, one of the highest rates among all sectors. K 12 school districts in particular have been hit hard, as they hold sensitive data on minors and may lack dedicated security staff.
One landmark incident that illustrates the impact was the PowerSchool breach of late 2024, which reverberated through 2025. PowerSchool is a major student information system provider, an attacker stole data on 62.4 million students and 9.5 million teachers across thousands of schools. PowerSchool decided to pay a $2.85 million ransom in January 2025 to supposedly secure deletion of the data. However, this turned out to be a cautionary tale: the hacker did not delete the stolen data as promised. Instead, by spring 2025 the same hacker started extorting individual school districts and state education departments by threatening to leak their students’ data. Dozens of districts across the U.S. and Canada received ransom notes demanding Bitcoin in exchange for destroying the data which was supposed to have been destroyed already. Essentially, one breach led to a cascade of secondary extortions even though the vendor paid, the data was weaponized all year long against the vendor’s clients. This incident underscores the never pay advice: PowerSchool’s payment not only failed to protect the kids’ data, it arguably emboldened the hacker to go after more victims since they got paid once, why not try again?. It also highlights the long tail of harm millions of students’ personal info names, birthdates, grades, even medical and disciplinary records are out in the wild, potentially subjecting families to scams or privacy violations for years. Schools had to notify parents, provide credit monitoring, and deal with frightened communities.
Statistically, education saw ransom demands and payments trending down like other sectors. In fact, education organizations faced among the lowest ransom demands on average in 2025 perhaps because attackers know schools can’t pay much. Sophos data indicated the median ransom demand in lower education fell to about $1 million in 2025, from ~$3.5M the year before, and in higher education down to ~$700k. Median payments in education also plummeted in some cases, lower ed median payment was only tens of thousands indicating many didn’t pay at all, pulling the median to near zero. Additionally, recovery costs in education dropped higher ed institutions in 2025 reported an average recovery cost of ~$900k down 77% from $4M in 2024, and K 12 around $2.3M down from $3.76M. These improvements suggest that the education sector, with help from government and cybersecurity partners, got better at response and perhaps fewer big game attacks occurred. Attackers might have shifted to other targets after some public outcry over attacking schools. Still, the fact remains that education holds uniquely vulnerable data student records including minors’ Social Security numbers, learning disabilities, etc. which can be abused in identity theft or coercion for years. A troubling trend is criminals using stolen school data to target individuals: e.g., after the PowerSchool leak, some parents received personalized extortion emails referencing their child’s data, demanding money not to publish it. This kind of secondary crime is hard to quantify but extremely damaging to trust.
In sum, education institutions face ransomware as both a data breach threat and a disruption threat. Many K 12 schools have had to close for days to rebuild systems, and universities have had research halted. The stats show high incidence but generally lower ransom payments the criminals know schools often simply can’t pay. Instead, they treat it almost like a smash and grab for data they can resell or exploit. The imperative for education is improving basic cyber hygiene. Many incidents start from phishing a school staff member or exploiting an outdated server and having strong backup/restore plans so that even if an attack occurs, classes can resume quickly.
Other Sectors Finance, Government, etc.:
Financial services and government entities also saw their share of ransomware in 2025. Financial firms, banks, insurance, and fintech are attractive for their money and data, they tend to have stronger security, but when breached the ransoms demanded can be huge and some pay to protect customer data. Government agencies, especially local governments, continued to be hit frequently, a 2025 survey indicated 68% of state/local governments had a ransomware incident recently, though only ~34% paid any ransom. Notably, many governments now legally prohibit paying ransom to avoid funding criminals and encourage reporting. This, combined with often tight budgets, means government payment rates are low. But attacks on city services, utilities, etc., can be very disruptive taking down 911 systems or civic infrastructure. For instance, in 2025 the city of St. Paul, MN declared an emergency after ransomware knocked out many municipal systems for weeks.
The professional services sector law firms, consultancies were actually identified by multiple reports as the single most targeted sector in Q3 2025 possibly because they are aggregators of data e.g. a law firm has many clients’ sensitive data and may pay to keep it confidential. Meanwhile, retail and logistics saw attacks often focusing on supply chain choke points e.g., in late 2025 a coordinated ransomware campaign hit several major UK retailers and their third party providers, causing store outages and delivery delays.
No industry is truly safe, but the motive differs: some sectors are hit for maximizing downtime pain manufacturing, government, healthcare, others for monetizable data finance, education, tech, and some for a mix of both. Ransomware groups themselves often specialize in a sector for instance, the Qilin gang appears especially focused on healthcare and critical orgs with no scruples about patient impact, whereas groups like Akira hit many small businesses across various sectors with smaller demands.
The industry by industry statistics helps organizations benchmark their risk. If you’re in manufacturing or healthcare, the likelihood of being targeted is unfortunately very high, a majority chance over a couple years. If you’re in finance or tech, the likelihood might be moderate but the potential ransom demand and regulatory fallout are very high. If you’re in education or government, you might be highly targeted but dealing with generally lower skilled adversaries and lower demands however the real risk is data exposure and service disruption to the community. Understanding these nuances can guide where to focus security investments e.g., hospitals might prioritize network isolation for life critical systems, manufacturers might heavily invest in reliable offline backups for PLC controls, schools might focus on phishing training and MFA for staff. The numbers make one thing certain: virtually every sector needs to assume it will face ransomware and plan accordingly.

Ransomware is a global menace, but the impact and response differ across regions due to varying levels of cybersecurity maturity, regulations, and attacker focus. Here we break down some regional insights from 2024–2025 ransomware data:
North America USA & Canada:
Primary Target and Primary Battleground, North America continues to experience the highest volume of ransomware attacks of any region. Various sources indicate roughly 40–50% of all ransomware incidents hit North American organizations, with the United States alone accounting for about 20–25% of global cases. In the first quarter of 2025, the U.S. saw around 1,000 reported ransomware incidents 21% of the global total in that period. The large number is unsurprising, the U.S. has a huge digital economy and many high value targets. Sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and finance in the U.S. have been prime ransomware victims.
However, the U.S. is also at the forefront of ransomware defense and resistance. A notable statistic: 63–64% of American ransomware victims now refuse to pay, which is above the global average refusal rate. This aligns with an observed trend that U.S. companies are increasingly taking a hard line no negotiation stance. There are a few reasons:
That said, North America still suffers severe ransomware impacts. Hospitals in the U.S. and Canada have had emergency procedures due to ransomware. Local governments, cities, and counties frequently deal with service outages from attacks, for example, several U.S. city 911 systems were hit in 2025, forcing backup manual processes. And critical infrastructure energy pipelines, food supply companies remain tempting targets. The 2021 Colonial Pipeline incident in the U.S. is a reminder, and while nothing of that scale happened in 2025, attempts are ongoing.
Europe including UK:
Strict Regulation, Still a Big Target, Europe saw a significant share of ransomware activity, roughly accounting for 20–25% of cases in 2024–25. In one count, Europe had 1,136 reported ransomware incidents in 2024/early 2025. The UK, Germany, Italy, France, and Spain have been among the most affected countries. The United Kingdom in particular faced several high profile attacks: e.g., the retail sector incident where Marks & Spencer, Boots, and others were hit in a coordinated campaign in 2025, and multiple attacks on NHS healthcare trusts prompting government action.
One notable aspect in Europe is the influence of the GDPR and new EU regulations NIS2, etc.. GDPR mandates that if personal data is breached which is almost always the case in ransomware due to data theft, the organization must report it to authorities and possibly to affected individuals. Non compliance carries heavy fines. This legal environment means European companies are less able to quietly pay a ransom to make it go away if data was stolen, they have to come clean regardless of paying. This likely contributes to a fairly high non payment stance as well in Europe. Why pay if you’ll still face regulatory penalties and reputational damage? Additionally, the EU’s NIS2 directive effective 2024 expanded breach reporting to more sectors and imposed security requirements on critical industries, again pushing for transparency.
Despite strong data protection laws, European organizations do sometimes pay ransoms, especially if they feel critical IP is at risk. But several countries have publicly stated opposition to paying for instance, in 2025 the Irish health service, which was famously hit in 2021, reiterated its policy of not paying criminals even if data leaks.
Europe also saw law enforcement successes: Europol coordinated operations that led to arrests of members of ransomware groups in 2023–2025, including affiliates of LockBit and Ragnar Locker. The collapse of the BlackCat ALPHV group’s credibility in 2024 after an apparent exit scam where they disappeared with affiliates’ money was partly due to pressure from European authorities after major hits in Italy and elsewhere.
One interesting stat: the UK reported only ~1% of businesses had a ransomware incident in the last year in a government survey, which seems low, however, that was self-reported across all businesses, many of whom might not realize or disclose it. At the same time, among UK organizations that did suffer cyber attacks, 7% said ransomware was involved. The UK government has been particularly vocal about ransomware, calling it the biggest threat to most businesses. They launched initiatives for greater info sharing and even floated the idea of outlawing ransom payments though not implemented yet.
Asia Pacific APAC:
Rising Wave of AttacksThe Asia Pacific region experienced a rapid increase in ransomware attacks through 2025. Countries like Australia and Japan have been heavily targeted. SonicWall’s 2025 report noted ransomware in APAC was climbing faster than in Europe or North America in terms of volume. Australia specifically saw about a 67% YoY increase in ransomware in 2025 as reported by a government cyber threat report it had multiple major breaches of companies for example, in 2022 23 Australia had headline breaches at Optus, Medibank, etc., which seemed to open the floodgates. By 2025, attackers view Australia as a lucrative yet perhaps less hardened environment than the U.S./Europe. The Australian government responded with very aggressive stances, even suggesting at one point that hacked companies should not pay and should consider the data already gone.
In East Asia, Japan has seen manufacturing firms like a recent one in automotive parts hit by ransomware causing production halts. Taiwan and South Korea also report increases. These countries have strong tech industries, which are targets for IP theft and extortion.
In South Asia, India has become a frequent target for data extortion ransomware, especially against its large IT services companies which can then spread to Western clients.
Overall, APAC had some of the highest raw counts of attacks simply due to population and number of businesses. One interesting data point from a phishing report: in 2025, over 117 million phishing links were clicked and blocked in APAC more than any other region. Since phishing often leads to ransomware, that highlights the scale of attempts in APAC.
However, reporting in APAC is variable, some countries have breach notification laws, others do not, so the true numbers might be undercounted.
Latin America and Africa:
The Next Frontier, Latin America, as mentioned, saw an explosion in attacks. Check Point recorded an 108% YoY jump in weekly attacks in LATAM in early 2025, the highest growth worldwide. Part of this is cybercriminals expanding into regions that historically had less focus. Many LATAM organizations may have comparatively less mature cybersecurity postures though that is changing. Also, global ransomware groups set up franchises or affiliates in LATAM for example, some Brazilian and Mexican cyber gangs started using leaked ransomware source code to run their own operations locally.
Brazil and Mexico, being the largest economies, had the majority of incidents in LATAM. A Dragos Q2 2025 analysis of industrial ransomware showed South America accounted for about 6% of global ransomware incidents with Brazil most affected. That might seem small, but it’s growing.
One LATAM challenge is that paying ransoms is not outlawed and often companies keep it quiet, so criminals face less deterrence. The stat that LATAM averaged ~2,640 weekly attacks per organization in Q1 2025 higher than global average implies criminals are hammering the region. We can expect LATAM governments to respond by boosting cyber defenses, indeed by late 2025 there were calls in countries like Chile and Argentina for national ransomware response strategies.
Africa likewise has seen rising attacks, although data is sparse. One checkpoint stat said African organizations averaged 3,286 weekly attacks in Q1 2025, actually the highest of any region though that covers all cyber attacks, not just ransomware. It suggests Africa, with many developing digital infrastructures and often outdated systems, is a growing target zone. There was a notable incident in 2025 where several South African government departments were hit simultaneously by ransomware, crippling services pointing to the region’s vulnerability.
Ransomware is truly global, but the distribution of attacks is shifting. North America and Europe remain high value targets and will get hit by the more sophisticated, higher demand attacks and in turn they have stronger defenses and lower payment rates. Regions like APAC and LATAM are where attackers see big opportunities for expansion, lots of potential victims that may not be as well prepared, and possibly more likely to pay due to lack of insurance or government support. The 2025 data shows that the easy victims pool is shrinking in the West due to better prep and willingness to say no, so criminals are increasingly looking elsewhere to maintain their profits. This global whack a mole means efforts to combat ransomware need to be coordinated internationally. A win less payments in the U.S. or EU could mean the criminals refocus on places like Brazil or India.
From a defensive perspective, organizations should note regional trends but ultimately not be complacent even if you’re in a country that hasn’t been hit as much yet, 2025’s lesson is that it’s only a matter of time. And regions that do have strong support like the US CISA or France’s ANSSI should leverage those for early warnings and best practices, as they may make the difference between a minor incident and a catastrophe.
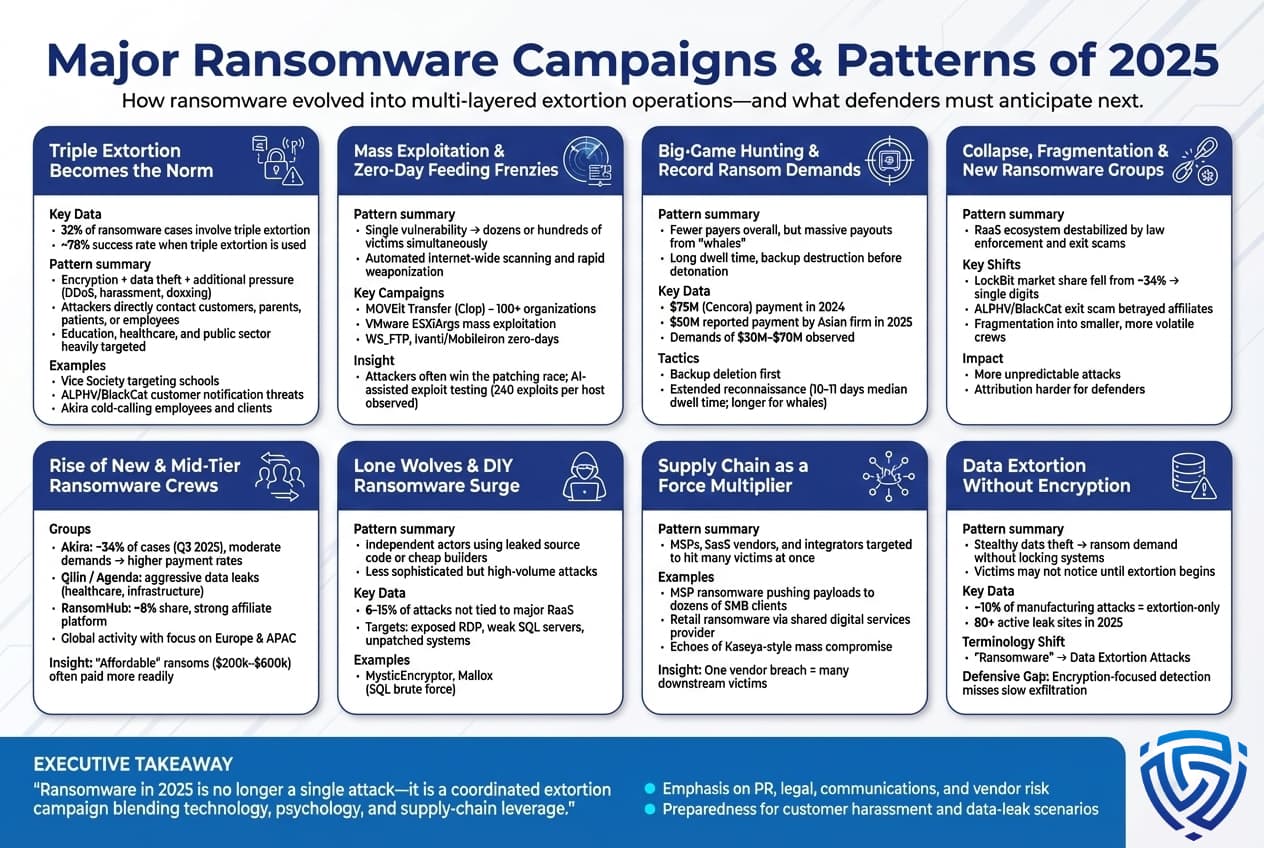
Statistics give us the aggregates, but it’s also valuable to look at specific notable campaigns and tactics that defined ransomware in 2025. These case studies and patterns illustrate how attackers operated and how victims fared:
The Rise of Triple Extortion Tactics:
By 2025, the era of encryption and ransom as a standalone tactic was effectively over for serious ransomware groups. Nearly all the major campaigns involved double extortion encryption + data theft, and an increasing subset added a third lever like DDoS attacks or harassment. One pattern was to threaten actors contacting victims’ customers or partners directly. For example, in late 2024 the Snatch ransomware group hit a school district and then individually emailed parents threatening to release their children’s data unless the school paid. In 2025, the Alphv/BlackCat group before their implosion did something similar after hitting a hotel chain they set up a fake website listing all the hotel’s customers and threatened to notify each one of the data breach.
Another notable campaign was by the Vice Society group targeting education: they would simultaneously encrypt school servers, steal student data, and then doxx the schools by posting snippets of kids’ private info on their leak site to pressure payment. When schools didn’t pay, they just leaked it all. This multi faceted extortion financial + reputational + emotional pressure characterizes triple extortion.
One chilling example of triple extortion was the attack on a Finnish psychotherapy clinic Vastaamo a couple years back attackers not only demanded ransom from the clinic, but also emailed the clinic’s patients individually to extort them for hush money pay us or we release your therapy session notes. That incident still reverberated in 2025 as a warning. We saw shades of that method when the Akira ransomware gang in 2025 started cold calling employees of victim companies, as well as their clients, telling them the company was hacked and data would be leaked causing panic and often forcing the company’s hand to negotiate.
These campaigns show that attackers were willing to cross ethical lines that even earlier cybercriminals avoided such as directly involving minors, patients, etc. Coveware’s data noted that triple extortion incidents which they defined as involving encryption, data theft, plus extra pressure like DDoS or contacting people made up about 32% of cases they handled. More importantly, those tended to have a higher success rate around 78% yielding some payment versus basic ransomware which was much lower. Criminals talk in their forums about leveraging every point of pressure to make victims pay since many can recover IT wise. Thus, these campaigns teach us that organizations must be prepared not just for technical recovery, but also for public relations crises and stakeholder communications if threatened with data leaks or harassment.
Mass Exploitation Events:
2025 saw several major campaigns where a single vulnerability led to dozens or even hundreds of simultaneous ransomware victims. The most prominent was the Clop ransomware’s exploitation of MOVEit Transfer, a file transfer software in June 2023 which continued into 2024/25 with victims identified. Clop siphoned data from over 100 organizations, banks, universities, even governments via that zero day, then issued ransom demands to each. Many refused, and Clop simply dumped the data. This kind of supply chain hit was a template that others attempted in 2025. For instance, in early 2025, a vulnerability in VMware ESXi a widely used virtualization platform was mass exploited in what was dubbed ESXiArgs attacks hundreds of VMware servers worldwide got hit by an auto spreading ransomware script exploiting an old vulnerability servers in France, Italy, Canada were heavily hit. While that particular campaign was somewhat amateurish flawed encryption that some admins reversed, it signaled the potential of mass exploits.
Another was the Progress WS_FTP zero day exploitation in October 2025. Within days of that FTP server flaw becoming public, ransomware groups had compromised dozens of companies. Similarly, the Ivanti/MobileIron zero day used by many orgs for VPN was exploited by a group linked to ransomware affiliates to breach multiple Norwegian government agencies in mid 2025, among others.
The pattern here: a race between attackers and defenders whenever a critical flaw emerges. In 2025, that race was often won by attackers. They have systems some even use automated scanning and AI to rapidly weaponize new CVEs. GreyNoise, a threat intel firm, documented one case over Christmas 2025 where an attacker was scanning the entire internet, testing 240 different exploits per target one after another essentially a shotgun approach to find any way in. That actor built a huge list of vulnerable servers which were then picked off in early 2026. This highlights the need for speed in patching, as well as alternative protections like virtual patching or segmenting critical systems away from direct internet access.
Big Game Hunting and Record Payouts:
While we noted average payments are down, 2024/2025 still had some eye opening ransom payouts. The $75 million Cencora AmerisourceBergen payment in 2024 sent shockwaves through a Fortune 50 company deciding it was worth that sum to possibly prevent patient data leaks and quickly restore distribution of pharmaceuticals. In 2025, there was a report Chainalysis of an Asian company paying $50 million to a ransomware crew. Details were scarce but it shows these big payments aren’t just a Western phenomenon.
These outliers suggest that for extremely critical organizations, attackers will still swing for the fences. The Dark Angels group who got the $75M essentially showed every other gang that while 99 victims might not pay, one whale can bankroll the operation for a long time. Thus, campaigns in 2025 against very large companies or critical infra often featured massive initial demands. We saw demands of $30M, $40M in some cases, which typically get negotiated down to single digit millions if paid. The LockBit group at one point demanded $70 million from a major aerospace manufacturer in 2025 which was not paid, they leaked the data instead.
From a pattern standpoint, these big game attacks often involve long dwell times and data exfiltration. The attackers might spend weeks in the network stealthily, stealing the crown jewels, before launching ransomware. The average dwell time for ransomware in 2025 was about 10-11 days median, but for big victims it can be longer. They often compromise backup systems first to cripple recovery a key pattern e.g., in 2025 the Black Basta gang hit a large Canadian utility and first wiped out the offline backups via a management console, then encrypted production servers. This counters the victim’s usual Plan A restore from backup, forcing them to consider paying.
Notable Group Activity and Shifts:2025 was also marked by the turbulent evolution or disappearance of certain major ransomware groups, and the emergence of others:
Targeting of Supply Chains:
2025 reinforced that supply chain compromise is a major ransomware force multiplier. Beyond the software exploits mentioned, attackers also directly target managed service providers MSPs or IT outsourcing firms because hacking one MSP can give access to many of its clients. In 2025, there was an incident where a regional MSP in the US was breached and the attackers pushed ransomware to dozens of the MSP’s small business customers simultaneously via remote management tools. This echoed the infamous Kaseya MSP incident of 2021, proving it’s still a relevant tactic. Attackers, especially those going after small and mid businesses, realize an MSP may have weaker security but keys to many networks.
Similarly, third party software integrators were targeted. The UK retail ransomware campaign in April 2025 Scattered Spider group started by compromising a third party company that provided digital services to multiple retail chains. Through that one breach, they gained a foothold in several retailers at once, then customized ransomware payloads for each. This taught the lesson that even if your company is secure, an attack might come through a less secure vendor integration.
Data Exfiltration Without Encryption Data Leaks as Ransomware:
A pattern emerging especially with certain groups was skipping encryption entirely. For instance, the group 0mega in 2025 primarily focused on data theft and extortion, rarely encrypting files. They realized some victims might not even notice an intrusion if nothing is encrypted, so they quietly exfiltrate data, then approach the victim with proof of stolen data and a ransom demand to not publish it. In manufacturing, as noted, 10% of attacks were extortion only. This stealth approach can sometimes catch companies off guard if their detection is heavily oriented towards catching encryption behavior, they might miss a slow data siphon. The proliferation of leak sites over 80 active in 2025 means even groups that never deploy locker malware still operate similarly to ransomware crews by monetizing stolen data via extortion. One might argue some of these are not ransomware by strict definition since no ransomware malware is used, but the impact of extortion payment for not leaking is the same. SecurityWeek and others in 2025 started using the term data extortion attacks to include these cases in the ransomware conversation. It’s a semantic shift but an important one, as defenders need to broaden focus beyond just stopping encryption, protecting sensitive data from exfiltration and improving network egress monitoring is key.
In conclusion, the campaigns and patterns of 2025 show a threat landscape in flux. Attackers are trying new techniques to counter improved defenses: if backups defeat encryption, then steal data and extort, if victims won’t pay, then torment their stakeholders, if big brands get too hot to handle due to law enforcement, then fracture into smaller crews and fly under the radar. The statistics we’ve discussed in earlier sections come to life in these examples. For instance, the stat 76% of attacks involving data theft is exemplified by essentially every case study above. The stat 23% pay ransom is reflected in cases like PowerSchool they paid, and it backfired versus JLR they didn’t pay, but took a huge hit.
Understanding these real incidents helps organizations scenario plan: What if attackers contact our customers? What if a key supplier is hit and we’re collateral damage? What if our employee’s home PC gets infected and their VPN creds stolen? These are not theoretical, they happened repeatedly in 2025. By studying the playbook of ransomware groups, defenders can anticipate moves and put controls in place for example, ensuring contracts with vendors include cybersecurity clauses, or having a communications plan ready in case of a data leak threat. The major ransomware campaigns of 2025 ultimately underscore the importance of an integrated defense technical security, yes, but also legal, communications, backup, and user awareness components to withstand the increasingly complex extortion plots wielded by these threat actors.

Looking at the trajectory of ransomware as 2025 closes and 2026 begins, several emerging trends and developments are likely to shape the threat landscape in the near future. These trends are driven by both attacker innovation often leveraging new technology and defender countermeasures, as well as broader geopolitical and economic factors.
Ransomware Without Ransom Data Extortion and Sabotage:
As noted earlier, encryption as the primary extortion method is waning. Going forward, we may see the term ransomware itself become a misnomer, as many attacks won’t involve ransomware malware at all. Instead, pure extortion campaigns will rise. Attackers may breach a network, steal sensitive data, and perhaps plant destructive malware not necessarily encryption, but maybe something to corrupt or destroy data to use as leverage, essentially data breach + sabotage rather than classic ransomware. The goal remains extortion, but the means change.
One scenario is what one might call hostage data: instead of locking your files with ransomware, the attacker exfiltrates them and then deletes them from your systems holding the only copy. If you have good backups, this fails, but if not, the effect is similar to encryption except the attacker has the data. Even if you have backups, they might extort by threatening to leak data publicly. This is already happening in extortion only attacks. By 2026, we expect these encryption less extortion attacks to possibly outnumber traditional ransomware incidents among sophisticated actors. Particularly, criminals will focus on stealing intellectual property, legal documents, R&D data that have high value. Imagine an attacker stealing a pharmaceutical company’s drug formula or clinical trial data and extorting them not to release it to competitors or markets even if the company can restore operations, the data confidentiality breach is extremely costly. We saw hints of this in 2025 e.g., the attack on tech company Nvidia in 2022 where hackers stole GPU schematics and tried to extort, or more recently some attacks on law firms purely for the sensitive client data.
Another angle is operational sabotage: some groups might threaten to not just encrypt but cause physical damage or safety incidents unless paid. For example, meddling with industrial control systems ICS in critical infrastructure. While most ransomware groups haven’t intentionally caused physical harm, the rhetoric is moving that direction with state nexus actors possibly blending in. The recognition of ransomware as potentially causing national security crises e.g., if a power grid or water system is hit means future attacks could carry a terrorism like weight. This could provoke even more government action, potentially even military cyber responses if a ransomware attack is attributed to a nation backed group and threatens lives.
Artificial Intelligence Both Sides of the Coin:
AI is playing an increasing role in cyber threats, and ransomware is no exception. On the attacker side, Generative AI like GPT models is being used to vastly improve phishing lures. We saw 80% of phishing emails are now AI crafted. But beyond phishing, we may soon see AI copilots for attackers that help them navigate a victim network faster and identify high value targets. For instance, an AI agent could analyze a stolen trove of documents to find which are likely most sensitive to threatening leaking, or to scan network logs and recommend which machines to hit first. Proof of concept ChatGPT for hackers tools already exist on dark web forums.
Another emerging threat is AI driven malware that can adapt or even partially learn from an environment. While we’re not at sci fi levels yet, researchers have demonstrated malware that uses machine learning to evade detection by morphing its behavior slightly. Ransomware could incorporate such features to automatically try different tactics if it senses it’s being blocked by an endpoint defense. Fully autonomous ransomware, an AI agent that independently executes an entire attack chain from phishing to exfiltration without human input, is a theoretical possibility in coming years.
Conversely, defenders are increasingly deploying AI for cybersecurity for anomaly detection, user behavior analytics, etc. By 2025, companies using AI driven security had significantly lower breach costs on average. In response, attackers will attempt to poison or evade AI. Expect to see ransomware groups probing how to bypass AI based email filters some already do by using AI to create text that looks legitimate. It’s a cat and mouse game: AI helps defenders catch subtle signs of attack, so attackers create subtle attacks that blend in, possibly using AI themselves.
One concrete trend: AI based voice deepfakes used in support of ransomware. We already saw deepfake voice used in some fraud, a famous case of a CEO’s voice faked. It’s not hard to imagine a ransomware attacker calling a company’s IT helpdesk using a deepfaked voice of an executive, instructing them to disable certain security, essentially using social engineering to facilitate the hack. Or post attack, using deepfake audio of a CEO to deliver the ransom message This is your CEO, we’ve decided to pay the hackers confusing employees. These scenarios sound wild but the tech exists.
Zero Trust and Stronger Security Postures:
On the defensive emerging trends: Many organizations are accelerating adoption of Zero-Trust architectures essentially, assuming breach and limiting lateral movement by requiring continuous authentication checks, micro segmentation of networks, and least privilege access. By the end of 2025, it’s estimated about 25-30% of businesses have some Zero Trust initiative underway. Some stats say 50% of large enterprises by 2026 will have at least piloted Zero Trust. This could dramatically reduce ransomware impact, because even if initial access is gained, the attacker finds it harder to spread to crown jewel systems. For example, an infostealer might give an attacker credentials, but if the company uses device authentication and conditional access policies don’t allow login from a new device without additional checks, the stolen creds alone aren’t enough.
Additionally, immutable backups and rapid restore technologies are improving. More companies are using cloud backups that are written once attackers can’t encrypt or delete them easily and can restore entire systems in hours via virtualization. This reduces downtime and the leverage of encryption. Cloud providers themselves are offering disaster recovery as a service that some companies are leveraging in lieu of paying ransoms.
Government and Policy Moves:
We might see new regulations that directly address ransomware payments. A few countries have considered outlawing ransom payments or fining companies that pay without notifying authorities. While it’s a complex issue, there is momentum in some legislatures for harsher approaches, especially after seeing the decline in payment rates. The logic: if everyone stops paying, the business model collapses. In the US, the state of North Carolina already bans government agencies from paying ransoms, New York considered a bill to ban state agencies and municipalities from using taxpayer money to pay. If more such laws pass, and possibly extend to the private sector less likely, but could be encouraged through insurance or tax policy, it will further drive down payments. Attackers may respond by focusing on jurisdictions where payments are allowed or on targets who will pay regardless e.g., criminals might target more in countries with less strict regimes or where paying quietly is easier.
Collaboration and Intelligence Sharing:
On a positive note, 2025 showed increased international collaboration in fighting ransomware e.g., the US and European law enforcement joint operations, and forums like the International Counter Ransomware Initiative CRI which includes 30+ countries sharing intel and best practices. Going into 2026, we expect more public private partnerships. Large tech and security companies are actively aiding governments with takedowns Microsoft, for instance, helped disrupt a botnet used by a ransomware group by seizing domains. Such coordinated strikes could potentially knock out some mid tier groups. However, completely eradicating ransomware is unlikely as long as the root causes profitable, safe havens for criminals, and systemic vulnerabilities remain.
Ransomware and Cryptocurrency:
Most ransomware transactions use cryptocurrency Bitcoin, Monero, etc.. As crypto tracing gets better Chainalysis and others can often follow the money, criminals look for ways to launder funds. 2025 saw a huge increase in use of cryptocurrency mixers and cross chain swaps to obscure money flow. The overall crypto crime revenue which includes ransomware was up because of things like sanctioned nations using crypto, at least $154 billion flowed to illicit crypto addresses in 2025, +162% YoY a figure inflated by sanctioned state actors moving funds. Ransomware accounts for a smaller slice of that pie now, but the infrastructure built to launder that large sum benefits ransomware actors too. The trend is criminals leveraging DeFi decentralized finance platforms to split and convert funds automatically. In response, regulators are starting to sanction mixer services and even crypto wallets tied to ransomware. This cat and mouse in the crypto space will continue, if it gets too hard to cash out Bitcoin ransom safely, attackers might demand alternative currencies or even prepaid cards, etc. But likely, they’ll stick to crypto and just find creative laundering methods.
Target Shifts Critical Infrastructure and Small Businesses:
As big companies harden and refuse to pay, there are hints that some gangs are refocusing on medium and small businesses who might not make headlines and might be more inclined to quietly pay moderate ransoms. Coveware explicitly noted in Q3 2025 that some groups are using a high volume, low demand strategy hitting many SMBs and asking for, say, $50k each, figuring those are easier yes’s. This is an emerging trend that could spread in 2026: essentially, the WalMart approach of ransomware sells cheap but sells a lot. It doesn’t grab news like a pipeline hack, but collectively could be lucrative.
Conversely, at least one or two big game attacks will likely happen in 2026, possibly probing sectors that have thus far largely avoided ransomware due to either strong security or sensitive repercussions. For example, cloud service providers or managed cloud infrastructure imagine if a major cloud company’s environment were compromised to deploy ransomware to many customers at once there was a close call in 2021 with Kaseya, but think bigger like Microsoft Azure or AWS, which thus far hasn’t happened and would be extremely difficult, but not impossible. Attackers always seek one to many opportunities.
Geopolitical Tensions:
Ransomware is mostly financially motivated, but geopolitics can influence it. In times of conflict e.g., Russia’s war in Ukraine, some hacker groups have splintered allegiances or face more crackdowns from certain governments. It’s been speculated that if certain nation state hacking units need funds, they might moonlight as ransomware gangs using those techniques for money rather than espionage. Also, regions in turmoil might see spikes in cybercrime from opportunists. The trick for 2026 will be separating nation state cyberattacks which might masquerade as ransomware to cause chaos or distraction from pure criminal ones. For defenders, the distinction doesn’t change the immediate response but could affect how it’s handled with law enforcement. We might also see more ransomware attacks on government agencies or critical national infrastructure as a form of pressure or sabotage e.g., a state backed group using ransomware techniques to disrupt another country’s infrastructure without overtly taking blame.
In summary, heading into 2026, we expect ransomware actors to become more extortion focused, more nimble, and possibly lean on new tech like AI, while defenders double down on resilience, zero trust, and cross border cooperation. Ransomware as a concept is not going away, but it will continue to evolve into a broader cyber extortion phenomenon. The statistics we saw in 2025 declining payments, more data theft, shifting targets are likely harbingers of these evolutions. Stakeholders should anticipate these changes: plan not just for encryption but also for data leaks and public extortion attempts, leverage emerging defensive tech but be aware of how it can be evaded, and keep an eye on the ever shifting threat actor landscape, which can change almost overnight with new entrants or exits.

Stepping back from the numbers, what do the 2025 ransomware statistics really tell us, and how should organizations act on this information? In practical terms, the data highlights key risk insights and priorities for defense:
Ransomware is Ubiquitous Assume Breach: The frequency states one attack every few seconds globally, thousands per day drive home that every organization is under constant threat. Even if you have not yet been hit, the odds are significant that an attempt will happen. This means adopting an assume breach mindset. It’s no longer if we get attacked but when we detect and respond to an attack. Practically, this means companies should focus on incident preparedness as much as prevention. For example, having an updated incident response plan specifically for ransomware scenarios, conducting tabletop exercises where executives practice decision making during a ransomware crisis, and ensuring off site backups are in place and accessible. The stats that 77% of victims don’t pay ransoms but still incur costs highlight that planning to recover without paying is both realistic and necessary.
Data Backups and Beyond Resilience is Key: One of the clearest implications of 97% of organizations being able to recover data via backups is that robust backup strategies work. If you can restore your systems and data quickly from clean backups, you drastically reduce the leverage attackers have. Organizations should ensure regular, automated backups of critical systems and data, stored in forms that ransomware can’t easily corrupt e.g., offline or immutable storage. Importantly, test those backups! A statistic not covered earlier but commonly known in IT: many companies don’t test restore procedures, only to find backups failed or were incomplete. Conduct routine restores to verify you can meet RTO/RPO recovery time and point objectives. Given the average downtime of ~24 days, challenge your team to beat that: How would we restore operations in, say, 3 days? What infrastructure do we need ready to do that?
But resilience must extend beyond just having backups. The rise of data theft extortion means you have to protect the confidentiality of data, not just availability. So, consider data governance and encryption for sensitive information. If your stolen files are strongly encrypted and attackers didn’t get the keys, leaking them won’t harm you. Also, segment networks so that an intruder cannot easily access crown jewel data stores. The fact that exploited vulnerabilities and stolen credentials are top vectors means securing those avenues is part of resilience to patching promptly, using MFA, etc. covered in Best Practices next.
Identity is the New Perimeter: Given ~25% of incidents started with compromised credentials and the flood of billions of stolen credits, organizations must tighten identity and access management. The stats show MFA adoption is increasing 87% of large firms use it, but attackers are adapting via token theft. So, this implies companies should move toward phishing resistant MFA like FIDO2 security keys or at least app based auth with number matching and monitor for compromised credentials e.g., services that alert if your employee emails show up in infostealer dumps. Zero Trust principles play in here: don’t inherently trust a login just because credentials were correct, use device posture, geolocation, user behavior analytics to continuously verify. For instance, if an employee suddenly tries to access a server it never has before at 3 AM, flag that it could be an attacker using their account. Statistics about cookie/session theft suggest maybe shorter session timeouts or re prompt for auth when accessing especially sensitive systems.
Patch Critical Vulnerabilities Fast Especially Edge Devices: The fact that 32% of attacks came via unpatched vulns, with a huge focus on VPNs/edge devices, screams that organizations need to get a handle on vulnerability management. That means maintaining an accurate inventory of internet facing systems and prioritizing those for patching or mitigation as soon as exploits are public if not earlier. The 48 hour weaponization stat vs 120 day patch cycle is alarming, closing that gap is critical. Strategies include using virtual patching e.g., web application firewalls or IPS rules to shield a vulnerability until you can patch it properly, and perhaps more radical, minimizing exposure by retiring or isolating legacy systems. If an appliance can’t be patched or monitored like some older NAS or IoT device, consider taking it off the internet or behind a VPN. Network segmentation again helps even if an edge device is breached, segmentation can limit reach.
Plan for Data Extortion Scenarios: Many companies’ traditional incident response plans were about restoring IT. Now, they need an element for data breach/extortion. The statistics showing triple extortion success mean you should ask: What is our stance if attackers steal our data? Are there data types we absolutely must prevent from leaking e.g., customer PII, intellectual property? If so, how do we protect those proactively DLP solutions, encryption at rest and in transit, etc.? Also, legal and PR preparedness: Have pre drafted communications for customers in case of a data leak, have outside counsel and breach coaches ready to engage. Ransomware events often entail compliance with breach notification laws knowing your obligations e.g., GDPR 72 hour notification rule. Essentially, treat ransomware not just as an IT disaster, but as a potential business and public relations crisis. The PowerSchool incident shows paying doesn’t guarantee confidentiality. Thus, many organizations now adopt a we will not pay extortion for data policy, focusing instead on mitigating impact by offering credit monitoring, etc., swiftly after a breach to reduce criminals’ leverage. Deciding your policy before an incident it’s easier than making a snap decision under duress.
Engage Law Enforcement and Share Intel: The shrinking payment rate to 23% is partially credited to better collaboration among victims, law enforcement, and cyber professionals. Companies should not fight ransomware in isolation. Building a relationship with agencies like the FBI or local cybercrime units can provide help. For instance, sometimes authorities have decryption keys if a ransomware strain was cracked with Hive in 2023. They also track the latest tactics e.g., CISA releases alerts about active exploits and IOCs Indicators of Compromise for known attacks. By consuming and acting on such threat intelligence, you can preempt certain attacks. The stat that multiple security firms confirmed the same top variants shows there is community visibility on threats leveraged by joining industry ISACs Information Sharing and Analysis Centers or other peer exchange groups. If your sector says healthcare or finance has an ISAC, the threat bulletins they issue will reflect the trends like those we’ve covered e.g., warning if a certain group is targeting your sector this month. Collective defense raises everyone’s game.
Don’t Count on Anonymity or We’re Too Small: The trends of automation and RaaS mean even small businesses can be hit by enterprise grade ransomware. The high volume of attacks and focus on softer targets show that no organization is beneath notice. If anything, smaller organizations need to be extra vigilant because they might lack resources and thus look appealing to attackers as an easy payday. The median ransom falling implies more small targets in the mix. So, SMEs should take the stats as justification to invest in basic security, maybe managed security services if they can’t do it in house. It’s cheaper than the cost of downtime or paying a ransom. The data also suggests insurers are still paying some ransoms particularly for smaller clients where cost benefit might lean toward paying a $50k ransom vs $500k recovery. But insurance is getting stricter, companies of all sizes increasingly need to meet certain security criteria to even get coverage MFA, backups, endpoint protection are table stakes. So these statistics likely mirror what insurers have found that reduced claims follow those best practices or you may not even qualify for insurance or it’ll be very expensive.
Measure and Drill Your Response: One way to internalize the meaning of these stats is to use them for internal benchmarks. For example, knowing the average dwell time is ~11 days measure how quickly your monitoring systems detect anomalies. Can you shorten that? IBM found that breaches that are contained faster under 30 days cost significantly less. Or consider the average recovery cost $1.5M do you have funds or insurance to cover a hit of that magnitude? If not, investing a fraction of that in prevention might be prudent. If manufacturing downtime is 5 weeks on average for a big attack, create a continuity plan to try to continue partial operations manually if IT is down, to reduce revenue loss. It’s not only about technology it’s about business resilience alternatives, workarounds, etc..
In essence, the statistics paint a picture of a threat that is systemic but increasingly manageable with the right approach. Paying ransoms is less and less the norm that’s encouraging. It means if you invest in resilience, you’ll likely be able to join that 77% who don’t pay and still recover. But it also means attackers will hurt you in other ways with data leaks, so data protection and response speed are paramount.
Perhaps the biggest takeaway is the value of not going it alone. The collective trends in the data, fewer payments, more cooperation, more pressure tactics all point to an arms race. Organizations that keep up to date with threat intelligence, learn from others’ incidents, and implement layered defenses will fare far better than those who ignore the numbers. If ransomware in 2020 blindsided many, by 2025 it’s a known quantity albeit an evolving one. Use these statistics as a reality check to ensure your security program addresses today’s ransomware tactics, not yesterday’s. For instance, if your whole plan is to have antivirus and we back up daily, the stats here infostealers, RDP attacks, etc. should spur you to broaden that plan.
Ultimately, what these statistics mean is that cyber risk from ransomware can be mitigated through preparation and smart investment. Companies that took the threat seriously invested in things like MFA, backups, endpoint monitoring are the ones driving the payment rates down and recovery costs down. Those that ignored it became part of the breach and payout figures. So, the data should galvanize leadership: if 2025 was the year of record attacks but also record resilience, make 2026 the year your organization falls on the resilient side of the stats. The trends are heading in a direction that rewards refusing to pay and being able to withstand attacks align your strategy to that reality.
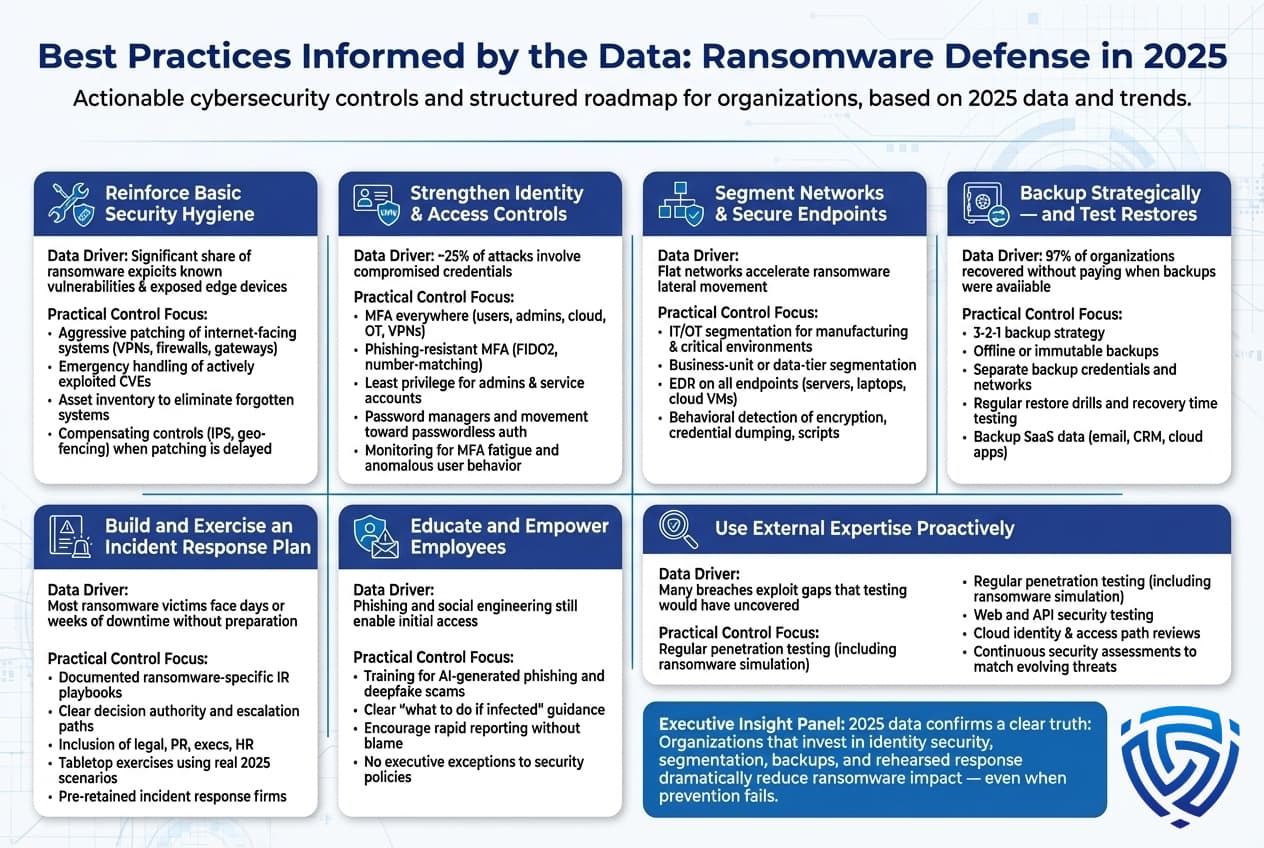
The hard numbers and trends from 2025 offer a clear roadmap of best practices for organizations aiming to fend off ransomware or minimize its impact. Here we translate the statistics into concrete defensive measures:
1. Reinforce Basic Security Hygiene: The fact that a large chunk of ransomware attacks began with known vulnerabilities and stolen credentials means the blocking and tackling of IT security is absolutely crucial. Ensure all your systems, especially those exposed to the internet, are regularly patched and up to date. Prioritize critical patches for example, if a CVE is being actively exploited in the wild as noted by CISA or threat intel, treat it as an emergency. Implement a rigorous vulnerability management program that scans your network and applications for weaknesses. Given how attackers exploited edge devices in 17% of cases, put special focus on things like VPN gateways, firewalls, and remote access servers. If patching such devices quickly is hard due to uptime requirements, consider compensating controls like intrusion prevention systems or geo fencing if you only operate in certain countries, and block access to admin interfaces from other regions.
Additionally, inventory all assets you can’t secure what you don’t know you have. Many breaches happen because an old server or web application was forgotten and left unpatched. The average organization has many shadow IT devices, conducting periodic scans to discover them. Once you have a handle, apply network segmentation to limit the blast radius if one asset is compromised.
2. Strengthen Identity and Access Controls: Use the data point that compromised credentials play a role in roughly a quarter of attacks as motivation to deploy Multi Factor Authentication MFA everywhere feasible. This includes not just employee VPNs and email, but privileged accounts, remote access to OT systems, cloud admin accounts, etc. Opt for phishing resistant MFA hardware security keys or mobile push with number matching to combat attackers stealing MFA tokens. Educate users about not approving unexpected MFA prompts to counter MFA fatigue attacks where an attacker bombard a user with prompts hoping they’ll approve one.
Implement least privilege access: ensure users have the minimum rights needed. Especially for domain admins or service accounts those keys to the kingdom should be tightly controlled and monitored. Use dedicated admin workstations or jump servers for performing administrative tasks, and don’t allow admins to check email or browse the web from those accounts reduces chances of admin creds getting stolen via phishing.
Look into passwordless or secure authentication methods. If 80-85% of people reuse passwords, reducing reliance on passwords will help. Encourage use of password managers to create unique passwords if passwords must be used. Continuous authentication monitoring user behavior for anomalies can also detect if a logged in user isn’t who they claim to be e.g., suddenly downloading tons of data at 2 AM.
3. Network Segmentation and Endpoint Security: Many ransomware infections spread laterally through flat networks. By segmenting networks e.g., separating IT from OT, segmenting by business unit or criticality, you can contain malware. For instance, manufacturing companies should isolate production networks from corporate networks with firewalls and strict access rules. Recall that in manufacturing only 40% of attacks led to encryption, partly due to improved segmentation. Aim for that kind of outcome: even if an office PC gets hit, it can’t easily reach the production line controllers.
Deploy Endpoint Detection and Response EDR tools on servers and workstations. These can catch suspicious behavior like mass file encryption, unusual script execution, or credential dumping tools, all hallmarks of ransomware staging. Modern EDR uses AI/behavioral analysis that was shown to cut breach lifecycle by 80 days on average, which could mean stopping an attack in progress. Keep these tools updated and ensure they’re actually monitoring all endpoints including remote laptops.
Also, don’t forget cloud environments many businesses now operate heavily in cloud AWS/Azure/GCP. Ransomware actors have started targeting cloud resources e.g., encrypting cloud VMs or S3 buckets. Use cloud native security tools to monitor for anomalies like a sudden mass deletion of data or encryption of cloud storage objects. Leverage identity and access management in cloud for example, don’t leave API keys with broad privileges lying around in code repositories attackers search for those.
4. Backup, Backup, Backup and Test Restores: The statistics could not be clearer that backups are a lifesaver: 97% recovery without paying. So invest in a robust backup strategy. Follow the 3 2 1 rule: 3 copies of data, on 2 different media, 1 of them off site and offline. Many companies now use cloud backups with immutability features once written, they cannot be altered for a set time. Also consider out of band backups for critical configurations e.g., export and store firewall/router configs, Active Directory details, etc., in case those systems get ransomed.
Crucially, practice restoring. Have drills where IT staff take random backups and try to restore a system from scratch. Measure how long it takes, see if everything works permissions, application functionality, etc.. This will surface issues to fix before a crisis. Since average downtime is ~24 days, challenge your team to do better. Perhaps you can get core systems up in 3 days if prepared. That kind of resilience might make a ransomware incident a non event for the business.
Also, ensure backup systems themselves are secure. Many attackers go after backups first like delete Volume Shadow Copies on Windows, or target backup servers. Use admin accounts for backups that are not the same as domain admin accounts, and ideally isolate the backup network. Some organizations even physically vault backups on tape or drives periodically. Backup strategies should extend to cloud SaaS data too like Office 365 email, which often isn’t backed up by default third party tools can back it up.
5. Develop an Incident Response Plan and Team: The chaos of a ransomware attack is not the time to figure out roles and procedures. Create a detailed incident response IR plan that covers ransomware scenarios. Include steps like: who makes the call to isolate network segments? Who communicates with employees, customers, regulators? When do we involve law enforcement or external IR firms? Having this mapped out saves precious time. The plan should include decision points for paying or not paying with a leaning towards not, given 77% now don’t pay.
Identify an incident response team not just IT security, but also executives for decision making, PR for communications, legal for breach law compliance, and HR if employees are affected. Conduct tabletop exercises regularly. For example, simulate that ransomware has hit and data is being leaked, walk through how the team would handle it. This builds muscle memory and exposes gaps. Many organizations bring in external facilitators for these drills or use scenarios based on real events. You can use case studies from 2025, like Our company has the same software that had a zero day exploited by Clop, what if we were hit the way Company X was?.
Consider retaining a specialized incident response firm on standby, some cyber insurance provides this. These firms handle ransomware cases daily and know the latest tactics and negotiation strategies. If you have one on retainer, you can get help within hours if needed. They can also do threat intel e.g., check if your stolen data appears on dark web forums, advise if a decryptor exists for that strain, etc.
6. Communicate and Educate: People often are the weakest link phishing accounted for ~16% of breaches and heavily contributes to initial access. Security awareness training is a must. Train employees to recognize phishing emails, especially ones that create urgency or ask for login credentials. Given 80% of phishing is AI crafted now, emails may look more convincing, so focus training on checking sender addresses, not clicking unexpected links, etc. Run regular phishing simulations to keep employees on their toes. Stats show training can cut click rates significantly.
Moreover, train staff on what to do if they suspect malware or ransomware e.g., disconnect network cable, shut down the PC, and report immediately quick isolation can stop an attack from propagating. Make sure they aren’t fearful of reporting mistakes, a culture of blame will just cause delays in reporting incidents.
For executives and higher ups, emphasize not to exempt themselves from protocols. Many breaches start because a VIP insisted on some security exception like not using MFA or having IT disable certain security tools. The data shows anyone can be a target, so policies must apply top down.
7. Leverage External Services Judiciously: If your organization doesn’t have the scale to implement all these practices alone, consider using managed security services. For instance, a continuous security testing program can help catch vulnerabilities and misconfigurations before attackers do. Many specialized firms offer penetration testing services to simulate ransomware attacks and find weak points that can be invaluable. Engaging in web application security testing for login and session flows ensures your web facing apps aren’t an easy credential stealing point. Likewise, cloud security testing focused on identity and access paths can uncover gaps in your cloud configurations. Essentially, bringing in experts to probe your defenses via penetration testing on a recurring basis keeps you aligned with current threats. As threats evolve like new RDP exploits or infostealer trends, these testers will emulate them and tell you where to fix them. This proactive approach is far preferable to finding out from an actual breach.
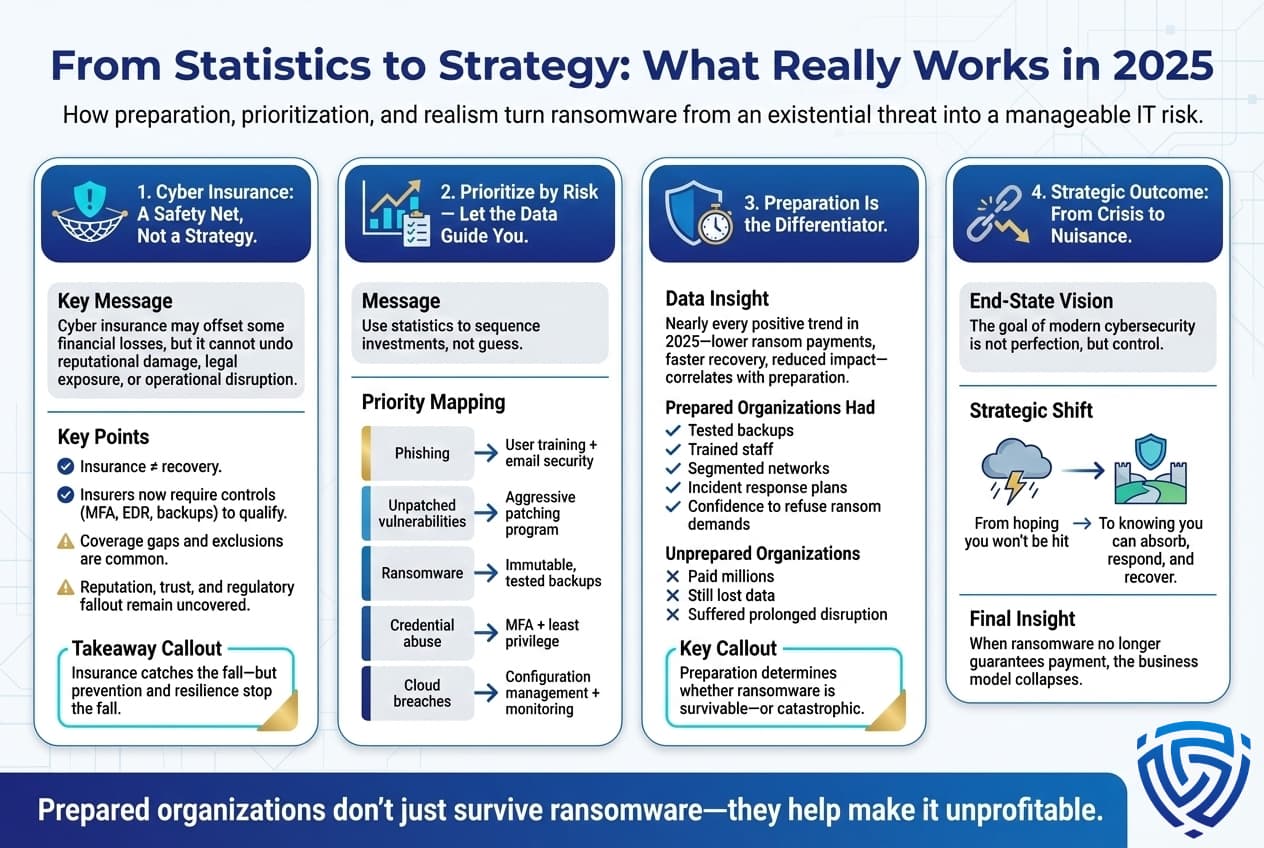
Finally, consider cyber insurance but don’t rely on it as a strategy. Insurance might cover some financial losses, but it cannot undo reputational damage or legal fallout. And insurers now require many of the above practices anyway MFA, EDR, backups to even qualify. Think of insurance as a safety net, not a plan. The plan is to never have to use it by preventing the incident or mitigating it swiftly.
In implementing these best practices, it’s wise to prioritize by risk and use the statistics as a guide to what’s most important. For example, since phishing is a leading vector, prioritize user education and email filtering. Since unpatched vulns are huge, prioritize a strong patching program. Since backups are your last line of defense, ensure they’re solid.
The overarching theme is being proactive and prepared. Almost every stat in this report, whether it’s declining payments or shorter recovery times, points to the difference preparation makes. Companies that had good backups, trained staff, segmented networks, etc., are the ones who could afford to say we won’t pay and still be okay. Those that didn’t often ended up in dire straits, perhaps paying millions and still suffering as evidenced by cases where payment didn’t fully restore data.
By adopting these best practices, organizations align their defenses with the realities shown in the data. It turns the odds in your favor so you’re not just hoping you won’t be hit, but confident that if you are, you’ll handle it with minimal damage. In other words, the goal of these best practices is to transform ransomware from an existential crisis into a manageable IT nuisance. The more companies that do this, the more we collectively push the ransomware business model toward failure.
Ransomware attacks have become extremely common, essentially a daily even hourly occurrence on a global scale. Recent data suggests a ransomware attack strikes a business or individual every few seconds worldwide. To put it in perspective, by 2025 there will be roughly 3-4 ransomware attacks every minute across the globe and projections indicate it could be one every 2 seconds by 2031. In 2024, one report counted over 5,000 known victims posted on ransomware leak sites, and 2025 saw even more estimated 6,500+ as attackers hit numerous targets. So, ransomware is pervasive and no industry or region is fully immune. This means organizations should assume that at some point they will likely be targeted, if they haven’t been already.
Initially, big game ransomware crews went after large enterprises that could pay huge ransoms millions of dollars. While those are still prized targets for example, in 2024 a Fortune 50 company paid a record $75 million ransom, attackers have increasingly shifted to a barbell approach targeting either very large entities or lots of small/mid sized ones. The data shows manufacturing, government, and healthcare were heavily targeted in 2025, likely due to the critical nature of their operations and higher pressure to pay. But we also see schools, small businesses, and municipalities frequently hit. Ransomware as a Service models have made it easy for attackers to cast a wide net, so even a small company with a few dozen employees could be attacked if it has weak security. Essentially, if you have IT systems and can possibly afford to pay a ransom even a small one, you’re a potential target. Attackers often use automated scans to find vulnerabilities, so it’s not always a human picking the victim many times victims are selected simply because they had an exposed weakness.
Many do not and that trend is growing. By late 2025, only about 23% of ransomware victims paid the attackers, which is a sharp drop from a few years ago in 2019, an estimated ~85% paid, and ~50% in 2021. So roughly 3 out of 4 companies now refuse to pay. This is largely due to better backups and incident response, as well as advice from law enforcement to avoid funding criminals. Those who do pay often do so because they feel they have no choice e.g., no backups, or attackers threaten life/safety, or regulatory fines from data leaks outweigh the ransom. However, it’s important to note paying doesn’t guarantee smooth recovery. Studies found 80% of organizations that paid got hit again later, and only a small fraction of those who pay single digit percentages get all their data back uncorrupted. So the trend is toward non payment, and investing in recovery capabilities instead.
It varies widely, but on average about 3 to 4 weeks of downtime is common for a significant ransomware incident. One report pegged average downtime at 24 days in 2025. Some sectors fare worse, manufacturing firms in 2025 averaged around 30 days to fully restore operations in some cases. That said, organizations with well prepared disaster recovery plans have managed to recover much faster, sometimes within a few days or less especially if they catch the attack early or have cloud failover environments. The median dwell time time the attacker is in the network before launching ransomware is around 10-11 days, which is time that could potentially be used to detect and stop them before detonation. After encryption, if backups are readily available, critical services can often be brought back in a matter of days, but full restoration of every system, plus rebuilding security may still take a few weeks. The key is preparation companies that have incident response plans and reliable backups have significantly shorter recovery times. For example, Sophos found 53% of organizations fully recovered within one week in 2025, up from only 35% the year before, indicating recovery times are improving with better planning.
Yes in the majority of cases now. Data exfiltration theft has become a standard part of ransomware attacks. By 2025, roughly 70-80% of ransomware incidents involved attackers stealing sensitive data before encrypting systems. This tactic, often called double extortion, gives criminals more leverage if you don’t pay, they threaten to leak the data publicly or sell it. In fact, some newer attacks forgo encryption entirely and are purely data extortion, stealing data and threatening to release it. For example, criminals have stolen customer databases, intellectual property, even emails and then used that as blackmail. The rise of dedicated leak sites on the dark web where gangs post samples of victim data is evidence: over 1,500 victims had their data posted in just one quarter of 2025 by various groups. So yes, if you fall victim to a modern ransomware attack, you should assume that some amount of your data has been compromised. This is why, even if you have backups to restore systems, a ransomware incident can still be a data breach situation requiring notification and response.
It’s tricky to give one average since it varies by victim size and attacker group. But data from late 2025 shows the median ransom payment was about $140,000 as of Q3 2025. The average ransom payment which is skewed by big cases was around $376,000 in that quarter, reflecting some larger payouts. However, these figures were a big drop from earlier for instance, earlier in 2024 the averages were in the millions due to some huge payments. The median ransom demand that attackers initially ask for is higher, one report put it around $1.3 million median in 2025, but most victims negotiate it down if they engage. For very large companies, we’ve seen demands of $10–50 million frequently, and a few outliers like $70M+ e.g., against a major corporation. For small businesses, demands might be in the tens of thousands. So, in summary: mid sized victims can expect attackers to ask for a few hundred thousand dollars on average, and if they choose to pay, many end up settling in the low six figures. Notably, ransom demands and payments have declined in recent times in Q3 2025, demands were about 30% lower than the previous year and payments were down ~65% from the previous quarter. This is due to victims pushing back and lower willingness to pay large sums.
Yes, it’s generally recommended to involve law enforcement like the FBI or equivalent in your country early in a ransomware incident. They can provide guidance, and in some cases, they might have decryption keys or knowledge of the threat group that can help. Involving authorities also improves the collective fight against these criminals the information you share anonymously if needed might help prevent others from falling victim or aid in eventual prosecutions. Some companies worry law enforcement will tell them not to pay or seize systems, but in practice the decision to pay or not remains with the victim except in cases where paying would violate sanctions. Law enforcement primarily wants to gather intel and assist. And as the stats show, most organizations are moving toward not paying ransoms anyway, aligning with what law enforcement advocates. Additionally, if you have cyber insurance, notifying law enforcement may be a requirement under your policy or under certain regulations for example, some sectors have mandatory reporting for ransomware. There’s also an upside: law enforcement might connect you with incident response resources and can liaise with other agencies if it’s a national security concern, etc.. In short, unless you have a specific legal counsel advising otherwise, involving law enforcement is considered a best practice in ransomware cases today.
About the Author
Mohammed Khalil is a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike Specializing in advanced penetration testing and offensive security operations, he holds certifications including CISSP, OSCP, and OSWE. Mohammed has led numerous red team engagements for Fortune 500 companies, focusing on cloud security, application vulnerabilities, and adversary emulation. His work involves dissecting complex attack chains and developing resilient defense strategies for clients in the finance, healthcare, and technology sectors.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us