October 29, 2025
Updated: October 29, 2025
Understand how manual and automated code reviews differ and why the 2025 best practice is a hybrid model that blends AI speed with human insight.
Mohammed Khalil

Modern development demands both speed and accuracy. In 2025, teams achieve this by blending manual inspections with automated tools. This balanced strategy catches simple issues automatically while reserving human expertise for complex logic and design. The following guide breaks down how each approach works, their trade offs, and how to implement a robust code review process.
Manual code review means people reading and discussing code to spot problems. Typically, developers examine each other’s code changes often via GitHub/GitLab pull requests to ensure they meet quality, style, and security standards.
Human reviewers understand context: they know the project’s architecture, business logic, and why the code was written a certain way. For example, a developer familiar with the app can notice an unusual authorization check that an automated tool would ignore. As Aikido’s guide explains, manual reviews shine at architectural decisions, business logic, or highly sensitive code contexts where tools often fail.
In practice, manual reviews occur during code merge requests. Peers comment on code style, design choices, and any logic issues. This promotes knowledge sharing and mentorship junior devs learn from seniors, and teams align on standards. For example, reviewers might spot a confusing function name or suggest refactoring for clarity, improving long term maintainability.

Manual review remains essential for security and quality, but its limits mean teams can’t rely on it alone. As OWASP notes, automated scanning can’t find every issue like XSS flaws, hence manual code reviews are important. In other words, without human review, you risk missing context sensitive vulnerabilities.

Automated code review uses software tools to analyze source code automatically. These include linters, static analysis scanners SAST, AI powered review bots, and security scanners. The tools parse the code against a set of rules or patterns to flag issues for example, syntax errors, style violations, or known security flaws.
For instance, tools like SonarQube or ESLint run static analysis on code to catch problems. As Relia Software explains, SonarQube performs static code analysis, scanning source code to identify potential issues like code smells, bugs, and security vulnerabilities, which helps improve maintainability and security. In practice, these tools run automatically during development: a CI/CD pipeline might fail a build if critical issues appear, or integrate with IDEs to give instant feedback.
Automated review is like a turbocharged spell check for code. It rapidly enforces known standards, but it’s rules based only. The Graphite guide sums it up: automated reviews detect syntax errors and known security issues at machine speed, whereas manual review is adept at understanding business logic, architectural decisions, and code readability.
Below is a comparison of how manual and automated code reviews stack up across common factors:
| Feature | Manual Code Review | Automated Code Review |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow requires careful, line by line reading and discussion | Fast scans thousands of lines in minutes with each run |
| Context & Insight | High understands intent and project context | Low checks only predefined patterns, blind to business logic |
| Consistency | Variable depends on reviewer’s thoroughness and mood | High applies the same rules every time without fatigue |
| Scalability | Limited bottlenecked by reviewer availability | Excellent handles large codebases or frequent changes easily |
| Bug Detection | Good at complex logic, design flaws, niche security issues | |
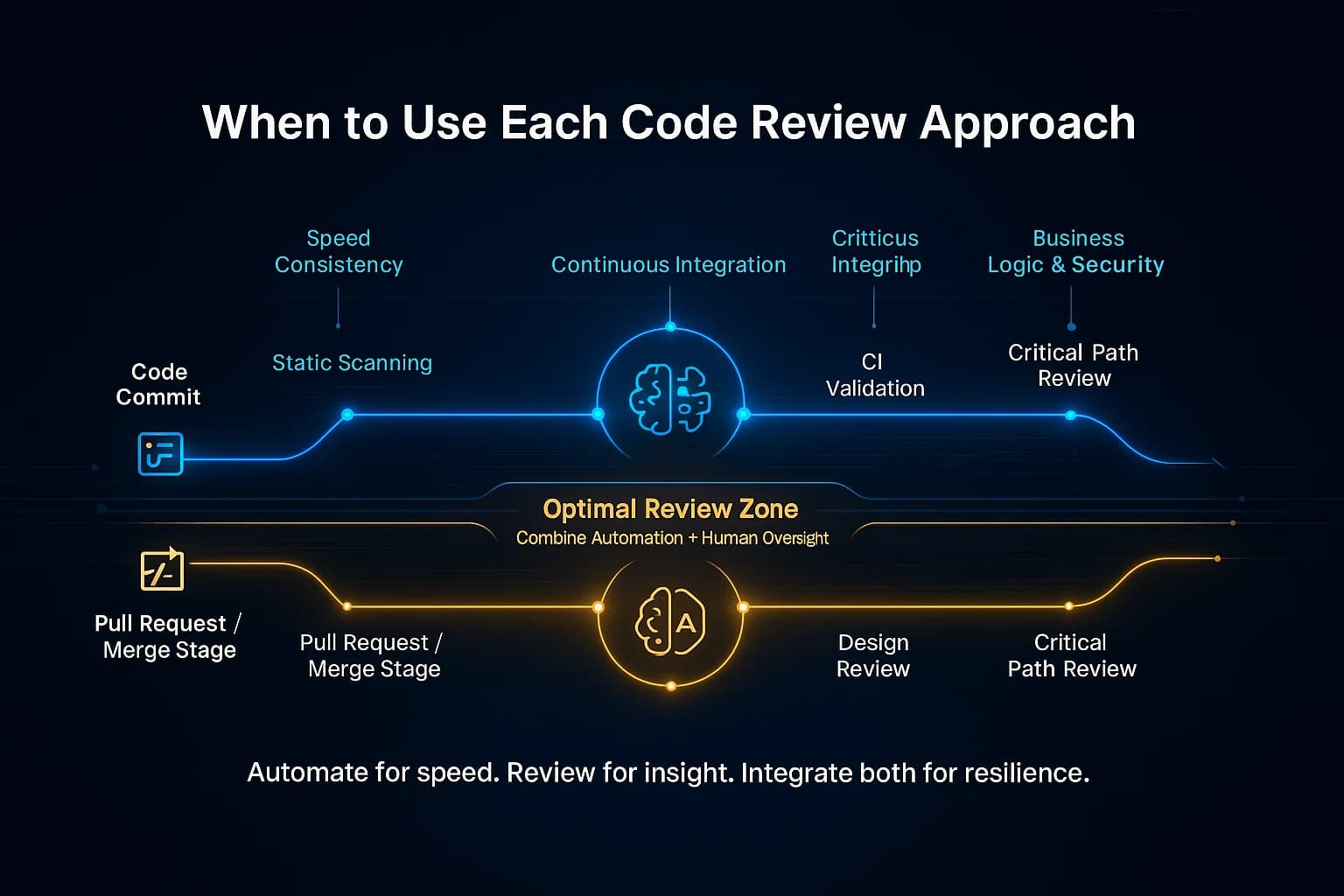
Combine them for best results. Automated scans should be the first line of defense, handling routine checks on every commit. Reserve manual review for the high value areas. For example:
Start with automated scans to handle repetitive or technical checks, then have team members focus on high priority areas like logic, architecture, and business critical sections.

A proven workflow is a hybrid approach that layers automation with human insight:
This multi layer process means automated tools catch the low hanging fruit, and human reviewers spend time where it matters most. For example, Graphite recommends using AI reviewers to highlight issues in PRs so humans can concentrate on architecture and business logic. Over time, your pipeline becomes self reinforcing: automation blurs the line to only serious or subtle issues for the human eye.
Example Workflow

Both methods improve quality, but in different ways. Automated tools enforce baseline standards. For instance, SonarQube identifies potential issues like code smells, bugs, and security vulnerabilities, helping developers proactively clean up code. Regular static analysis reduces technical debt: common mistakes are caught early and fixed, keeping the codebase more stable.
Manual reviews add the qualitative layer. Reviewers often spot problems beyond syntax: poor documentation, missing comments, or inefficient algorithms. They can suggest refactorings that make future work easier. From a security standpoint, a human might notice a missing authorization check or incorrect API usage that a generic scanner never flags.
Organizations that mix both see the greatest gains. Research cited by Aikido Security shows projects using both manual and automated reviews often ship higher quality code and resolve security issues more rapidly. In fact, Gartner found 45% of teams are now adopting AI driven reviews to speed delivery while keeping bugs in check. Meanwhile, studies have noted that automation excels at repetitive flaws, whereas humans catch nuanced logic issues. This indicates that the hybrid model is key automation enforces guardrails, and humans handle the intricate parts.

Code review is a security control. Automated scanners run security lint rules e.g. OWASP Top 10 checks on your code base. Many tools map their findings to compliance standards for example, flagging insecure coding practices related to PCI DSS or HIPAA. However, they only catch known patterns.
Manual review fills the gaps. For example, OWASP’s guide points out that tools can’t find every instance of Cross Site Scripting; manual code reviews are important to catch what scanners miss. Similarly, business logic flaws like flawed payment processes usually require a human understanding the rules to identify.
Industry standards explicitly expect code review. NIST’s Secure Software Development Framework SSDF mandates that organizations perform the code review and/or code analysis based on the organization’s secure coding standards and document all issues. In other words, both manual and automated code reviews are considered best practice for secure development. Evidence of reviews, comments, tickets, approvals often becomes part of audit trails for SOC 2, PCI DSS, etc., proving that code changes were vetted.
Neither method alone meets every requirement. Automated tools help enforce policy e.g. denying merge on critical flaws, while manual reviews verify context specific compliance e.g. confirming a credit card field is handled securely. Companies often tie pull requests to compliance tickets and use both reviews to satisfy auditors. For example, automated scans might ensure no secrets are committed addressing Git secrets detection for SOC 2, while a human reviewer confirms that the logic matches privacy policy requirements.
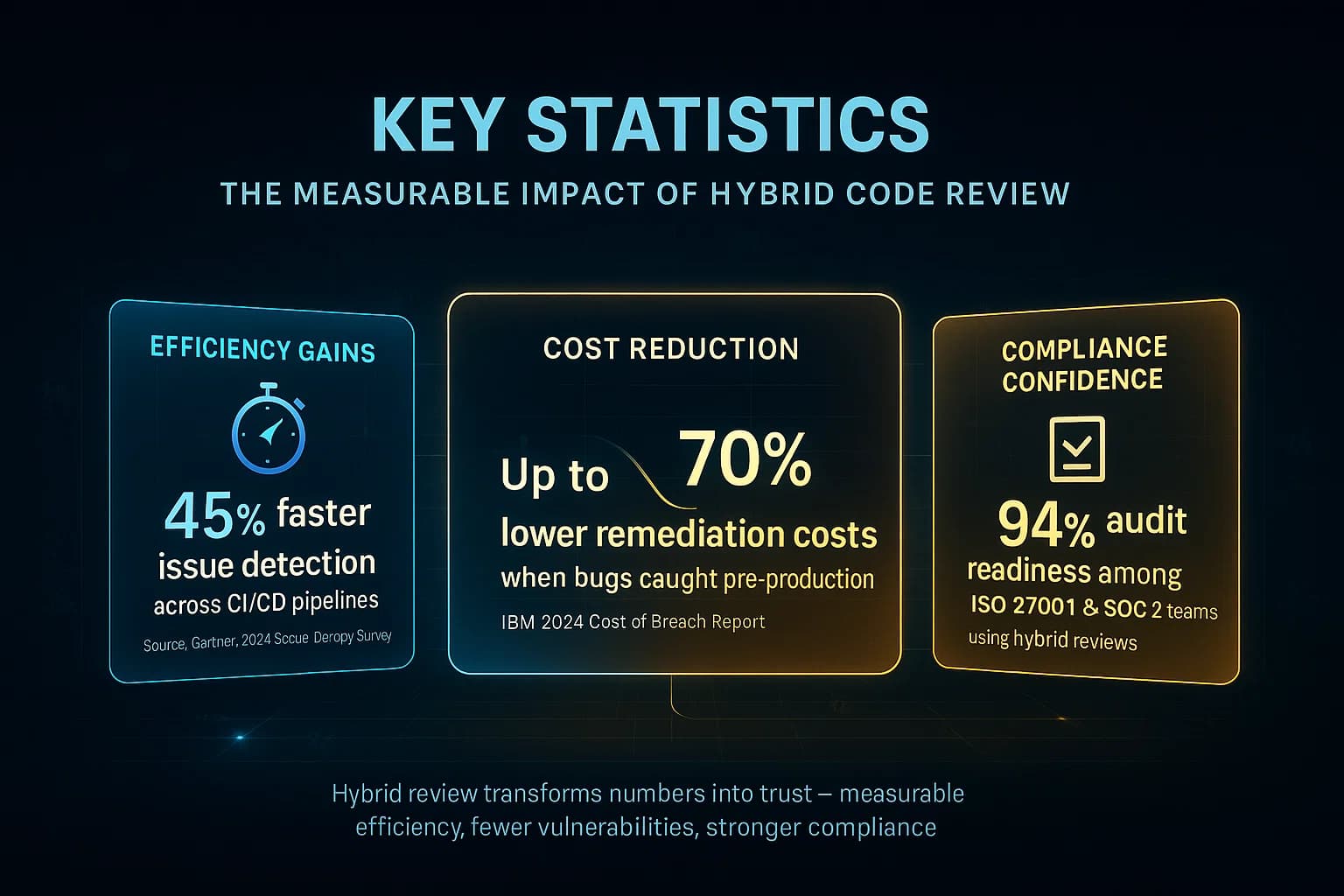
These figures underline that while automation is on the rise, experienced reviewers remain vital. Security and quality improve when you combine both approaches.

The fix is to set a clear policy: use automation for routine enforcement, and focus human effort on high risk areas. Over time, tune your tools so they support not hinder the review process.
In 2025, code quality and security demand both brains and automation. Manual reviews give the depth and context that only people provide, while automated tools give speed and consistency. Together, they form a powerful combination.
Ready to strengthen your defenses? If you want to verify your security posture and uncover hidden risks, DeepStrike’s team is here to help.

Our penetration testing services complement strong code review practices by simulating real attacks on your apps and systems. Talk to us to build a resilient defense strategy with clear, actionable guidance from experienced security practitioners.
About the Author
Mohammed Khalil is a Cybersecurity Architect at DeepStrike, specializing in advanced penetration testing and offensive security. Holding certifications like CISSP, OSCP, and OSWE, he has led red team engagements for Fortune 500 firms, focusing on cloud security and application vulnerabilities. Mohammed dissects complex attack chains and builds resilient defenses for clients in finance, healthcare, and tech.
Manual code review is done by human developers reading the code, bringing context, design insight, and shared knowledge. Automated code review uses tools to scan code against rules or known issues, delivering fast and consistent feedback but without understanding intent.
No, they complement each other. Automated tools catch obvious bugs and enforce standards quickly, while manual reviews uncover complex logic or security flaws that tools miss. Industry best practice is a hybrid approach, using both.
It depends on your needs. Automated review is better for speed, scale, and catching common issues. Manual review is better for understanding business logic, architecture, and context. The smartest teams use both: automate the mundane and let humans handle critical thinking.
It varies. Manual reviews can take hours for large changes and slow down delivery. Automated checks run in minutes, but setting them up takes initial effort. Overall, combining both tends to save time in the long run by catching defects early.
Tools include SonarQube static analysis, ESLint/Pylint for linting, Snyk or Veracode for security scanning, and CI integrations like GitHub Code Scanning. These tools scan code for style, bugs, vulnerabilities, and report results automatically.
Yes. Penetration testing attacking a running app finds live issues, but code review finds problems earlier in development. Code reviews especially automated SAST catch issues that might not be exploitable yet. Together they form a stronger security posture. For complete coverage, pair code review with regular penetration testing services and vulnerability scanning.
Absolutely. Even with advanced AI tools, humans are needed for nuance. As OWASP and industry studies note, automation has blind spots. Manual reviews ensure that critical logic and requirements are correctly implemented.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us