August 30, 2025
Updated: August 30, 2025
Everything you need to know about penetration testing in 2025 from costs and compliance mandates to methodology, ROI, and choosing the right provider.
Mohammed Khalil

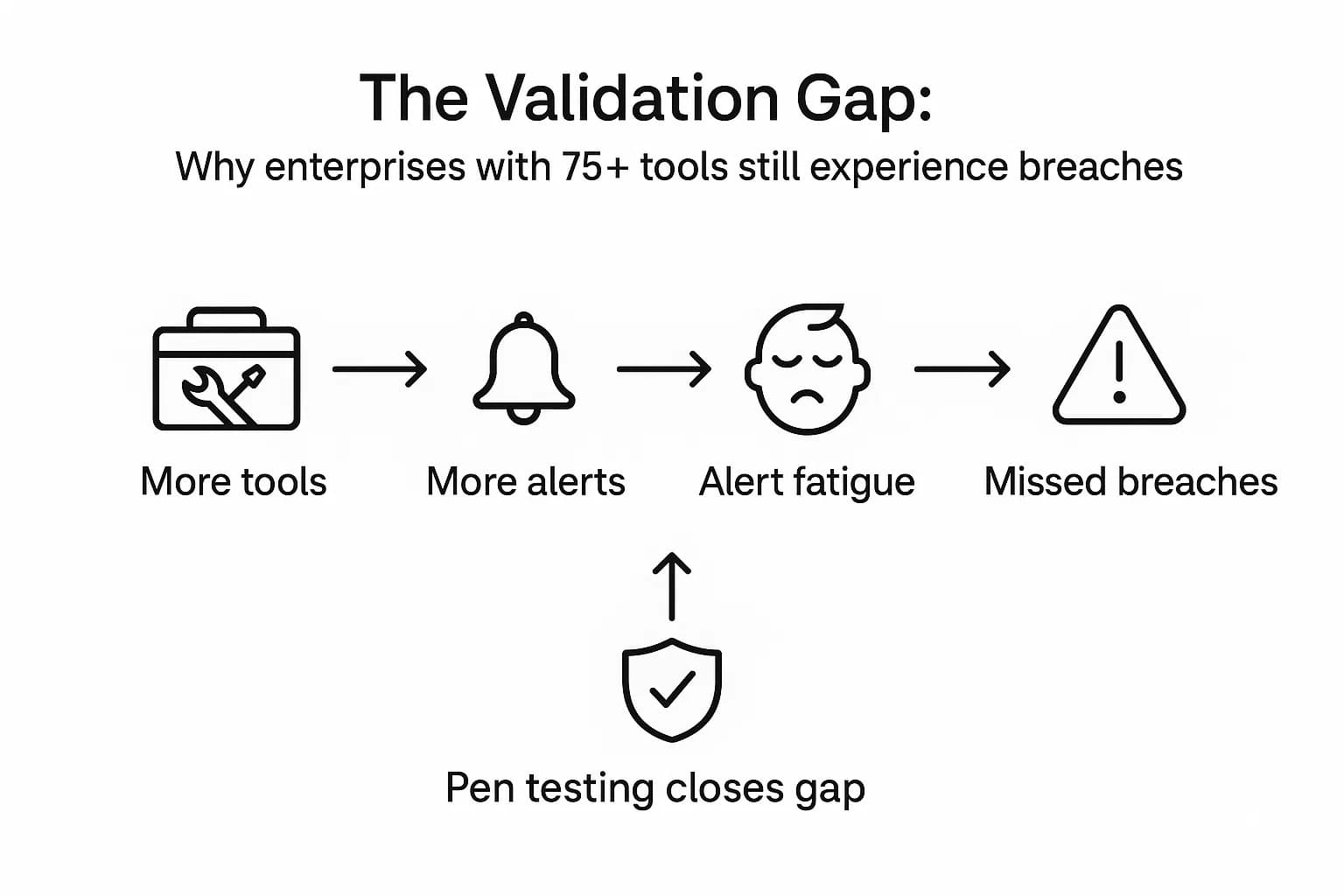
In an era of AI powered defenses and rapidly expanding security toolsets, a frustrating paradox shapes the cybersecurity landscape: why are data breaches more frequent and costly than ever? The answer lies in what's increasingly referred to as the "validation gap."
According to The 2025 State of Pentesting Report by Pentera, while 45% of enterprises increased their security stack to an average of 75 tools, a staggering 67% still experienced a data breach within the past two years. This illustrates a sobering reality: organizations are rich in tools but poor in validation. Without continuous, real world testing to validate what actually works against attackers, even the most advanced controls can leave dangerous blind spots.
A penetration test is a controlled, human led simulation of a cyberattack designed to close that gap. It moves beyond the theoretical vulnerabilities flagged by automated scanners to provide tangible, undeniable proof of what a determined attacker could actually achieve. This guide serves as the definitive FAQ resource for 2025, providing clear, practitioner driven answers on the strategy, cost, compliance requirements, and ROI of penetration testing.
The modern cybersecurity landscape is defined by a fundamental paradox: organizations are investing in more security tools than ever, yet the frequency and cost of data breaches continue to rise. This reality has shifted the strategic function of penetration testing. It is no longer a simple compliance checkbox but a critical tool for validating risk, cutting through the noise of automated alerts, and simulating the true capabilities of a human adversary.
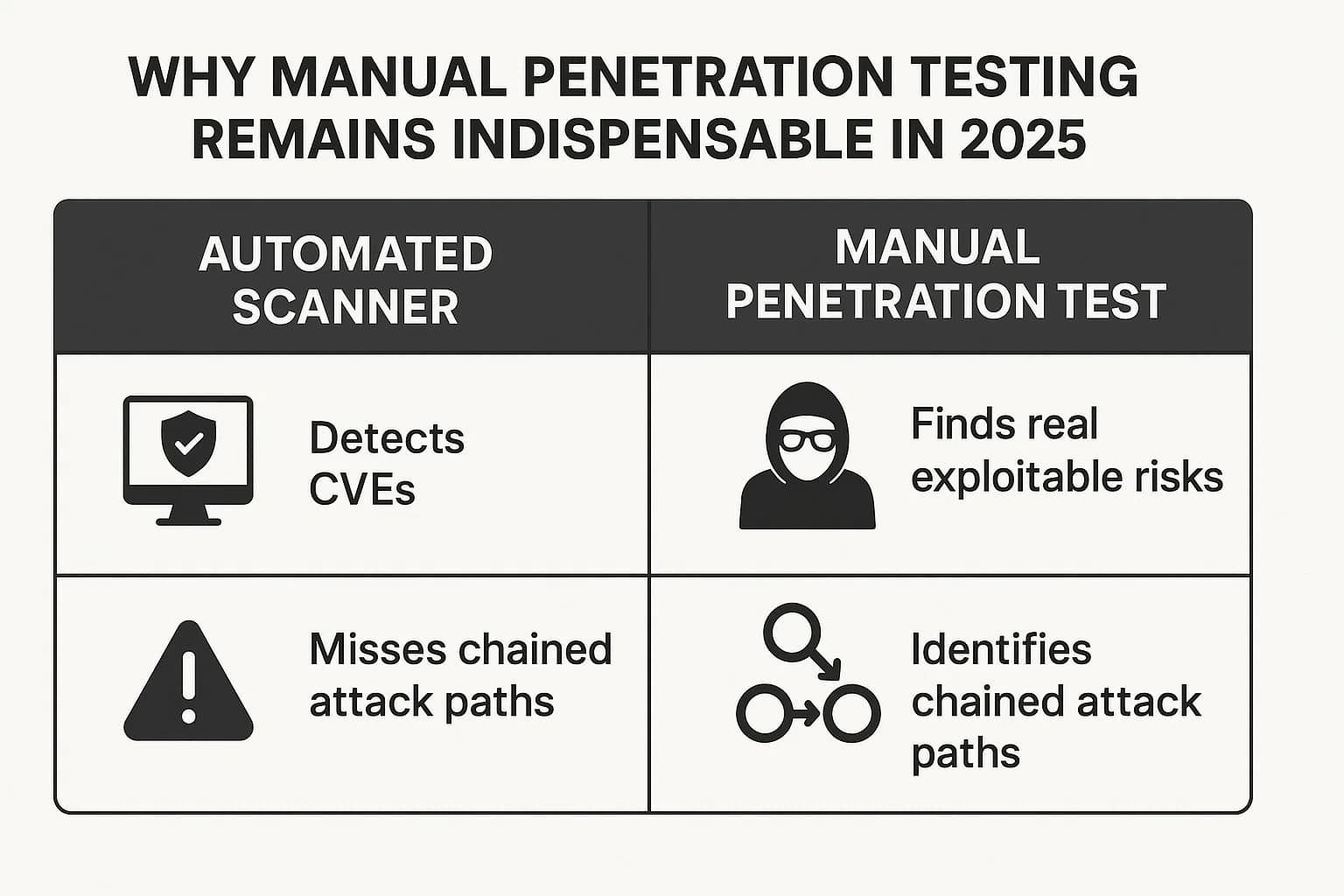
In 2025, the reliance on manual, human led penetration testing remains indispensable, primarily because the proliferation of automated security tools has failed to guarantee protection. The sheer volume of data these tools produce has created a crippling side effect: alert fatigue.
Enterprises managing over 75 security solutions now face an average of 2,000 alerts per week, a number that balloons to over 3,000 for those with more than 100 tools. Security teams are inundated, making it nearly impossible to distinguish between low risk anomalies and the precursors to a major breach.
Manual penetration testing directly addresses this problem. Instead of generating more noise, it focuses exclusively on identifying and proving the exploitability of security gaps. It answers the CISO's most pressing question: "Of these thousands of alerts, which ones can an attacker actually chain together to cause real damage?"
Furthermore, automated scanners, while valuable for identifying known vulnerabilities (CVEs), are ill equipped to detect business logic flaws, chain vulnerabilities across different technology layers, or replicate the creative, multi step attack paths of a sophisticated human adversary.
The distinction between manual vs automated penetration testing is that manual, scenario based testing remains the only method to prove how far a determined attacker could go, making it essential for understanding true business risk.

The choice of penetration testing methodology black, white, or grey box is a foundational decision that dictates the scope, cost, and objectives of an engagement. This choice is not merely technical; it reflects an organization's security maturity and what it aims to achieve with the test.
Here’s the deal: In 2025, with the traditional network perimeter dissolved by cloud services and remote work, the "assumed breach" mindset is paramount. A grey box test perfectly simulates this scenario, answering the more relevant question: "What can an attacker do once they are inside?" This is a key point of contrast in the black box vs white box testing explained debate.
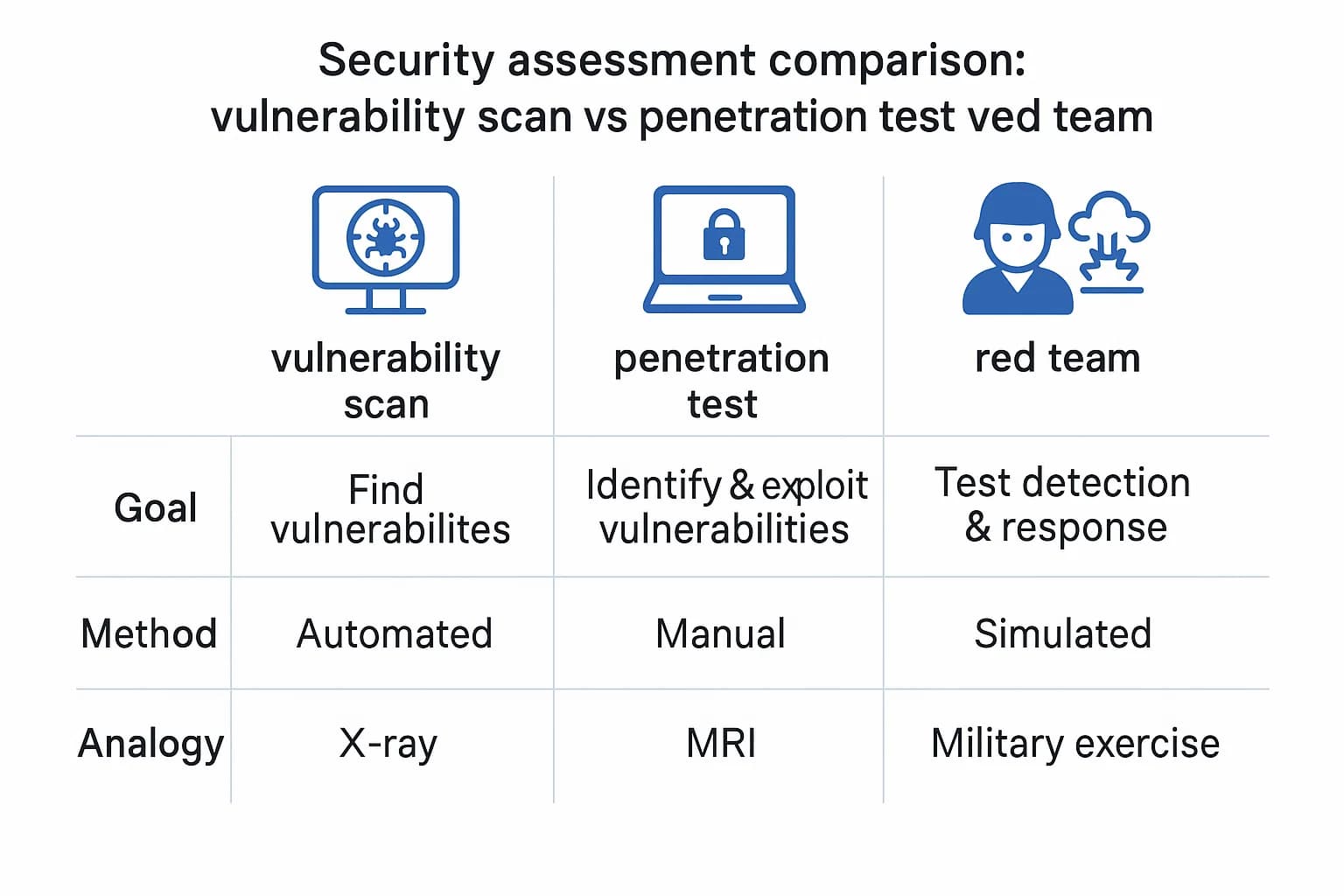
Understanding the differences between these three common security assessments is crucial for choosing the right one for your goals.
For a deeper dive, explore our guides on vulnerability assessment vs penetration testing and the red team vs blue team explained.
For business leaders, the most pressing question is often one of budget. Penetration testing is a significant investment, and its cost can vary dramatically. This section provides a detailed breakdown of 2025 cost benchmarks, explores the key variables that influence pricing, and offers a clear framework for calculating the return on investment (ROI).
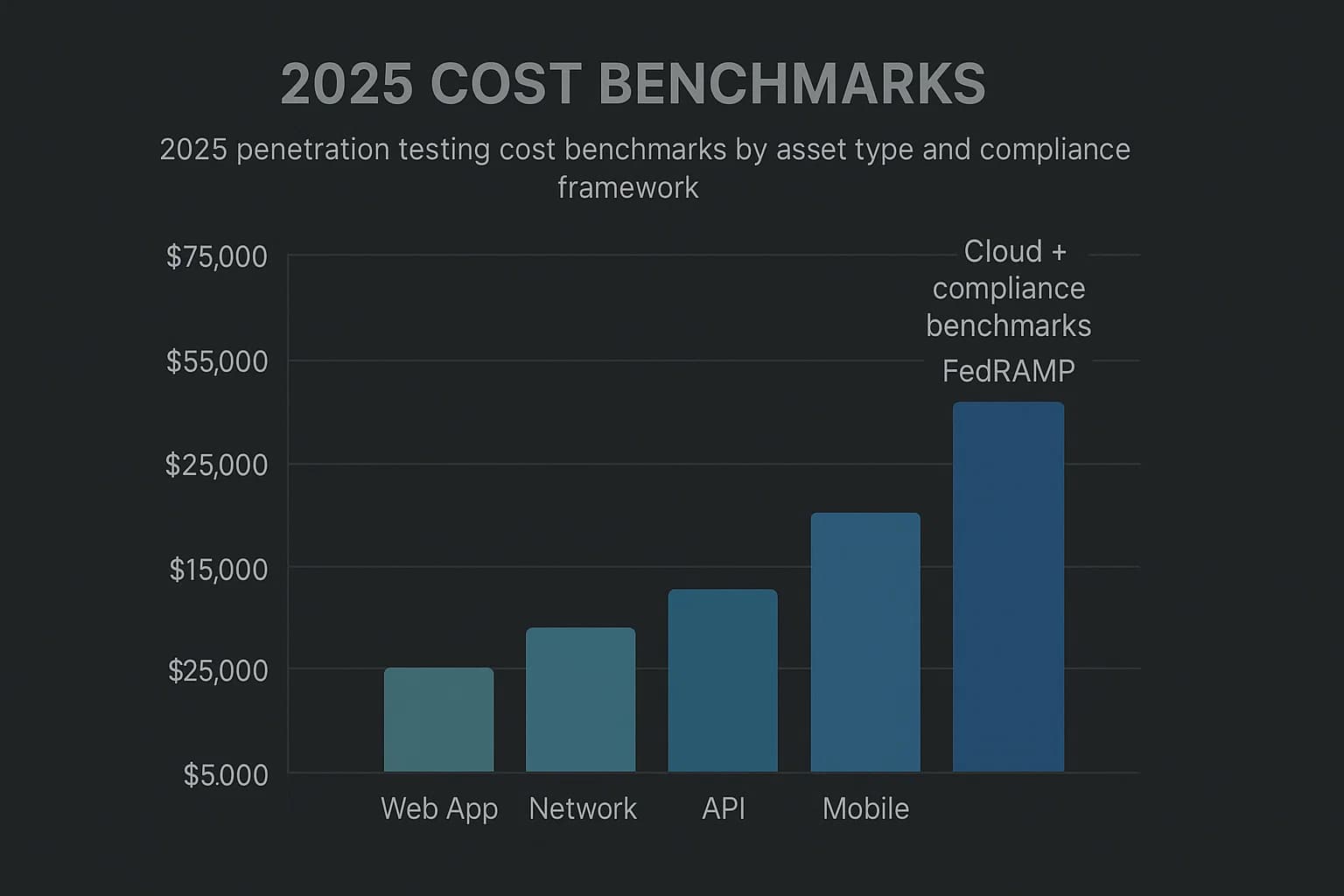
In 2025, a professional, high quality penetration test typically costs between $5,000 and $50,000, with most organizations falling in the $10,000 to $30,000 range. Large scale enterprise projects can easily exceed $100,000.
Be wary of services advertised for less than $4,000, as these are almost certainly lightweight, automated vulnerability scans rather than comprehensive, manual led assessments. Understanding the true penetration testing cost is vital, especially for penetration testing for startups and SMBs.
Here is a synthesized overview of typical cost benchmarks for 2025 :
2025 Penetration Testing Cost Benchmarks
By Asset Type
By Compliance Mandate
The data reveals a clear "compliance tax." For instance, while a standard web application test might start at $5,000, a test for the same application to meet HIPAA or FedRAMP requirements can cost two to three times as much. This premium is for the rigorous documentation and specialized reporting required by auditors.
The wide cost range is driven by a few key variables:

Justifying the budget for a penetration test becomes straightforward when framed against the potential cost of a data breach.
The core calculation is a direct comparison: the average cost of a penetration test ($10,000–$30,000) versus the average cost of a data breach, which stood at $4.45 million globally in 2025 and an even higher $10.22 million in the U.S.. Using this data, a single $20,000 engagement that prevents one major breach can yield an ROI of over 200x.
Mini Case Study: The ROI of Compliance Driven Pen Testing A 20 person financial services administrator was required by its large enterprise partners to conduct annual penetration tests to achieve a SOC 2 audit. Initially resistant, the company realized that failing to comply would mean losing key partnerships.
They engaged a firm to perform an OWASP based test on their proprietary and third party applications. The test uncovered several fixable security holes, which they remediated. The final, clean report satisfied their partners and the SOC 2 auditors, securing their business relationships. In this case, the ROI wasn't just about preventing a breach; it was about enabling business and revenue by demonstrating trustworthiness.
For many organizations, the primary driver for a penetration test is meeting the stringent requirements of industry regulations. A pen test serves as the crucial, independent evidence that security controls are not just designed correctly but are also operating effectively.
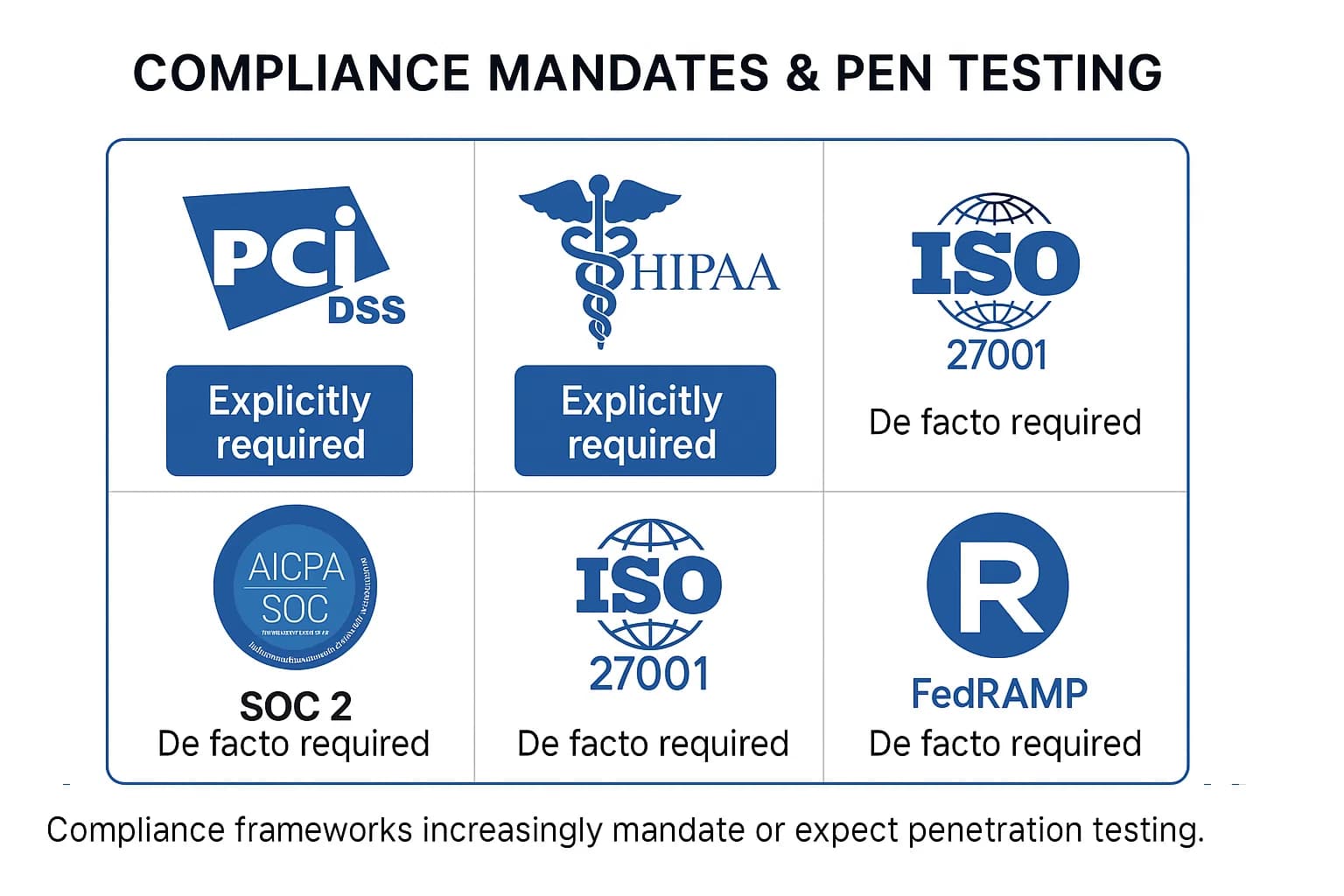
While a standard like ISO 27001 may not explicitly state "you must perform a penetration test," it mandates controls (e.g., A.12.6.1, "Management of technical vulnerabilities") that are effectively satisfied by one. Other frameworks are more direct. PCI DSS Requirement 11.3 explicitly mandates annual penetration testing. For regulations like HIPAA and standards like SOC 2, penetration testing has become the de facto method for conducting the required risk analysis.
Mini Case Study: The Target Breach and PCI DSS The 2013 Target data breach is a textbook example of compliance failure. Attackers compromised a third party HVAC vendor with network access, pivoted into Target's main network, and stole 40 million credit card numbers.
This incident highlighted a failure to meet a core PCI DSS principle: network segmentation. A proper internal penetration test would have simulated this exact scenario and discovered that an attacker could move from a low trust zone to the sensitive Cardholder Data Environment (CDE). The lesson was clear: compliance requires proving that controls work in practice, not just on paper.
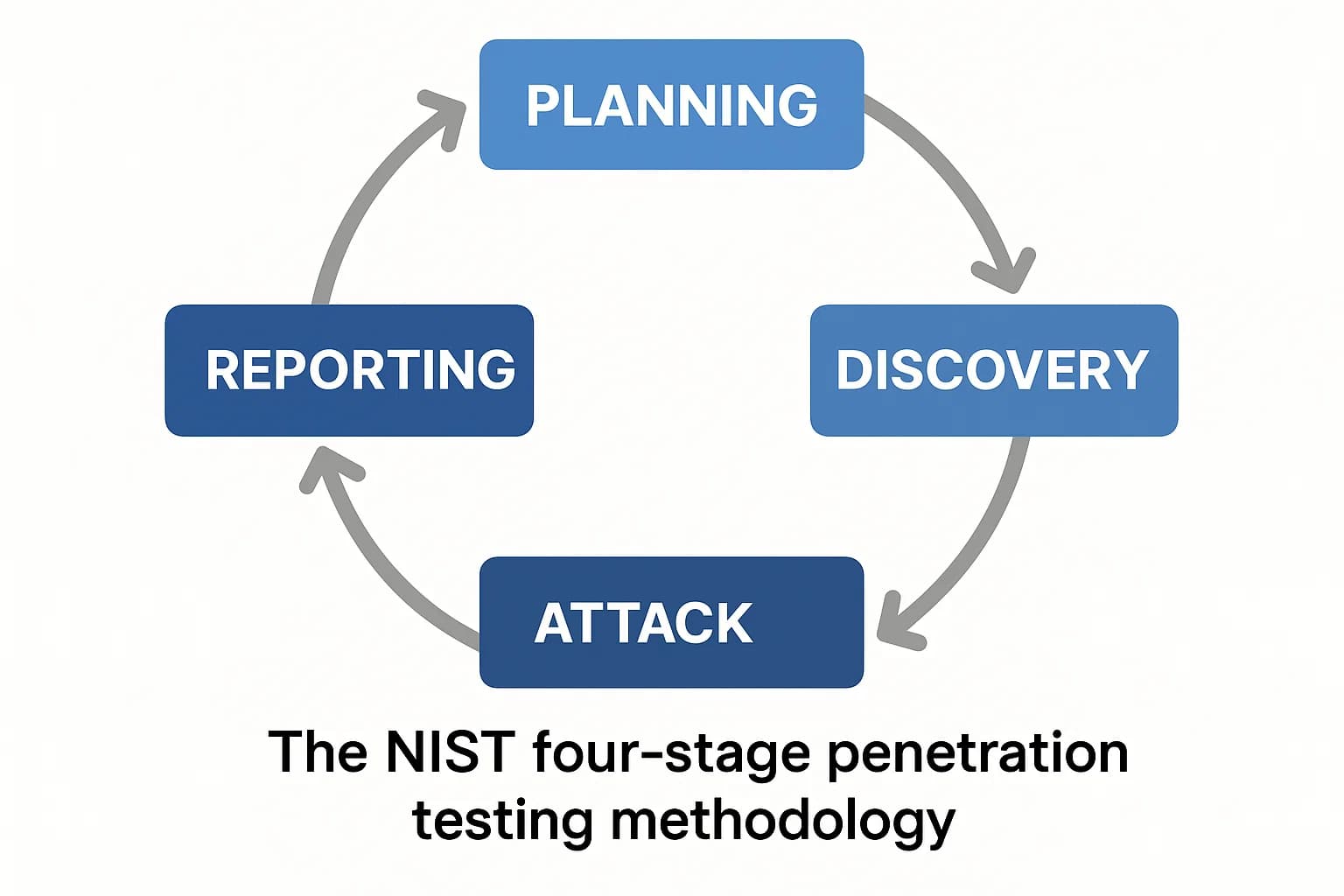
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides a foundational framework in the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). It outlines a systematic, four stage process:
This process fits within the broader NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), helping organizations identify vulnerabilities, validate Protect controls, and test their ability to Detect, Respond, and Recover.
A significant trend shaping the cybersecurity landscape is the growing influence of cyber insurance providers. According to the 2025 State of Pentesting Report, a remarkable 59% of CISOs implemented at least one cybersecurity solution they weren't previously considering, solely due to requirements from their cyber insurer.
Insurers now demand evidence of robust security controls before issuing or renewing a policy. A comprehensive, professional penetration test report has become a key piece of that evidence. This trend is creating a universal, market driven security baseline, making penetration testing for cyber insurance eligibility a mandatory prerequisite for coverage.
A professional penetration test is a blend of art and science, relying on the tester's skill, augmented by a powerful suite of specialized tools. Understanding these tools provides insight into the testing process.

Professionals rely on a curated toolkit for each phase of an engagement:
The OWASP Top 10 is a globally recognized document that represents a consensus on the most critical security risks to web applications. It serves as the foundational baseline for any credible web application penetration test. The list is periodically updated, with data collection for the 2025 version running through late 2024, ensuring its continued relevance.
Choosing the right provider is a critical decision. The market is diverse, and making an informed choice requires looking beyond the price tag to evaluate methodology, team expertise, and the quality of deliverables.

A cheaper quote often translates to fewer testing days or less experienced consultants. Use this checklist to evaluate potential partners:
A good provider will help you build a strong scope, but a penetration testing RFP writing guide can help structure your requirements.
1. How often should I get a penetration test?
At a minimum, annually. However, it's also required after any significant changes to your network or applications. For compliance like PCI DSS, this is a strict mandate.
2. What happens if a pen test finds critical vulnerabilities?
This is the purpose of the test. The provider's report will include prioritized guidance for remediation. The provider should then conduct a retest to validate the fixes.
3. Can a penetration test cause a system outage?
While there is a small risk, a professional provider mitigates this through a rigorous Planning phase and clear Rules of Engagement (RoE) to prevent disruption.
4. What's the difference between a vulnerability assessment and a pen test?
A vulnerability assessment is an automated scan that identifies potential weaknesses. A penetration test is a manual process that exploits those weaknesses to prove they are real and determine their business impact.
5. How long does a typical penetration test take?
The duration depends on the scope. A simple web application test might take one to two weeks, while a complex network assessment could last a month or more.
6. What is the main goal of penetration testing?
The primary goal is not just to find flaws, but to measure the real world effectiveness of security controls and provide an evidence based assessment of business risk.
7. Are penetration testers the same as hackers?
Penetration testers are "ethical hackers." They use the same tools and techniques as malicious hackers but do so with explicit, written permission to improve security, not cause harm.

Ready to Strengthen Your Defenses?
The threats of 2025 demand more than just awareness; they require readiness. If you're looking to validate your security posture, identify hidden risks, or build a resilient defense strategy, DeepStrike is here to help. Our team of practitioners provides clear, actionable guidance to protect your business.
Explore our penetration testing services for businesses to see how we can uncover vulnerabilities before attackers do. Drop us a line, we’re always ready to dive in.
Mohammed Khalil is a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike, specializing in advanced penetration testing and offensive security operations. With certifications including CISSP, OSCP, and OSWE, he has led numerous red team engagements for Fortune 500 companies, focusing on cloud security, application vulnerabilities, and adversary emulation. His work involves dissecting complex attack chains and developing resilient defense strategies for clients in the finance, healthcare, and technology sectors.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us