October 23, 2025
Updated: October 23, 2025
How extensions get weaponized, what changed with Manifest V3, and the exact controls that keep your data safe
Khaled Hassan

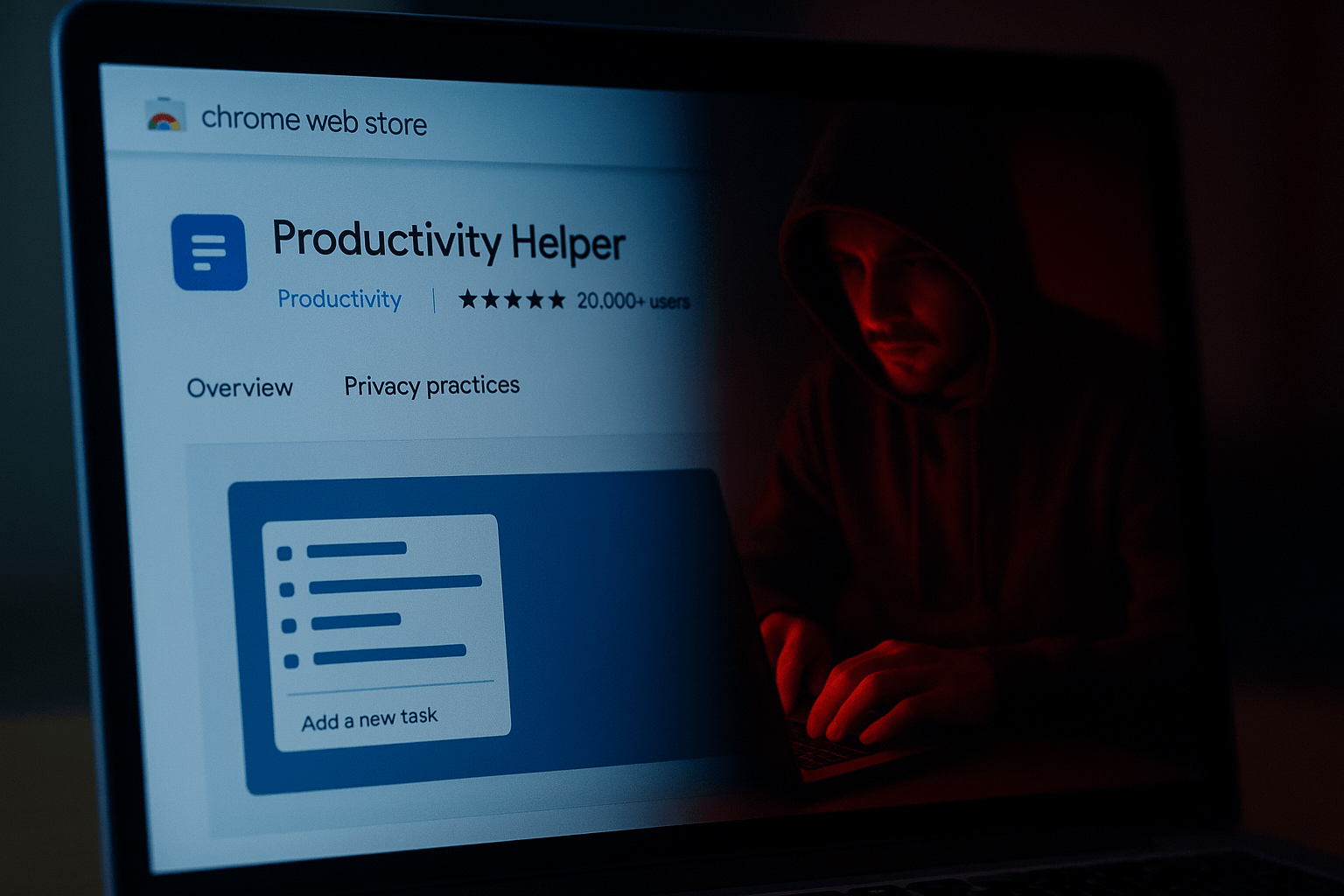
Browser extensions are tiny apps with big power. They can read pages, modify content, copy clipboard data, and call external APIs. That power is useful for productivity, yet it also attracts attackers. In the last year, researchers and newsrooms documented malicious or compromised Chrome extensions that tracked users, took screenshots of every visited page, or quietly redirected traffic for fraud. Many of these add-ons looked legitimate, had good reviews, and even appeared in the official Web Store. This guide explains how the threat works, what has changed with Chrome’s Manifest V3, and how organizations can reduce risk with a simple, enforceable policy. We use recent incidents and official sources, and we finish with a practical checklist that security and IT teams can apply today.
Chrome extensions security threats are risks that arise when extensions misuse or overuse permissions, receive malicious updates, or get hijacked to exfiltrate user data and manipulate web sessions at scale.
Power vs Risk
| Threat signal | 2024–2025 evidence | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Mass installs of malicious extensions | 1.7M installs across nearly a dozen add-ons on the official store | Popularity and ratings do not guarantee safety. |
| Cross-store campaigns | 18 extensions hit Chrome and Edge, total impact ~2.3M | Supply chain and multi-store reach increase blast radius. |
| Developer hijack | Reuters reported widespread extension compromises via phishing | Trusted extensions can turn hostile after an update. |
| Clone armies | 131 rebranded clones targeted WhatsApp Web users in Brazil | Look-alikes bypass user skepticism and flood the store. |
| Privacy abuse by “utilities” | FreeVPN.One secretly captured screenshots of all pages | Abuse can hide behind security or productivity branding. |
chrome://extensions, remove anything you do not recognize, then toggle Developer mode and review each extension’s site access and permissions.Attackers publish a useful tool, gather installs and reviews, then push a new version that adds tracking or data theft. Multiple reports in 2025 described extensions with millions of installs that later collected browsing activity or altered search results.
Phishing or OAuth abuse can give attackers publishing access. Once inside, they ship a malicious update to a trusted user base. A January 2025 analysis detailed a phish that spoofed Chrome Web Store policy notices to trick maintainers, which led to compromise and harmful releases. Reuters also reported a broader campaign against developer accounts.
Threat actors copy a legitimate extension, change branding, and flood the store with look-alikes that automate spam or harvest data. Researchers recently exposed 131 rebranded clones that targeted WhatsApp Web users.
Wide permissions like tabs, scripting, or host-permission wildcards let an extension read and alter content across many sites. A popular VPN add-on was found capturing screenshots of every visited page and shipping them to a remote server.
Google updates store policies and removes known bad items, but investigators still find waves of spammy or borderline extensions that stay live for months, which increases exposure windows.
Chrome~Update
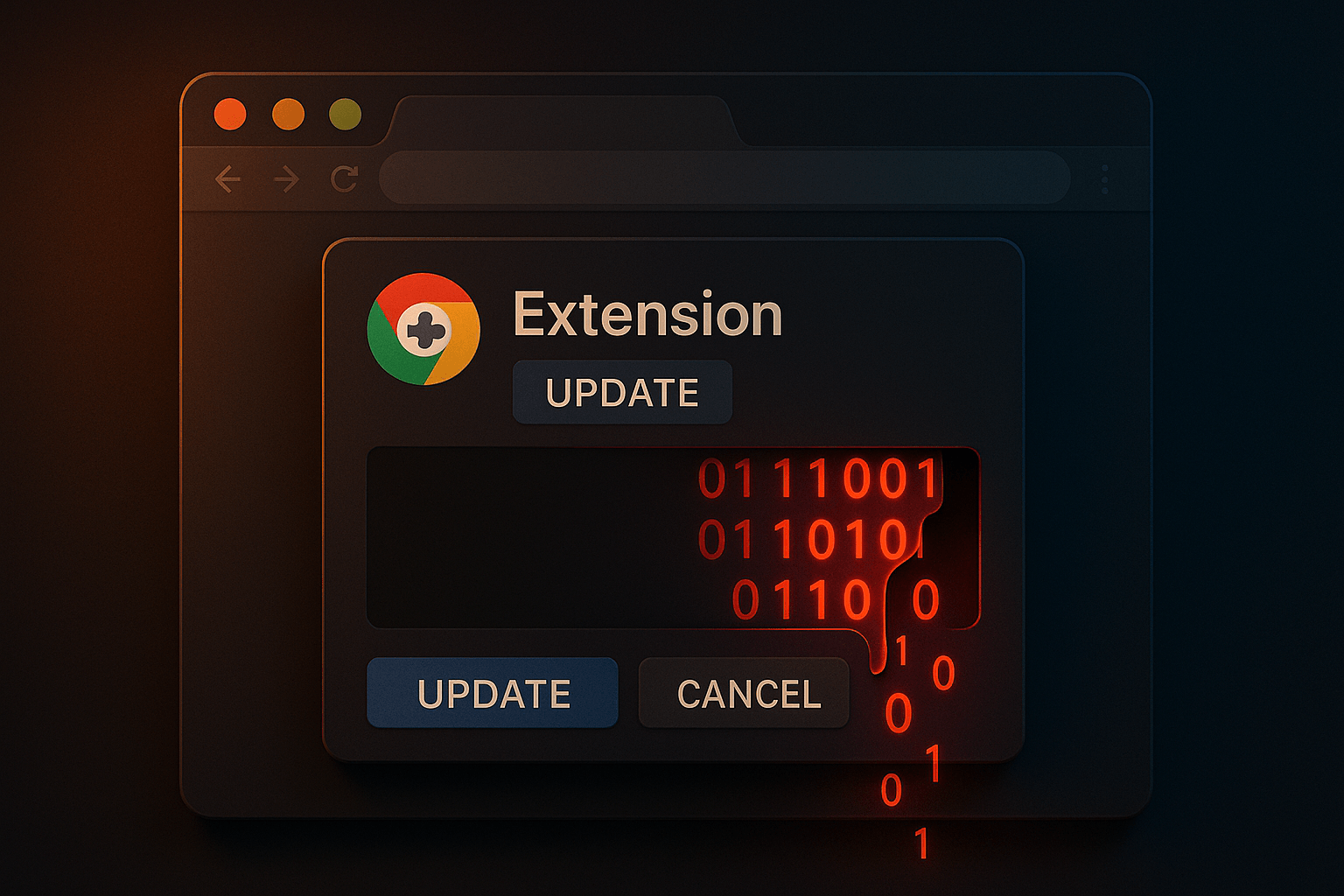
Manifest V3 replaces long-running background pages with event-driven service workers, and moves network blocking to declarativeNetRequest. The goal is fewer always-on scripts and tighter control over filtering logic. This is a step up for privacy and performance, and it limits some abuse patterns. It does not eliminate risky permissions, social engineering of developers, or post-install malicious updates. Users also saw popular MV2 extensions disabled as Google advanced the migration. Security improved, yet organizations still need policy and monitoring.
Google tightened several Web Store rules in 2025, including stricter affiliate ad policies and ongoing policy refreshes. Enforcement promises removal for violations, which raises the bar for spammy monetization in extensions. These steps help, but they are not a substitute for enterprise controls. Treat store vetting as a useful filter, not a guarantee
tabs and scripting APIs.Recent research shows determined attackers can still publish and run malicious code in official stores, which validates a defense-in-depth approach.
Assess before approval.
Function and scope
Publisher trust
Data behavior
Operational signals
Use the checklist with recent examples in mind. Even Featured or verified items have gone wrong in practice.
chrome.storage writes, new host permissions, or mass content scripts.MV3 reduces some always-on behaviors and makes blocking more declarative, which is good. Organizations still need policy control and telemetry. Chrome for Developers
Chrome extensions increase productivity, yet they introduce serious security threats when permissions are broad or when attackers hijack developer accounts. Manifest V3 improves privacy and performance, but it is not a silver bullet. The reliable approach is policy control, structured vetting, and continuous monitoring. Use the checklist and implementation plan above, and you will reduce risk quickly while keeping the tools your teams need
Are Chrome extensions safe in 2025?
Safer than years past, but not safe by default. Treat store vetting as a starting filter, then apply an organizational allowlist and monitoring.
Does Manifest V3 stop malicious extensions?
It reduces certain abuse paths and long-running scripts. It does not stop permission abuse, developer account hijacks, or clone campaigns.
What permissions should I consider red flags?
Wildcards for host permissions, full tabs access coupled with scripting, and clipboard or download access without a clear reason.
How do I know if an extension turned malicious after install?
Watch for permission changes, new outbound domains, or behavior like pop-up redirects and injected search results. Monitor updates and remove on suspicion, then scan endpoints.
If the store removes an extension, am I covered?
Not always. Users may need to manually remove it, and endpoints might still hold artifacts. Follow removal instructions and run a malware scan.
What is the fastest path to a safe extension program?
Adopt allowlisting, apply the checklist, and enforce re-review at each version change. Start with a 90-day refresh cycle.
Stay secure with DeepStrike penetration testing services. Reach out for a quote or customized technical proposal today
Contact Us