August 6, 2025
Updated: August 6, 2025
From deepfake scams to AI-generated malware the evolving AI cybersecurity threats and how to fight back.
Mohammed Khalil


Simultaneously, defenders are using AI for predictive threat detection and automated incident response, significantly reducing breach costs and response times. The key to survival is not just adopting AI tools, but implementing effective AI governance through frameworks like the NIST AI RMF to manage risks like "Shadow AI". Real world incidents show that while technology is critical, the ultimate defense often relies on a combination of proactive security validation and a well trained, vigilant workforce.
The central question for security leaders in 2025 isn't if AI will change cybersecurity, but how to survive the "AI arms race" that's already here. Artificial intelligence is now the primary engine driving both the sophistication of AI cyber attacks and the evolution of our defenses. It is a powerful dual use technology that has permanently raised the bar for both offense and defense, reshaping the modern threat landscape.
The stakes have never been higher. We are operating in an environment where cybercrime is projected to cost the global economy a staggering $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. This isn't a distant forecast; it's the current operational reality. This surge is fueled by the rapid, and often ungoverned, adoption of AI, which is widening security gaps at an alarming rate. According to recent research, a staggering 90% of companies currently lack the maturity to effectively counter today's advanced AI enabled threats.
This report moves beyond the hype to provide a practitioner's analysis of this new reality. We will dissect how threat actors are weaponizing AI, backing our analysis with real world case studies and hard data. We'll then pivot to the defensive playbook, detailing how security teams are leveraging AI to fight back and build resilience. Finally, we will cover the essential governance frameworks required to deploy AI not just effectively, but responsibly and securely.
To build an effective defense, you must first understand the offense. Threat actors are systematically integrating AI into their operations to enhance the scale, speed, and sophistication of their attacks. This section breaks down their primary methods, from mass market deception to highly targeted, adaptive threats.
For years, security awareness training has coached users to spot the tell-tale signs of a phishing email: poor grammar, awkward phrasing, and generic greetings. That era is over. AI has fundamentally changed the phishing landscape, making it the top email threat of 2025.
From Awkward Emails to Hyper Realistic Lures
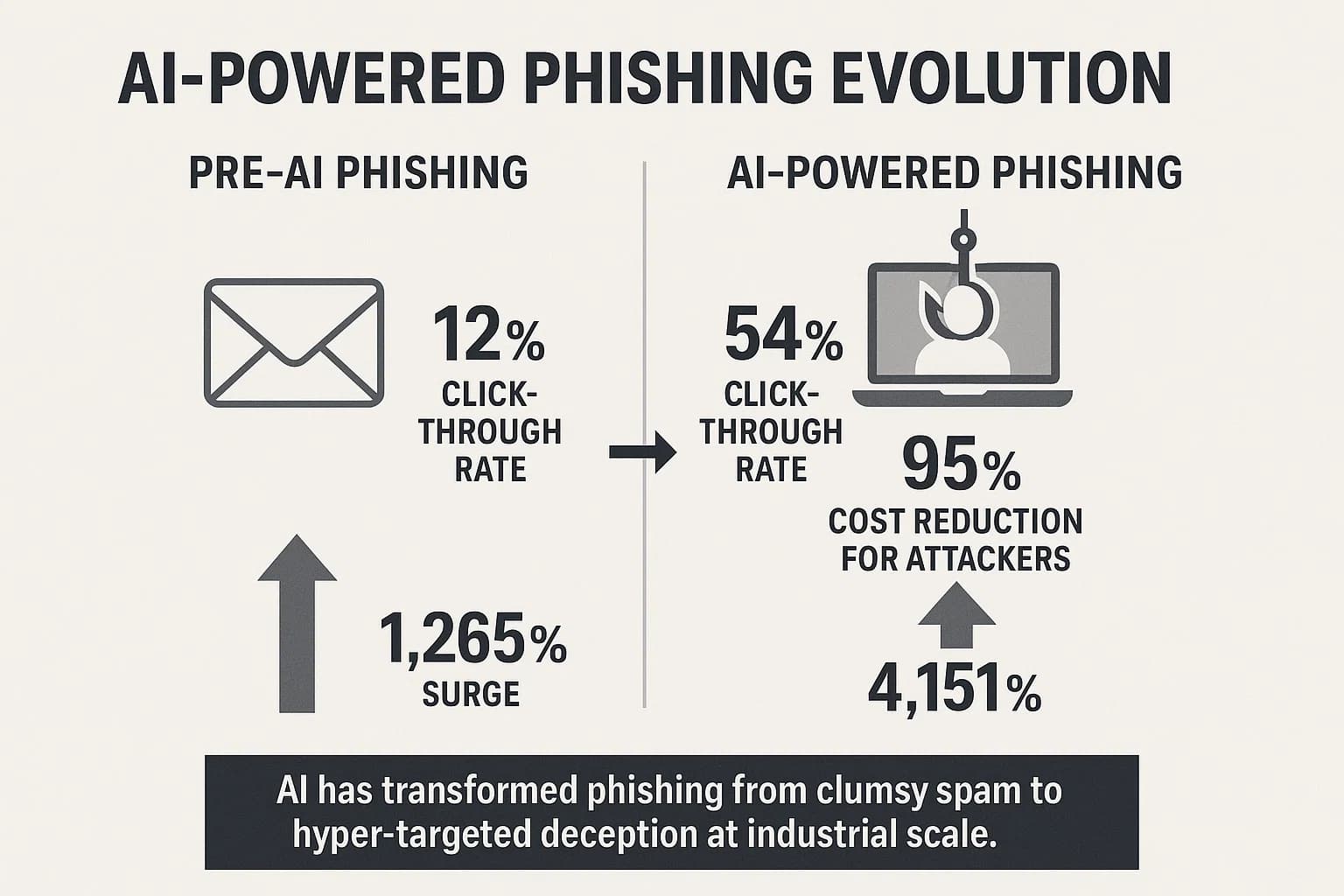
The fundamental shift is from easily spotted spam to AI generated phishing that is grammatically perfect, contextually aware, and deeply personalized. Modern large language models (LLMs) can scan a target's public digital footprint, social media posts, professional profiles, company news to craft bespoke, convincing narratives that exploit human trust.
The numbers behind this trend are alarming:
These figures highlight a critical shift. The traditional "human firewall" is becoming increasingly unreliable. The burden must shift from subjective human intuition towards objective technical verification and a Zero Trust approach. The latest phishing attack trends and statistics confirm this is a top priority.
Case Study: The Rise of Malicious Chatbots (WormGPT & FraudGPT)
The threat is further amplified by the democratization of advanced attack tools. In 2023, malicious AI models like WormGPT and FraudGPT emerged on dark web forums. These chatbots, which mimic popular generative AI tools but lack any ethical safeguards, are explicitly marketed for illicit activities. Researchers found that these tools can generate "remarkably persuasive" Business Email Compromise (BEC) messages and other malicious content with ease, effectively providing "crime as a service".
The next evolution of AI powered social engineering moves beyond text to exploit our most fundamental senses. Deepfakes hyper realistic audio and video generated by AI are no longer a novelty but a potent weapon for cybercriminals. The technology has become so accessible that it is fueling a dramatic rise in fraud. In the first quarter of 2025 alone, there were 179 deepfake incidents recorded, surpassing the total for all of 2024 by 19%.
The $25 Million Wake Up Call: The Arup Deepfake Fraud
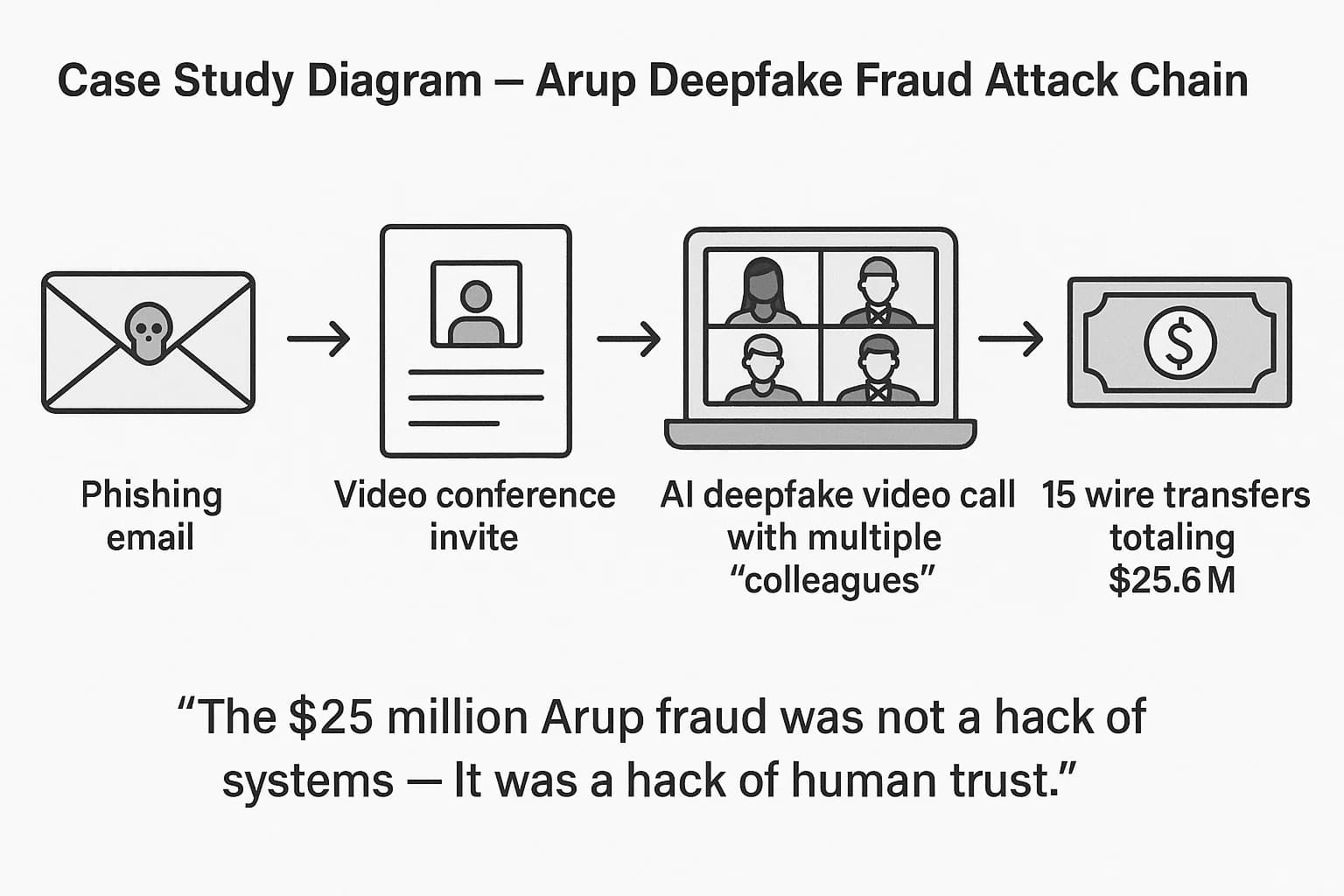
The 2024 incident at global engineering firm Arup serves as a stark wake up call. The attack chain was a masterful blend of old school phishing and new age technology:
This incident was not a traditional hack. As Arup's Global CIO later described it, it was a case of "technology enhanced social engineering". The attackers didn't breach firewalls; they breached human trust, amplified by technology.
Foiled Attempts and Critical Lessons: The WPP and Ferrari Incidents

While the Arup case demonstrates the devastating potential of deepfakes, two other high profile incidents from 2024 show how they can be defeated.
These incidents reveal a crucial truth. While technical deepfake detection tools are emerging, they are locked in a continuous arms race with the generation technology. For now, the most reliable defense is procedural. Organizations must embed simple, mandatory verification steps for any sensitive or unusual request. These incidents are prime examples of a Real world account takeover case study where the goal is not just credential theft but the direct manipulation of human action.
Attackers are also using AI to revolutionize malware development, creating threats that are more evasive and resilient than ever before. The most significant development in this area is the rise of AI generated polymorphic malware.
What is Polymorphic Malware?
Polymorphic malware is malicious code designed to constantly change its identifiable features such as its file hash or code structure each time it replicates. This shapeshifting ability allows it to evade detection by traditional antivirus tools that rely on static signatures. AI supercharges this capability, with some advanced strains generating a new, unique version of themselves as frequently as every 15 seconds during an attack.
The Threat in 2025
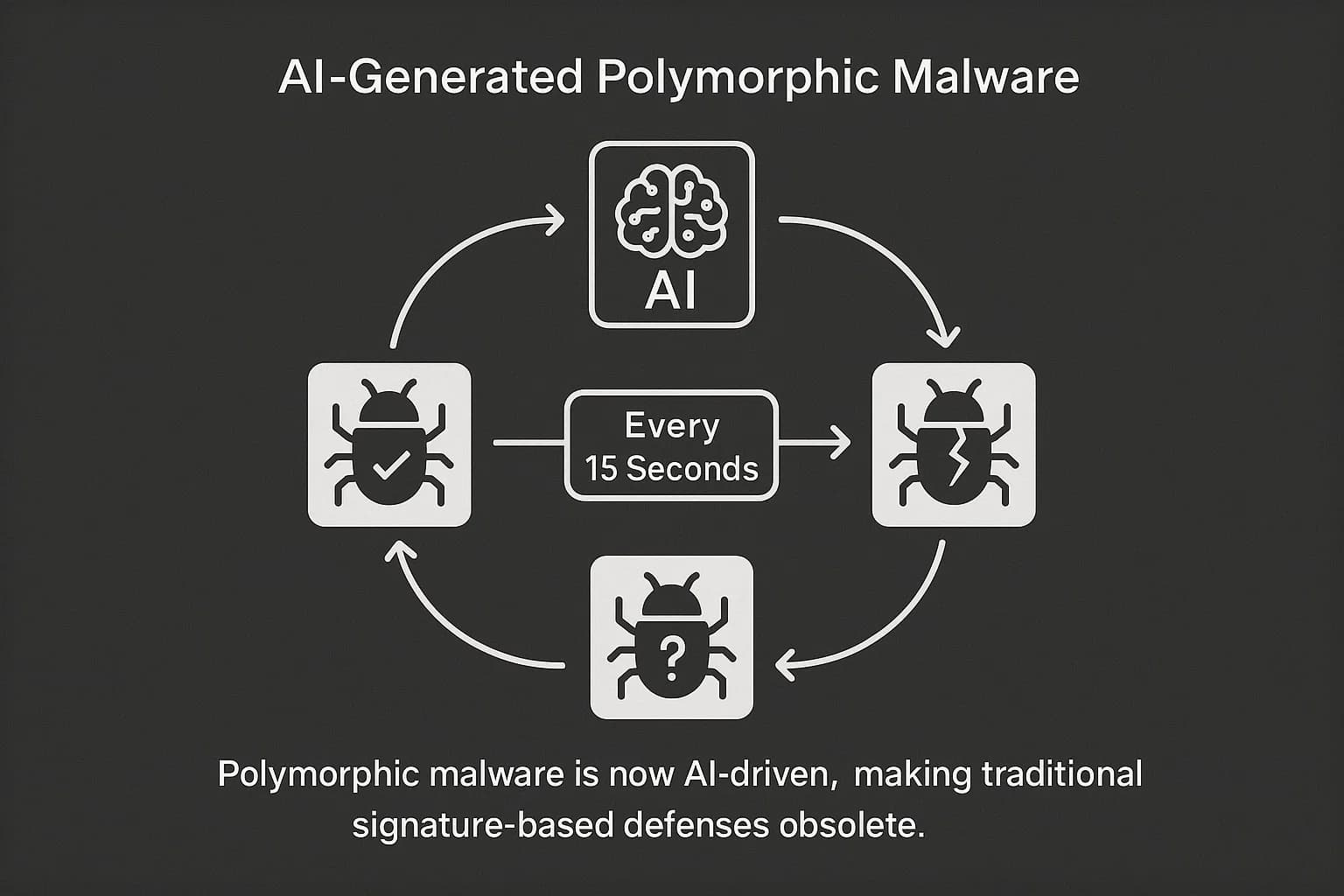
This advanced evasion technique is no longer a niche threat. In 2025, polymorphic tactics are now present in an estimated 76.4% of all phishing campaigns. Other reports indicate that over 70% of major breaches now involve some form of polymorphic malware. This threat is further amplified by the growth of the Malware as a Service (MaaS) ecosystem, with kits like BlackMamba or Black Hydra 2.0 available for as little as $50. The evolution of these threats is a critical component of today's malware attack types and infection trends.
The final frontier of AI powered offense is the "AI vs. AI" battle, where adversaries attack not just the network or the users, but the defensive AI models themselves. These techniques, broadly known as adversarial machine learning, represent a sophisticated threat aimed at undermining the very tools we rely on for protection.
There are two primary methods:
The core risk of these attacks is the erosion of trust in our own defensive systems. This underscores the importance of adhering to robust security frameworks from authoritative bodies like the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP), which provide guidance on mitigating these advanced threats.
While attackers have been quick to weaponize AI, defenders are harnessing the same technology to build more intelligent, adaptive, and automated security postures. AI is not just a threat; it is also a powerful tool in the modern defensive arsenal.
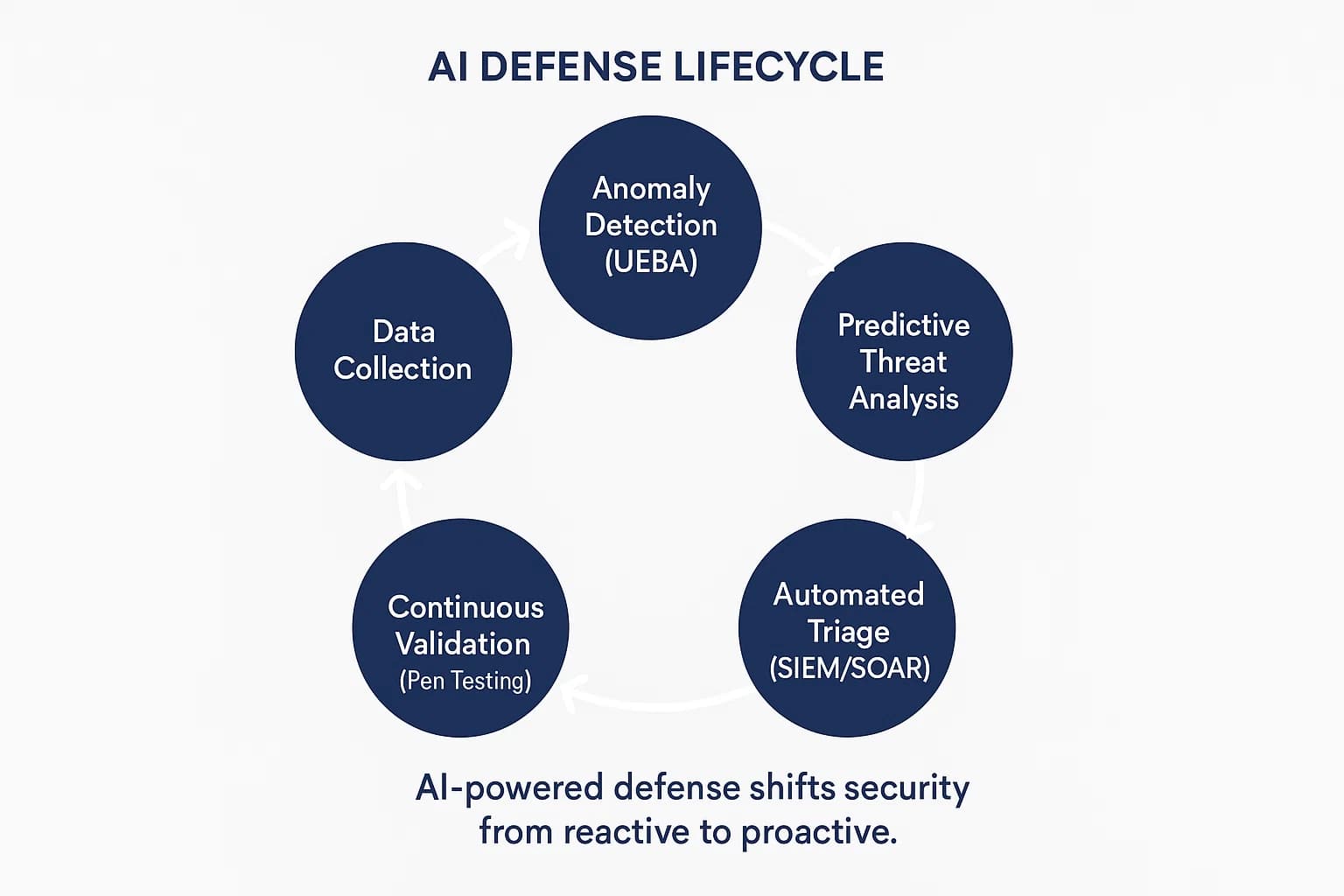
The most significant advantage AI offers defenders is the ability to shift from a reactive to a proactive security model.
Beyond Signatures: Anomaly and Behavior Based Detection
AI's greatest defensive strength is its ability to learn what "normal" looks like across a complex digital environment. By analyzing massive volumes of data, AI builds a dynamic behavioral baseline for every user, device, and application. Instead of searching for known malware signatures, AI powered systems hunt for anomalies subtle deviations from established patterns. This capability, often referred to as User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), allows security systems to detect novel, zero day, and polymorphic attacks that would be invisible to traditional tools. In high risk environments, AI driven systems have demonstrated threat detection rates as high as 98%.
Predicting the Future: How AI Forecasts the Next Attack
Beyond real time detection, AI is enabling predictive analytics in cybersecurity. AI powered threat intelligence platforms continuously ingest and analyze immense volumes of data from a wide range of sources. By identifying subtle correlations and emerging patterns, these platforms can forecast future threats, such as predicting which vulnerability is about to be widely exploited. This predictive capability is a key differentiator between a simple vulnerability assessment vs penetration testing, as it shifts the focus from finding existing holes to anticipating where the next ones will appear.
One of the most pressing challenges in cybersecurity today is human burnout. Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are often overwhelmed by a relentless flood of alerts.
The AI "Skills Multiplier"
AI is providing a powerful solution to this problem by acting as a "skills multiplier" for security teams. AI driven platforms for Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) are transforming SOC operations:
The results of this automation are dramatic. According to IBM's 2025 Cost of a Data Breach Report, organizations that make extensive use of security AI and automation cut their average breach costs by $1.9 million and shorten their breach lifecycles by an average of 80 days. This automation frees up human analysts from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on more complex work like threat hunting and investigation. This efficiency gain is a core reason why continuous penetration testing matters; it enables teams to continuously validate the effectiveness of these complex, automated defense systems.
Adopting defensive AI tools is only half the battle. To truly build resilience, organizations must also implement strong governance to manage the risks associated with this powerful technology.
One of the most significant challenges is that AI adoption is dramatically outpacing security oversight. Business units are frequently deploying "Shadow AI" unsanctioned AI tools and applications without the security team's knowledge, creating massive visibility gaps.
The High Cost of Ungoverned AI
The financial impact of this governance gap is severe. According to IBM's 2025 report, data breaches involving Shadow AI cost organizations an average of $670,000 more than breaches that did not involve unsanctioned AI.
The root cause is a failure of governance. A staggering 97% of all AI related security incidents occurred in systems that lacked proper access controls, governance policies, and security oversight. While organizations are rightly concerned about sophisticated AI attacks, the data shows they are being breached today due to fundamental, preventable governance failures.
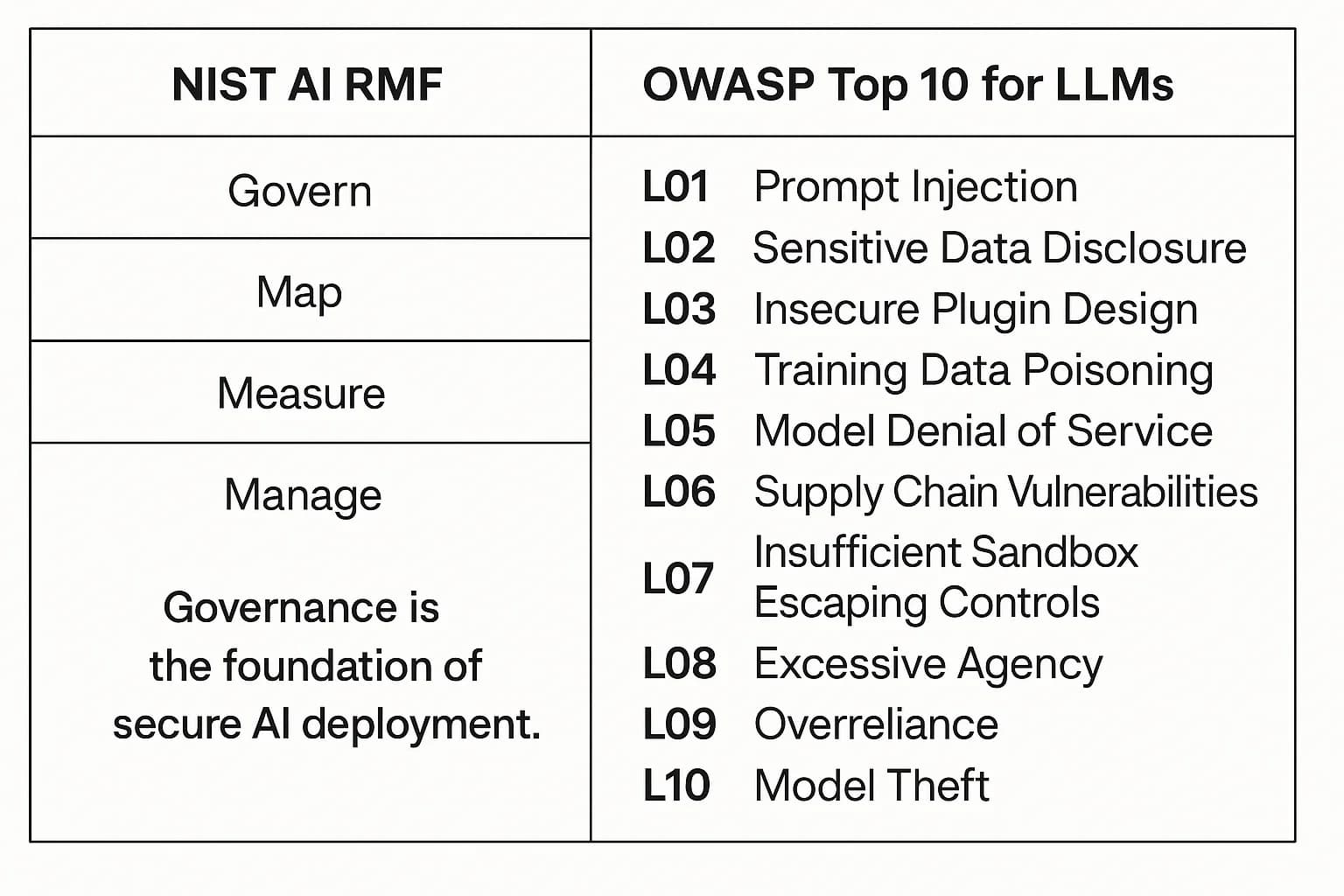
Establishing a strong governance foundation is the most urgent and impactful action a CISO can take to mitigate AI risk in 2025.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) Explained
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) is an essential guide for managing AI risks in a structured and responsible manner. The framework is built around four core functions:
Adopting the NIST AI RMF is a critical step toward building trustworthy AI systems and demonstrating due diligence.
The OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Models (LLMs)
For organizations using generative AI, the OWASP Top 10 for Large Language Model Applications is another indispensable resource. This guide identifies the most critical vulnerabilities specific to LLMs. Two of the most relevant risks are:
Securing LLM powered applications against these threats requires a combination of input/output filtering and strict access controls, making concepts like OAuth security best practices highly relevant.
A How To Guide: 5 Steps to Strengthen Your AI Security Posture
1. What is the main role of AI in cybersecurity? AI plays a dual role. For defenders, it automates threat detection, analyzes vast amounts of data to spot anomalies, and speeds up incident response. For attackers, it's used to create more sophisticated threats like hyper realistic phishing and deepfakes, and to automate attacks at scale.
2. How do hackers use AI for attacks?
Hackers use AI to automate, scale, and enhance their attacks. Key methods include generating highly convincing phishing emails , creating deepfake videos and voice clones for social engineering fraud , developing polymorphic malware that evades detection , and automatically scanning for vulnerabilities.
3. Can AI prevent all cyberattacks?
No. While AI significantly enhances defensive capabilities, it is not a foolproof solution. AI systems themselves can have vulnerabilities, such as susceptibility to data poisoning, and determined attackers can still devise novel ways to bypass them. A layered defense combining AI technology with strong security processes and human oversight is essential.
4. What are the biggest risks of using AI for security?
The primary risks include adversarial attacks, where attackers fool an AI model with deceptive inputs; data poisoning, where an AI's training data is corrupted; model drift, where an AI's accuracy degrades over time; and inherent biases in the training data that create blind spots. A major operational risk is over reliance on AI without sufficient human oversight.
5. How does AI help with phishing detection?
AI improves phishing detection by moving beyond simple filters. Defensive AI can analyze the context and language of an email to spot social engineering cues. More importantly, AI powered behavioral analytics can detect anomalies that occur after a user interacts with a phishing email, such as an unusual login attempt, even if the email itself looked benign.
6. What is an adversarial AI attack?
An adversarial AI attack is a technique used to intentionally fool a machine learning model. An attacker makes subtle modifications to an input such as an image or file that are often imperceptible to humans but are specifically designed to cause the AI to make an incorrect classification, such as labeling a malicious file as safe.
7. Is AI making cybersecurity better or worse?
It is making it both more challenging and more effective. AI is arming attackers with more sophisticated weapons. At the same time, it is providing defenders with powerful new tools for detection and prediction. According to research from Gartner and IBM, organizations that effectively deploy and govern security AI see significantly better outcomes including lower breach costs and faster response times.
The AI arms race of 2025 has created a new reality: the baseline for attacks has been permanently elevated. Human centric threats like deepfake fraud and hyper realistic phishing are now mainstream tactics. Adaptive, AI generated malware has rendered traditional signature based defenses increasingly obsolete.
Surviving in this landscape requires a strategic pivot to a proactive posture built on a non-negotiable foundation of Zero Trust and validated through continuous testing. However, the most critical takeaway is that governance is not optional. The data is clear: the most damaging AI related incidents are not the result of some unstoppable super powered attack, but of fundamental and preventable failures in oversight. Your organization's AI security posture is only as strong as the governance framework that underpins it.
The threats of 2025 demand more than just awareness; they require readiness. If you're looking to validate your security posture, identify hidden risks, or build a resilient defense strategy, DeepStrike is here to help. Our team of practitioners provides clear, actionable guidance to protect your business.
Explore our penetration testing services for businesses to see how we can uncover vulnerabilities before attackers do .Drop us a line, we’re always ready to dive in.

Mohammed Khalil is a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike, specializing in advanced penetration testing and offensive security operations. With certifications including CISSP, OSCP, and OSWE, he has led numerous red team engagements for Fortune 500 companies, focusing on cloud security, application vulnerabilities, and adversary emulation. His work involves dissecting complex attack chains and developing resilient defense strategies for clients in the finance, healthcare, and technology sectors.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us